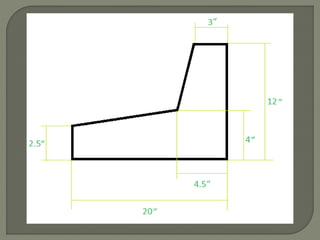
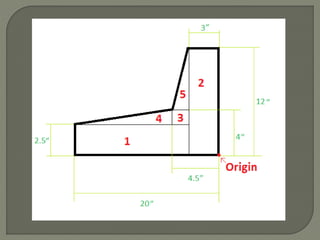
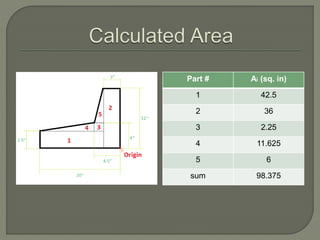
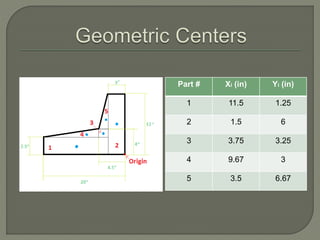
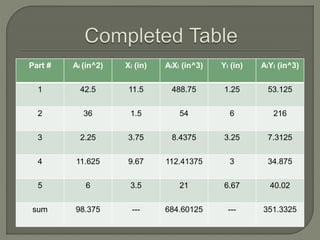
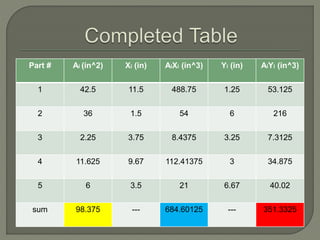
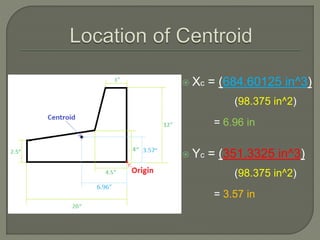
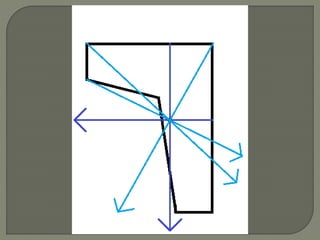
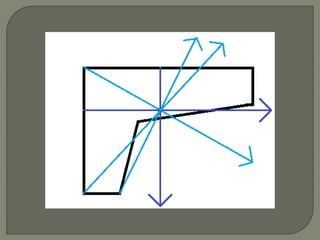
The document provides steps to calculate the geometric center of an irregular shape:
1. Divide the shape into components with easily calculable areas and add the areas.
2. Find the geometric center and distance to the origin for each component.
3. Use the calculated areas and distances to determine the overall geometric center of the shape using formulas that sum the weighted distances.