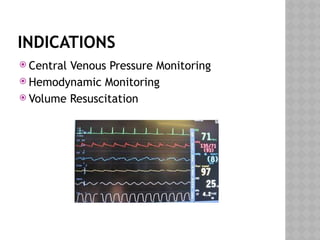
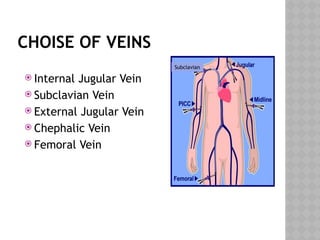
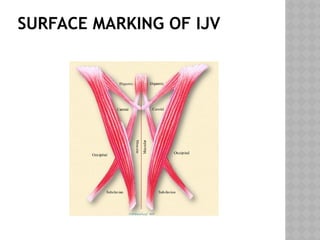
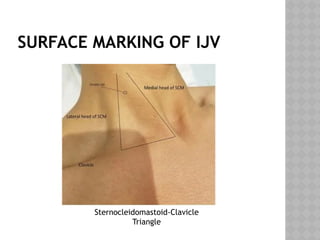
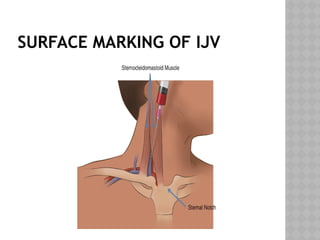
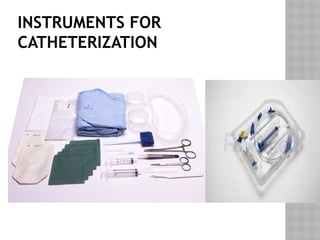
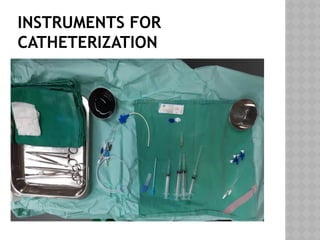
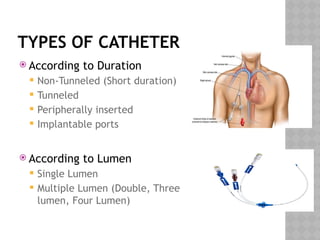
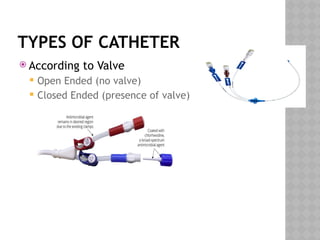
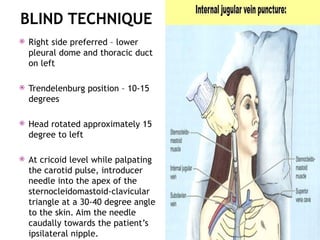
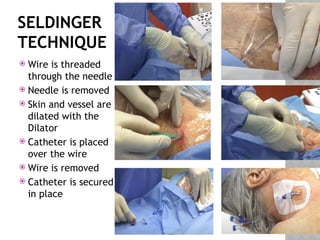
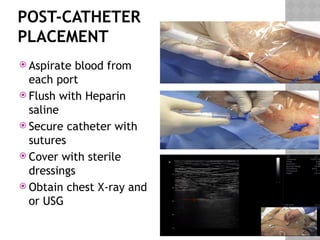
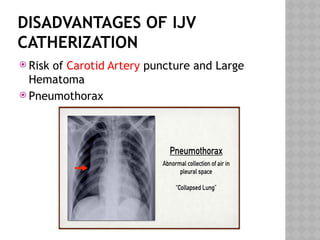
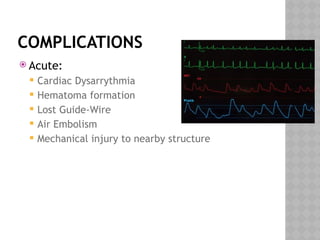
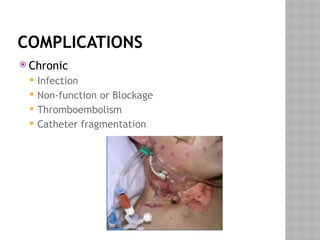
This document outlines the indications and techniques for central venous catheterization, emphasizing the choice of the internal jugular vein for cardiac anesthesia due to its anatomical advantages. It details the types of catheters, methods of insertion, and post-insertion protocols, while also addressing potential complications. The document highlights the use of ultrasound guidance and the need for specific equipment to enhance the safety and effectiveness of the procedure.