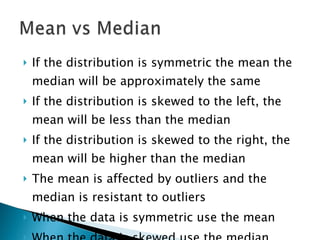
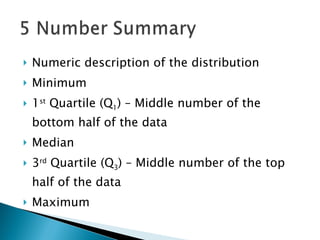
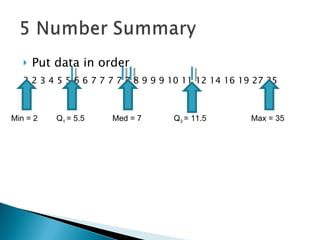
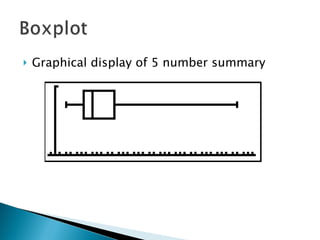
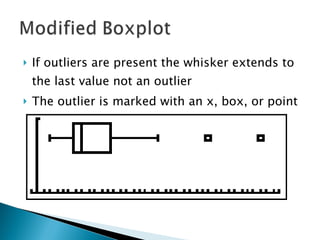
The document defines and compares the mean and median as measures of central tendency. The mean is the average value found by summing all values and dividing by the number of values, while the median is the middle value when data is arranged from lowest to highest. The mean can be affected by outliers, while the median is resistant to outliers. When data is symmetric, the mean and median will be similar, but if the distribution is skewed, the mean will be higher or lower than the median depending on the direction of skew.