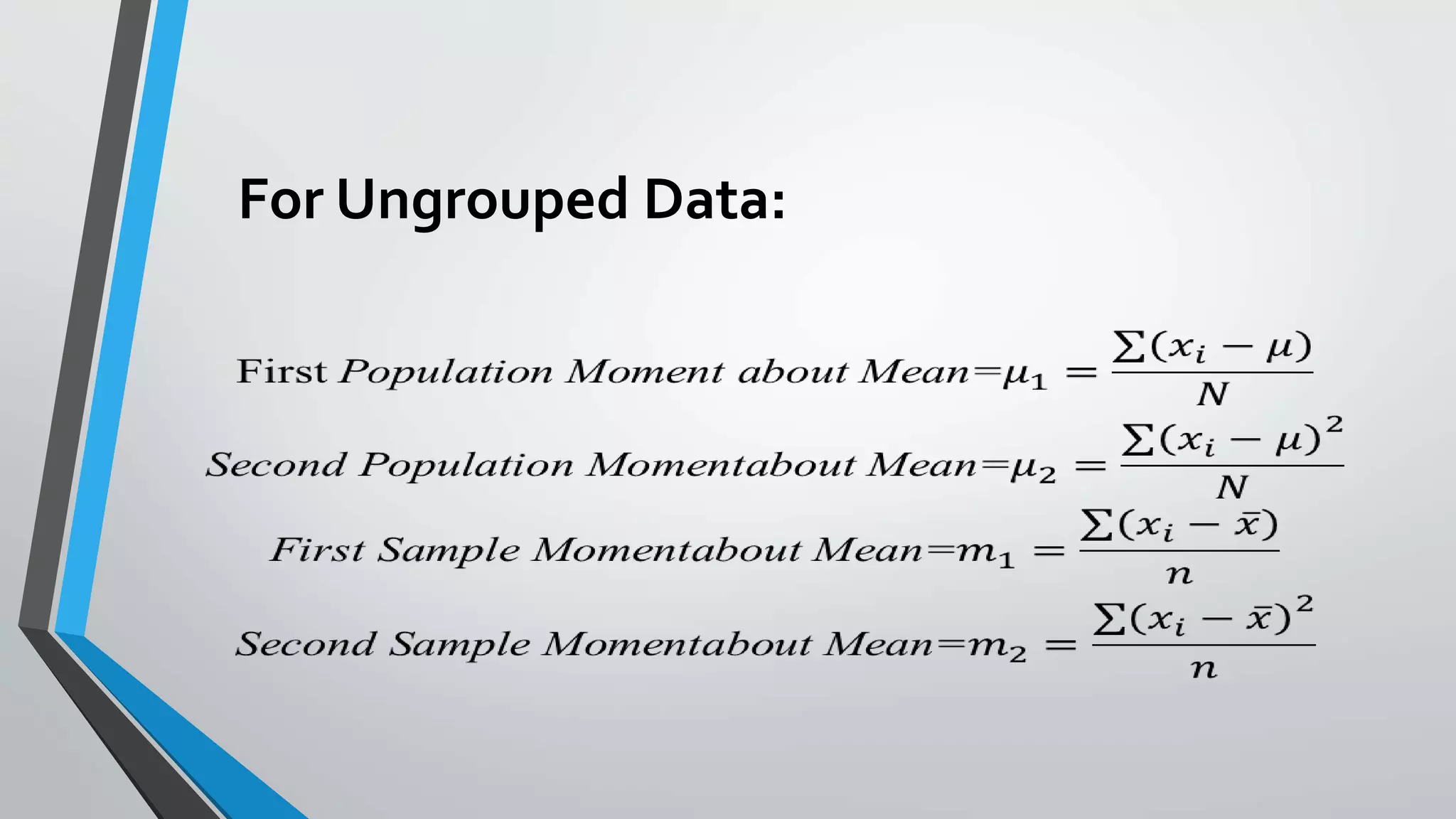
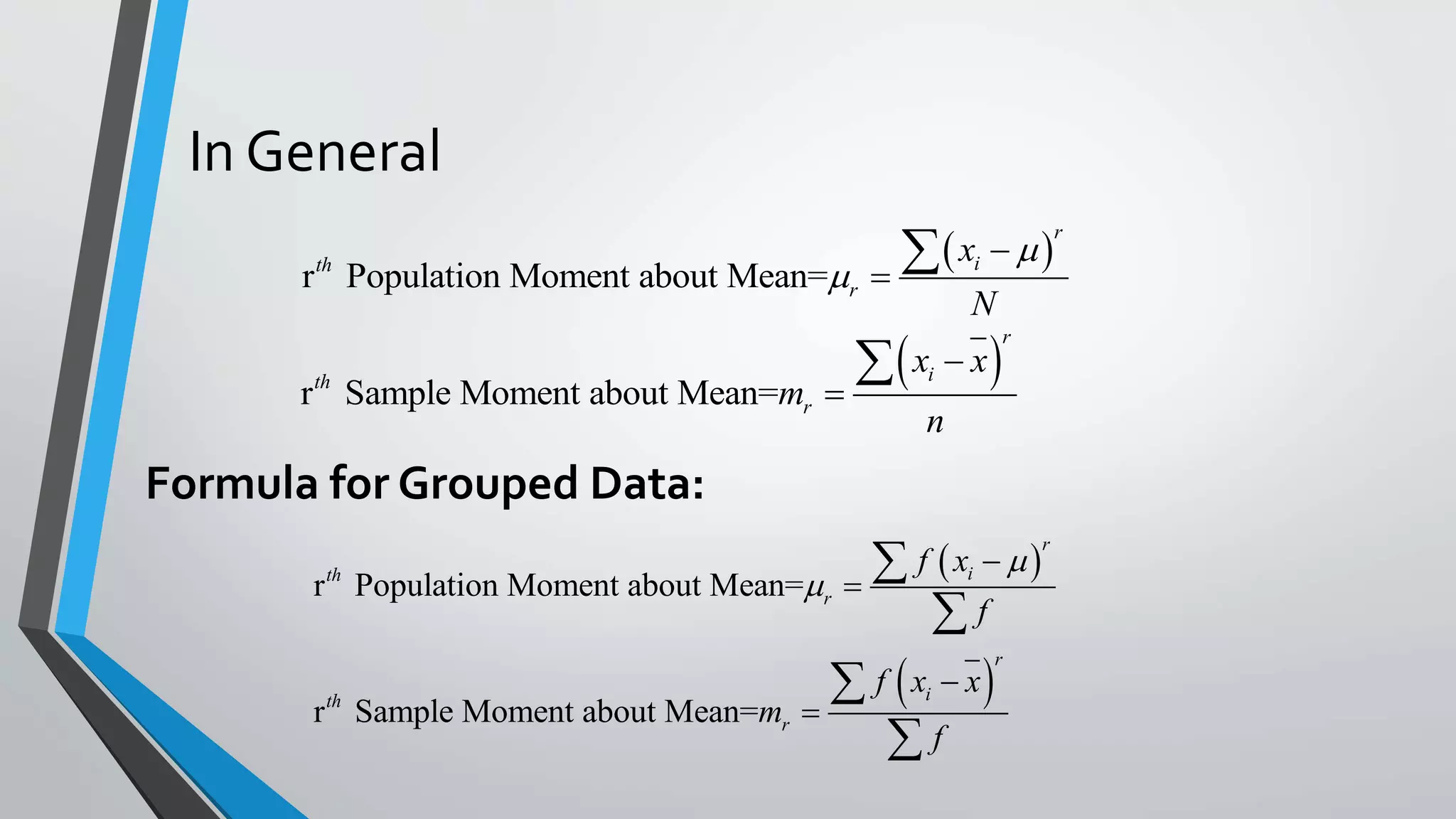
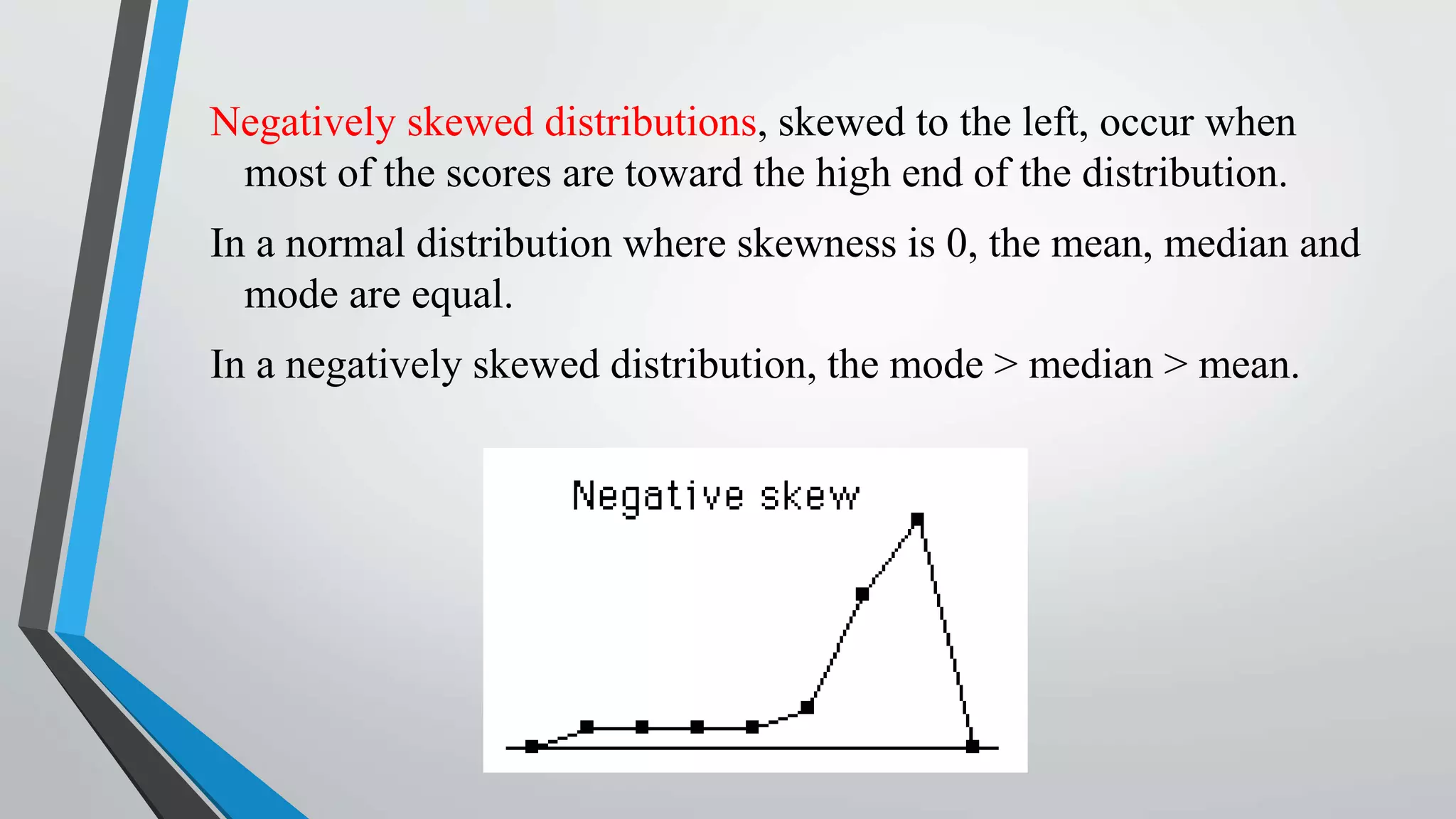
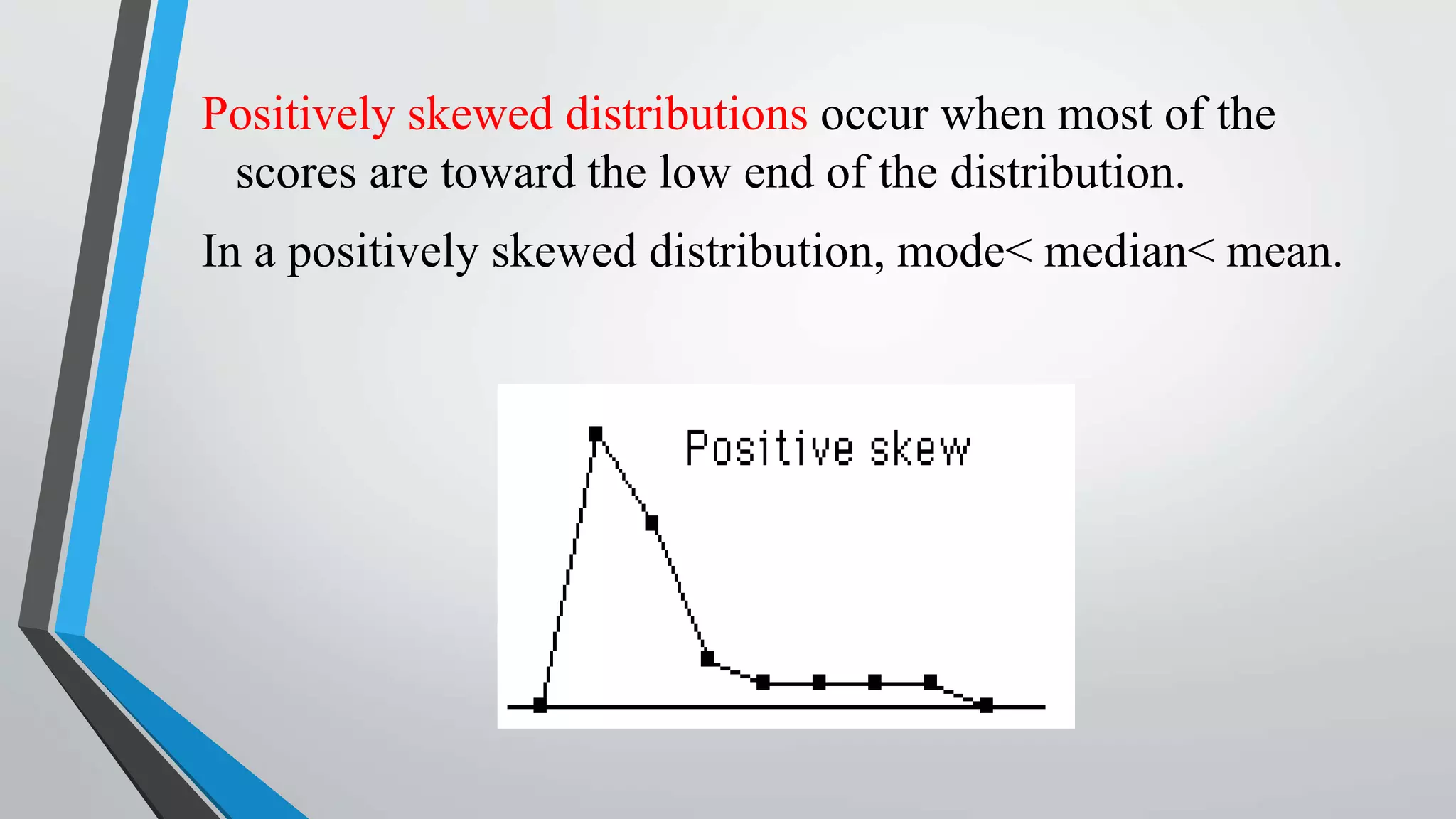
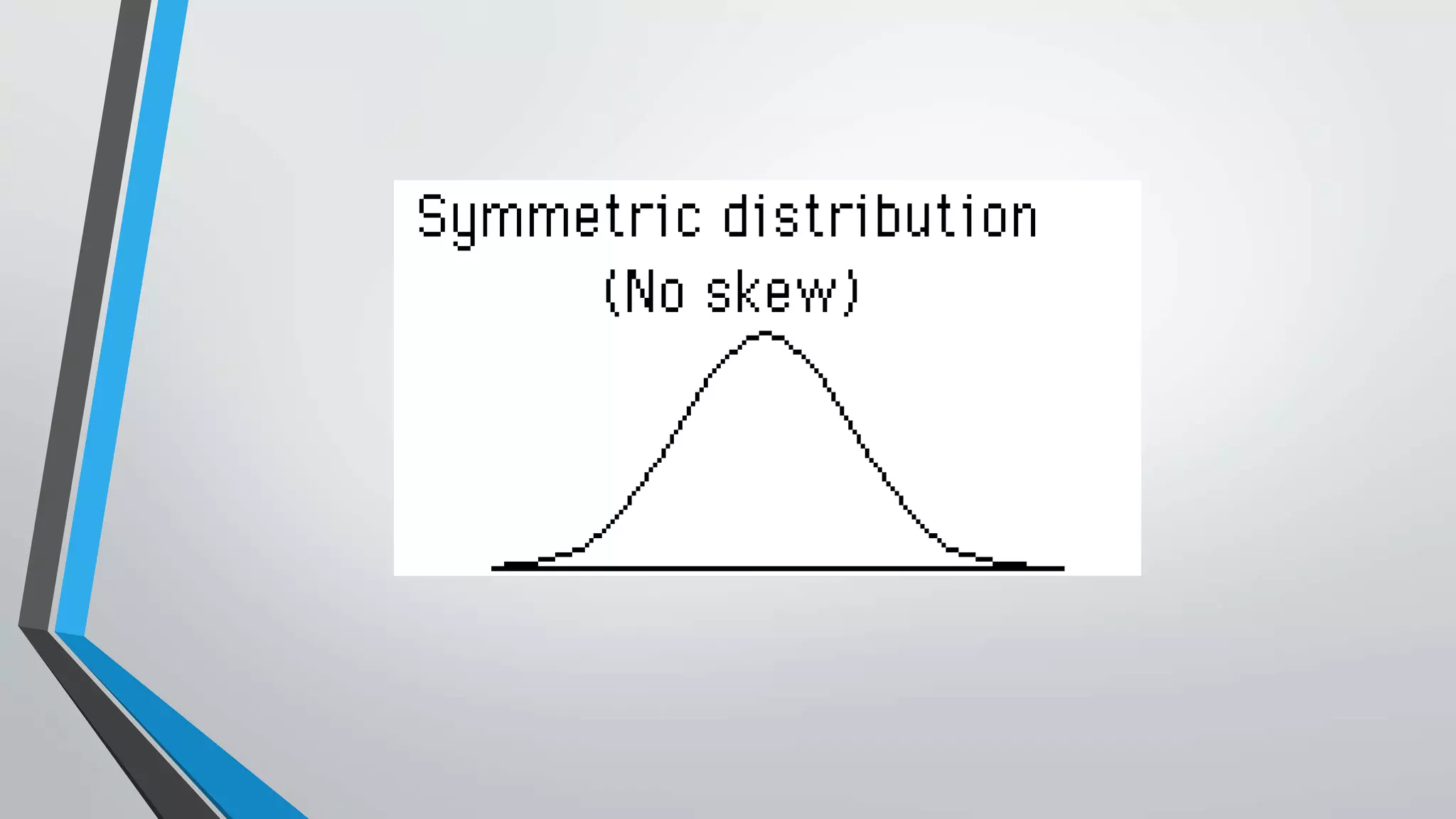
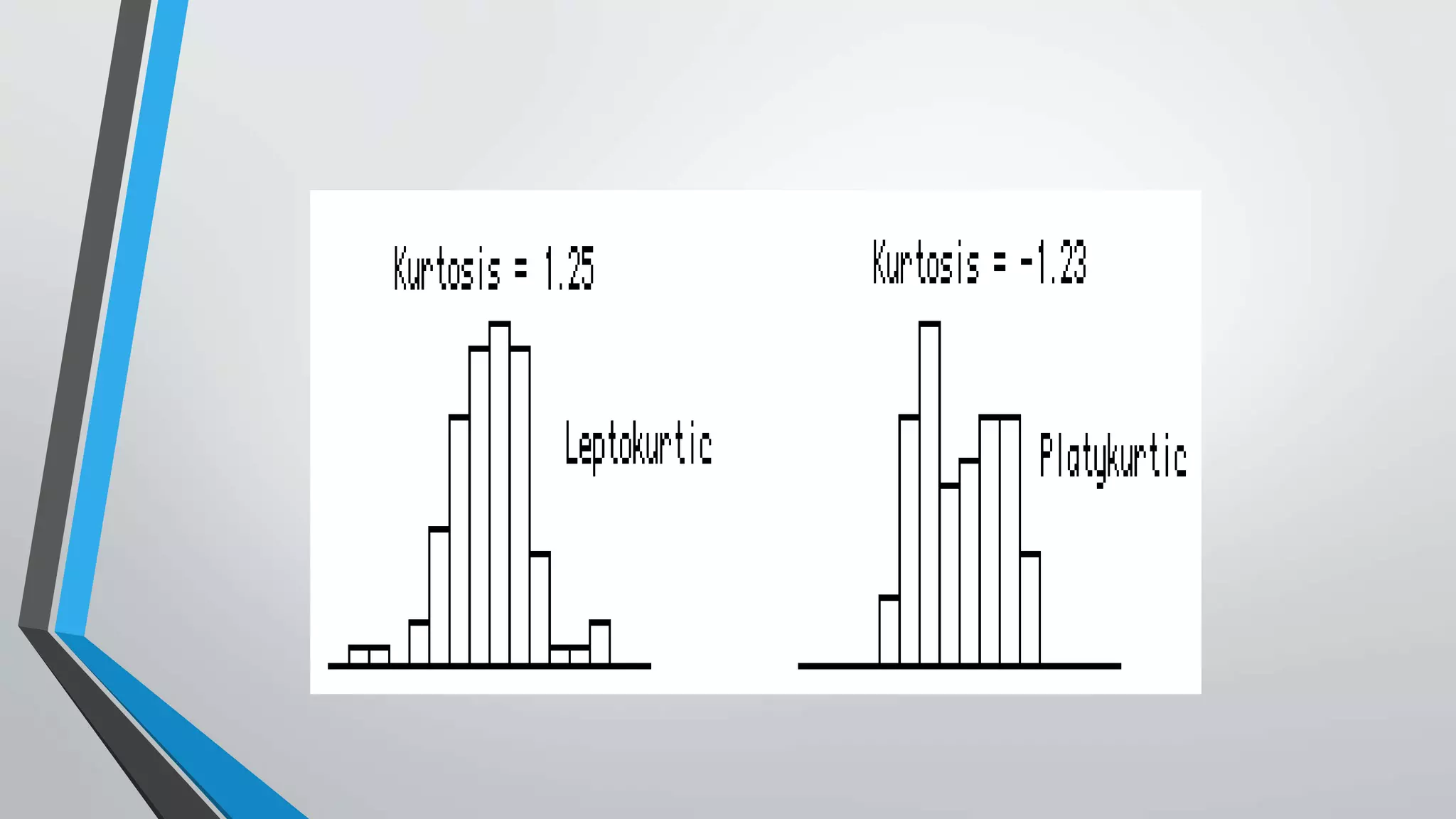
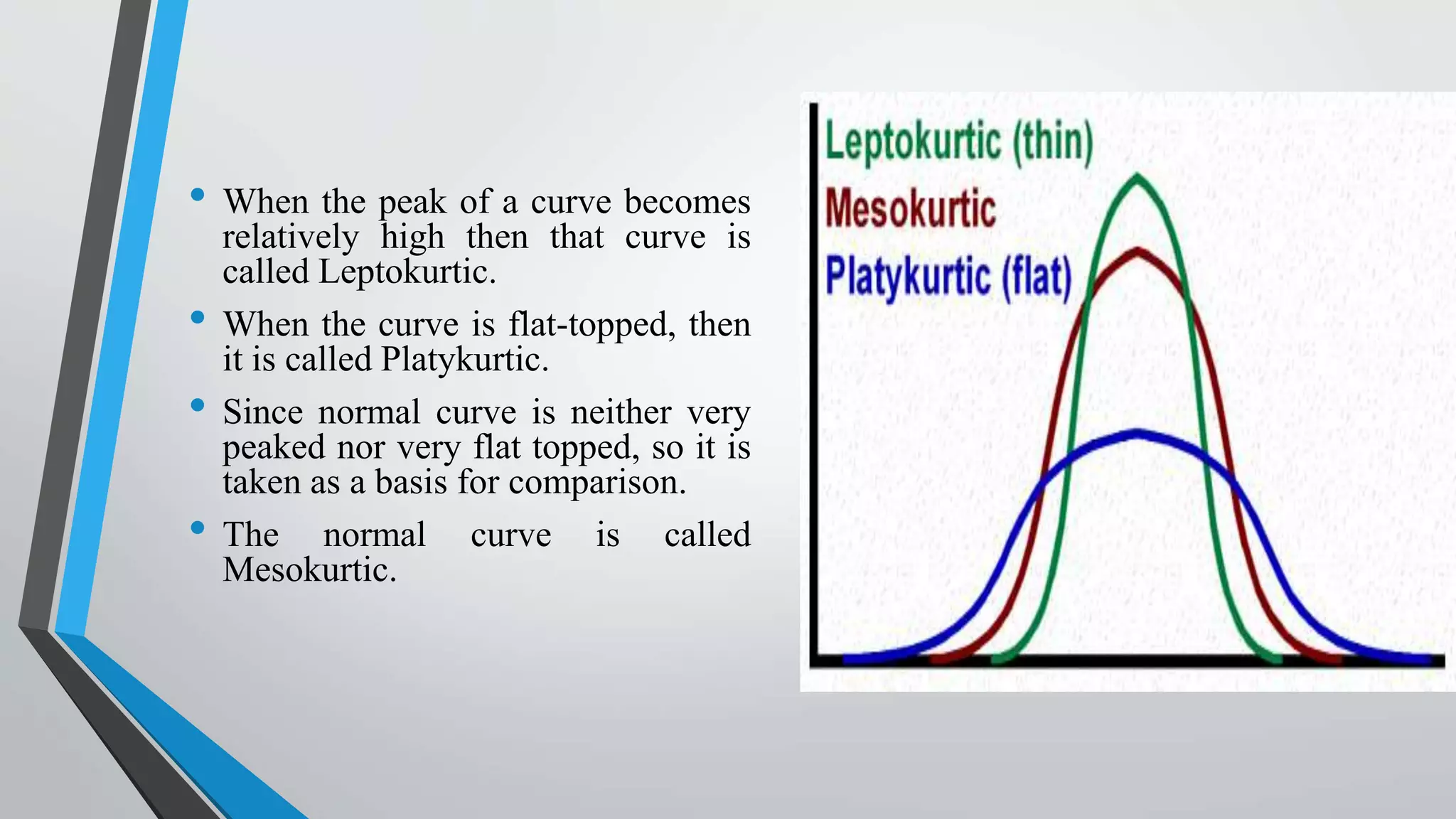
This document discusses central moments, which are measures of the dispersion of data around the mean. It defines the first four central moments: variance, skewness, and kurtosis. Variance is the second central moment and measures how far data points are from the mean. Skewness describes the asymmetry of a distribution, while kurtosis measures the "peakedness" of a distribution compared to a normal distribution. The document provides formulas for calculating central moments for both ungrouped and grouped data, and explains how to interpret skewness and kurtosis values.