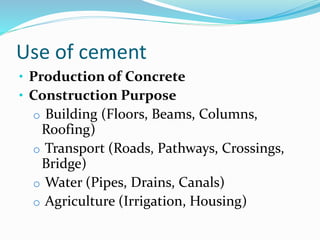
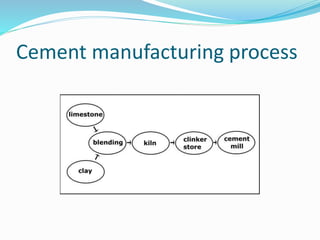
The document discusses the Indian cement industry. It notes that cement is used for construction purposes like buildings, transport infrastructure, and water systems. The main raw materials used are limestone, sand, shale, clay, and iron ore. The manufacturing process is highly energy intensive. Major players in the Indian cement industry are listed along with regional production capacities. India is currently the 2nd largest cement producer in the world and is expected to require a total capacity of around 480 million tonnes by 2025 to support continued infrastructure growth.