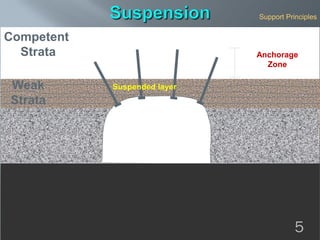
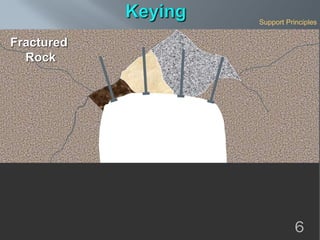
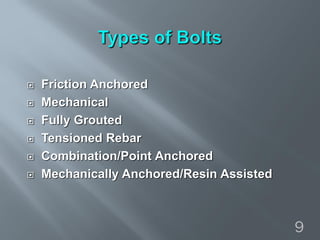
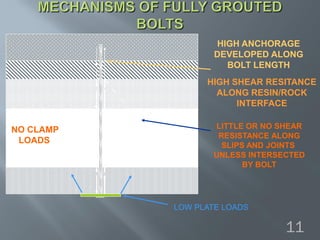
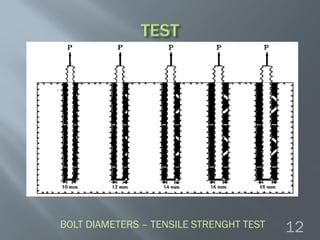
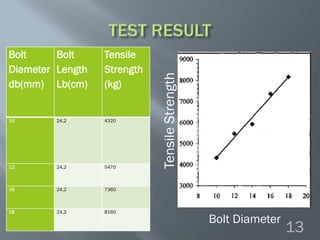
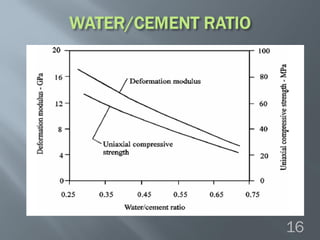
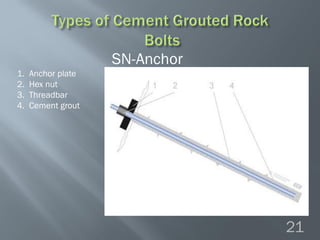
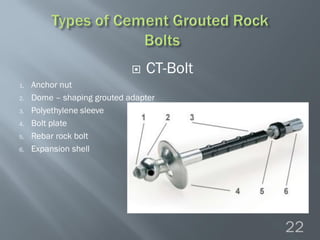
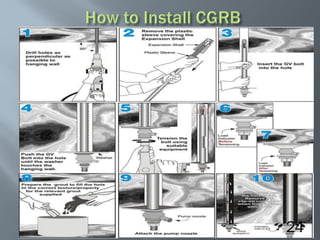
This document discusses cement grouted rock bolts used for supporting underground structures like tunnels and mines. It covers bolting principles, critical parameters, types of bolts and grouting. Specifically, it explains the mechanism of fully grouted rock bolts, effect of water/cement ratio, types of cement grouted bolts and how to install them. Cement grouted rock bolts provide rapid strength gain, are durable and resistant to groundwater, reaching optimum strength within days. They are ideally suited to support medium-stiffness zones and are mainly used for permanent support.