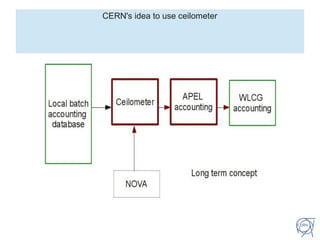
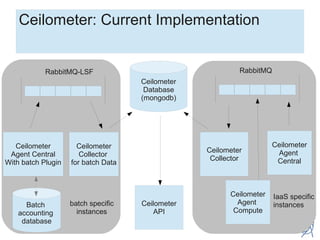
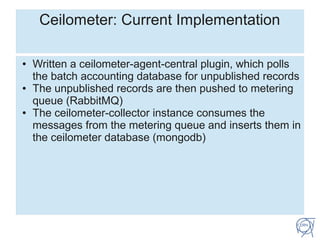
CERN uses ceilometer as a single source of truth for accounting data from both virtual machines and batch computing. Ceilometer implements a plugin to poll CERN's batch accounting database for unpublished records, which are then pushed to RabbitMQ. A ceilometer collector consumes the messages and inserts the data into a ceilometer database. This decreases load on the OpenStack messaging server by using separate instances and RabbitMQ servers for VM and batch metering data. Most batch data is published within two runs processing around 200,000 job records each, which takes approximately 5 hours to complete. The average publishing rate to the batch RabbitMQ server is 11 records per second.