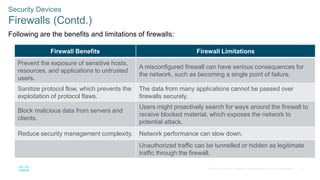
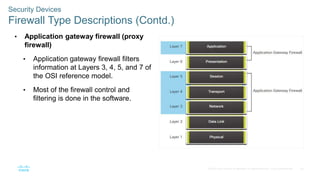
The document outlines the objectives and key concepts related to network security infrastructure, particularly within the Cisco CyberOps Associate curriculum. It discusses various network topologies, the hierarchical design model, and common security architectures such as firewalls and intrusion prevention systems. Additionally, it covers security services like access control lists (ACLs), SNMP, and network time protocol (NTP), emphasizing their roles in enhancing network security.