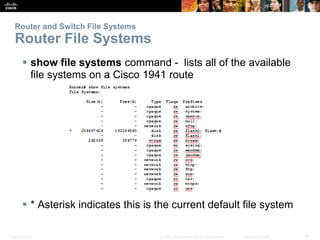
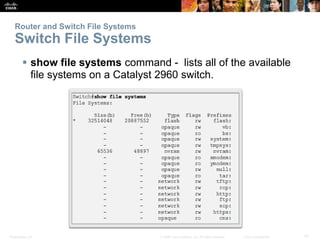
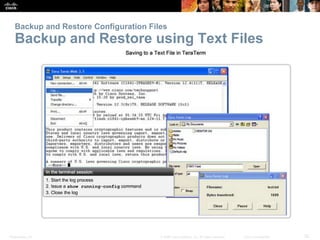
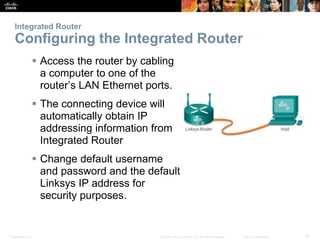
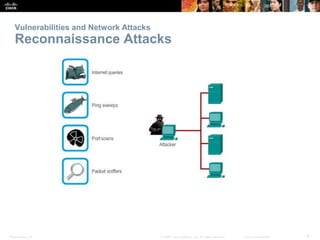
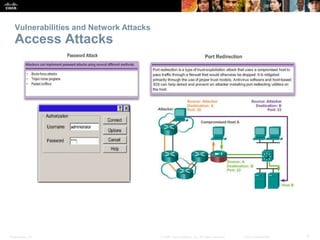
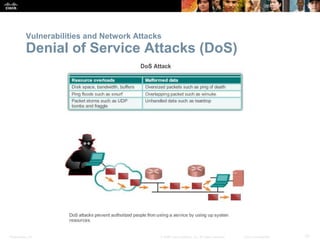
The document provides an overview of network security, detailing the importance of securing devices against various threats such as malware and unauthorized access. It outlines mitigation strategies, including authentication, firewalls, and endpoint security, while also highlighting operational practices like backup and configuration management. Additionally, it discusses integrated routers used in home and small business networks that combine multiple functions including routing, switching, and wireless connectivity.















![Presentation_ID 20
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
Ping
Leveraging Extended Ping
The Cisco IOS offers an "extended" mode of the ping
command
R2# ping
Protocol [ip]:
Target IP address: 192.168.10.1
Repeat count [5]:
Datagram size [100]:
Timeout in seconds [2]:
Extended commands [n]: y
Source address or interface: 10.1.1.1
Type of service [0]:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-230107153051-b549a9ec/85/Network-Security-pptx-20-320.jpg)