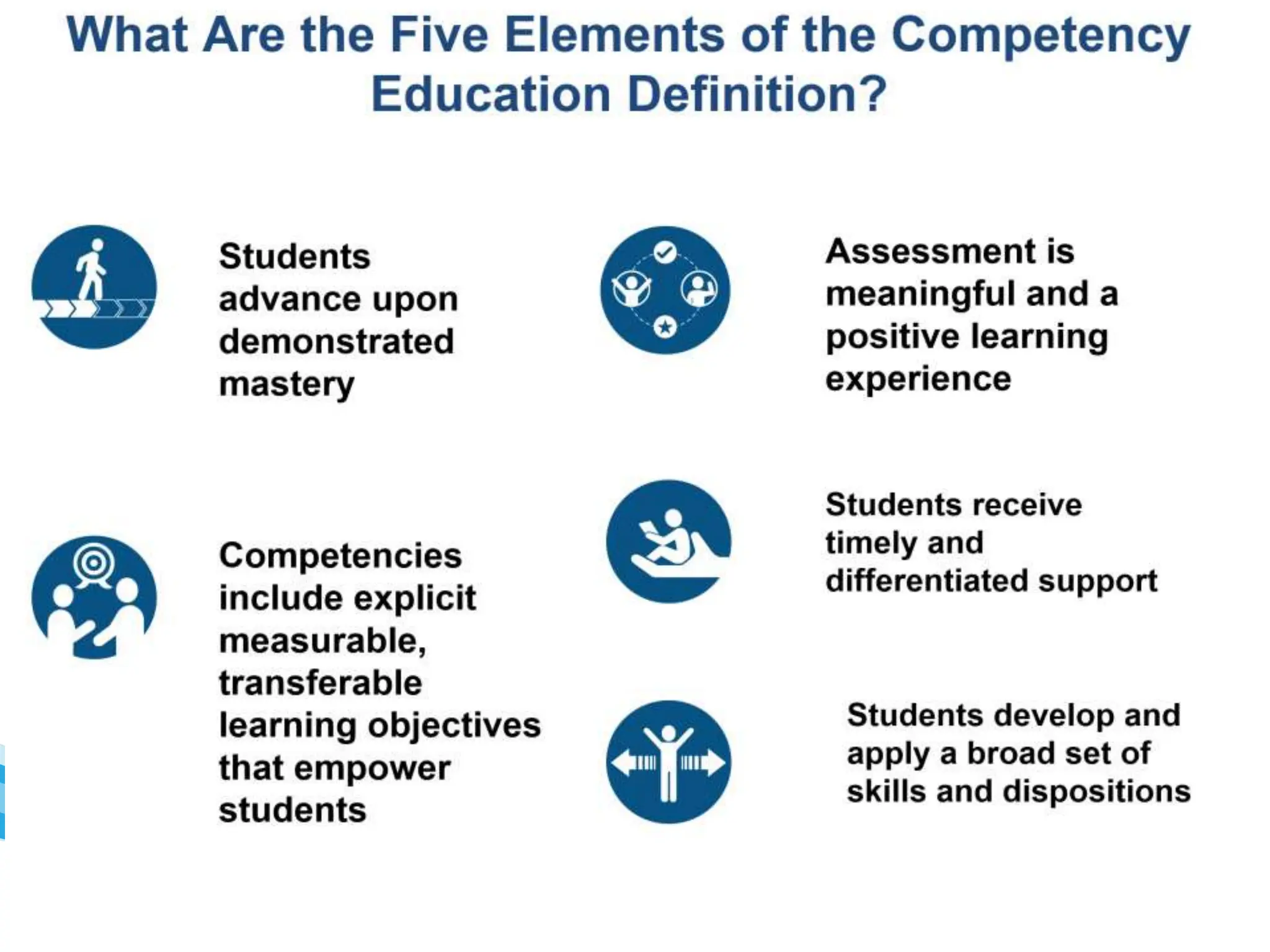
Competency-based education (CBE) is a learning approach centered on students demonstrating mastery of skills and knowledge applicable to real-world contexts, rather than mere memorization. The model emphasizes equitable support, clear learning objectives, and various assessments to track progress, ensuring that each student receives the necessary help for their individual learning paths. CBE is increasingly popular in education as it fosters meaningful experiences and encourages students to take ownership of their learning journey.