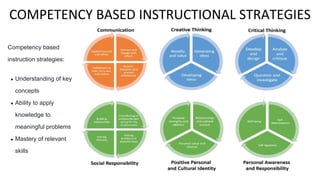
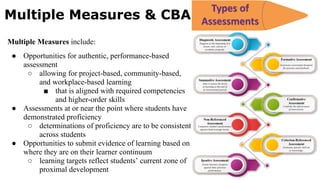
The document outlines a tentative training program for 25 secondary schools in Belize to implement a competency-based curriculum approach. Schools are grouped by region - North, Central, West, and South. The initial round of training will cover competency-based assessment strategies, competency-based teaching strategies, and an introduction to competency-based education. Training sessions will take place in September 2022, with groups of schools attending workshops on specific dates. The goal is to transition 11 schools new to competency-based education, as well as provide varied training to schools based on their existing needs and experience with the approach.





![Curriculum & Assessment Unit
Mrs. Ines Paquiul and
Ms. Michelle Turton
NATIONAL CURRICULUM FRAMEWORK
[COMPETENCY-BASED EDUCATION]
COMPETENCY-BASED CURRICULUM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/competency-basedcurriculumimprovingsecondaryteachinglearning-221020192818-35aa2f0e/85/Competency-based-Curriculum_Improving-Secondary-Teaching-Learning-pdf-6-320.jpg)