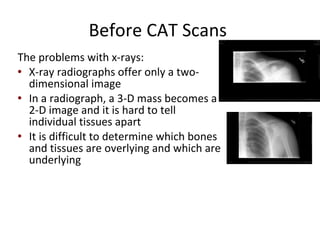
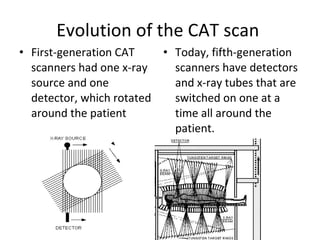
CAT scans were developed to address limitations of x-rays in providing only 2D images that made differentiating tissues difficult. Godfrey Hounsfield and Allan Cormack invented the CAT scan, with Cormack developing the theoretical principles and Hounsfield building the first machines. Modern CAT scans have detectors and x-ray tubes that rotate around the patient to provide 3D images of internal organs, bones, soft tissue, and blood vessels with greater clarity than x-rays. CAT scans work by emitting x-rays from multiple angles that are detected and processed by a computer to construct 2D cross sections.