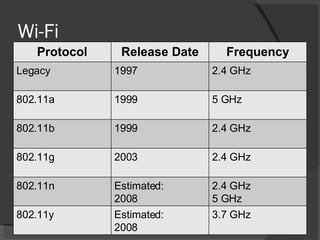
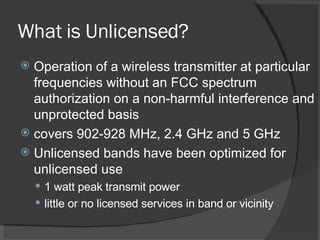
The document provides an overview of wireless technology, focusing on the transfer of information without wires, including Wi-Fi and WiMAX. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of Wi-Fi, such as higher power consumption and encryption vulnerabilities, while also highlighting licensed vs. unlicensed spectrum operations and cellular data technologies like CDMA and GSM. Additionally, it touches on regulatory aspects by the FCC regarding spectrum management and upcoming wireless auctions.