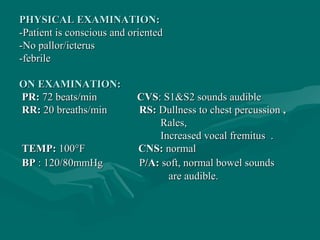
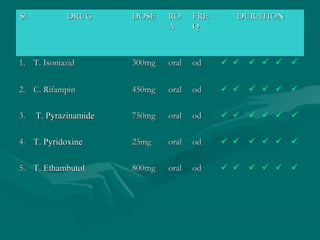
A 22-year-old male patient was admitted to the hospital with a chief complaint of intermittent fever, night sweats, weight loss, and a productive cough over the past month. Examinations found the patient to be febrile with dullness and rales in the chest, and laboratory tests showed an increased white blood cell count with lymphocyte predominance. A chest radiograph showed patchy infiltrates in the left lung apex, and a positive tuberculin skin test and sputum smear confirmed a diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis. The patient was prescribed a daily multidrug regimen including isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, ethambutol, and pyridoxine for 6