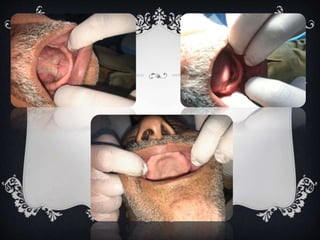
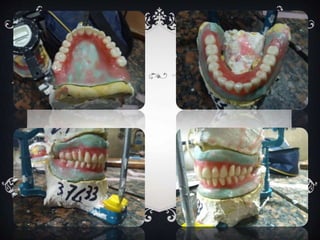
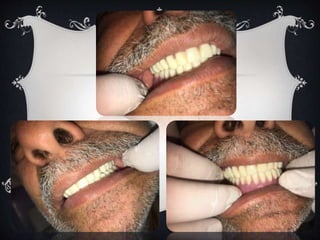
This case report describes the treatment of a 60-year old edentulous patient who was referred to restore mastication, speech, and esthetics. An examination found that the patient had low vertical dimension due to tooth loss, but ridges were well-developed with no excessive resorption. The treatment plan was to fabricate a complete denture using alginate impressions, border molding with rubber base, and registering the vertical dimension of rest and occlusion with wax rims. The denture was delivered after checking retention, stability, support, borders, and selective grinding to eliminate premature contacts. Post-insertion care instructions included soft foods, soaking, and speech exercises.