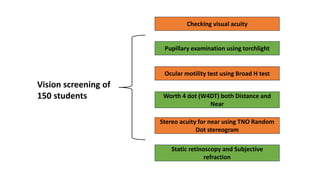
This study investigates the relationship between accommodation and vergence abnormalities among myopic adolescents in India, highlighting the importance of binocular vision for cognitive development and academic performance. A total of 150 myopic children underwent vision therapy, with pre- and post-assessments revealing significant improvements in various binocular vision parameters. The findings emphasize the need for early diagnosis and treatment of binocular vision disorders in myopic children to prevent further complications and enhance visual acuity.