This radiology case conference document discusses multiple cases involving abdominal calcifications:
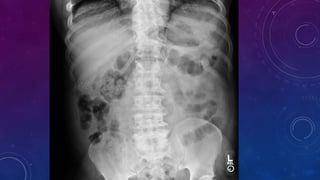
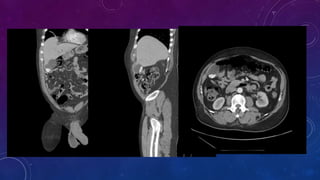
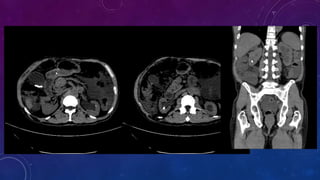
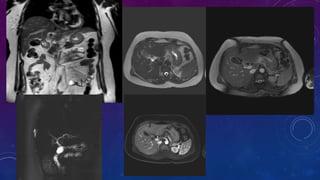
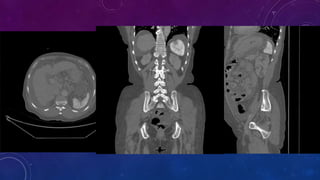
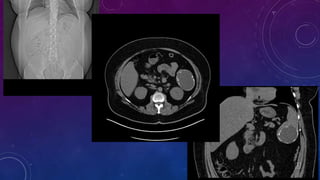
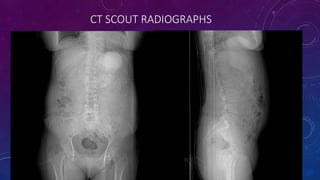
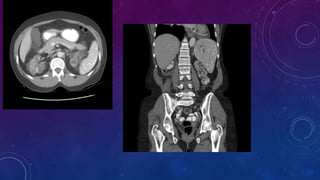
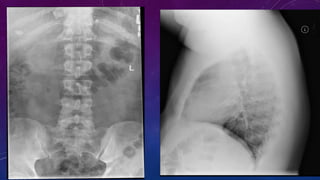
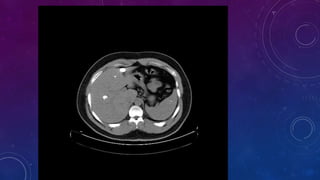
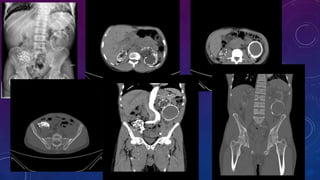
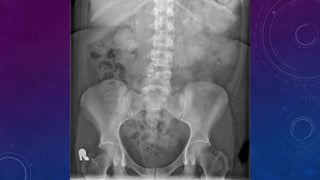
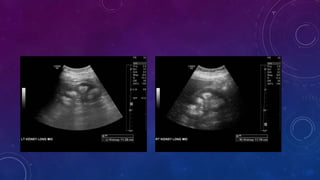
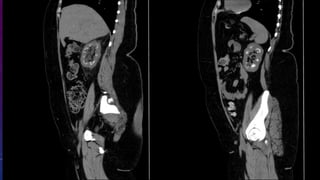
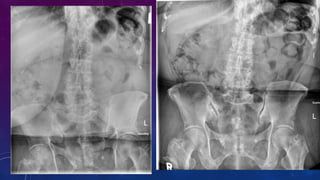
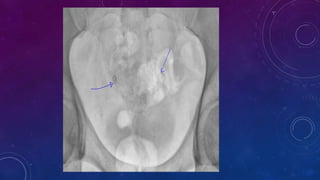
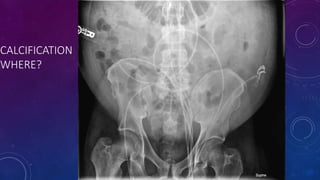
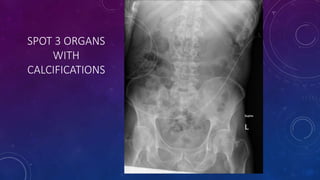
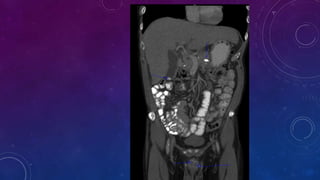
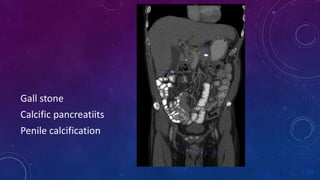
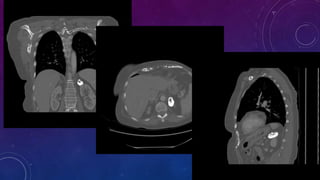
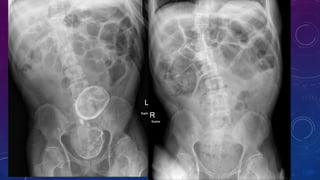
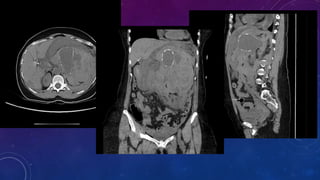
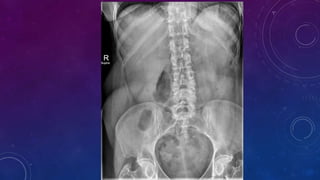
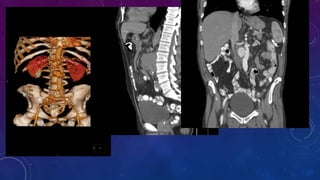
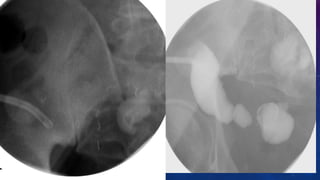
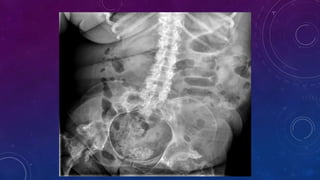
- Case 1 involves gallstones, gall bladder and renal calculi, and a diagnosis of chronic calcific pancreatitis.
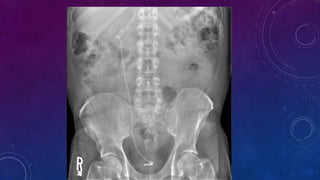
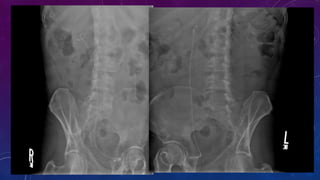
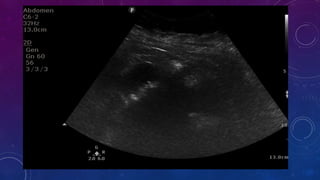
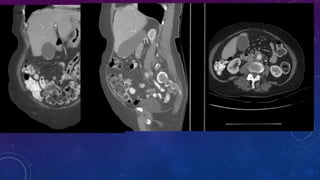
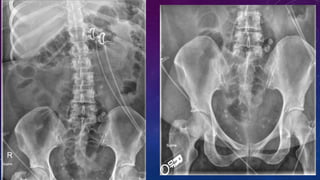
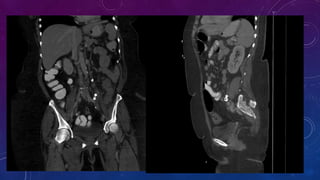
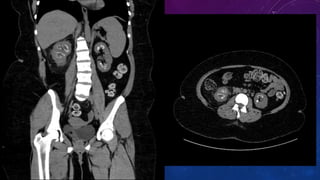
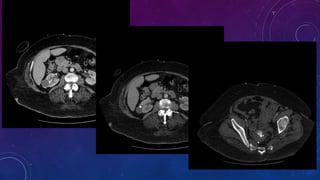
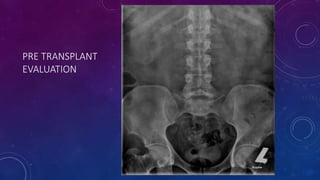
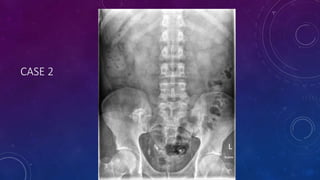
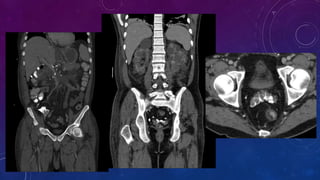
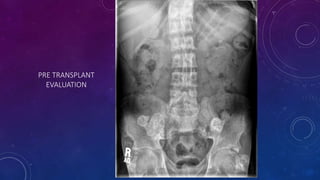
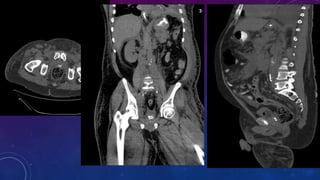
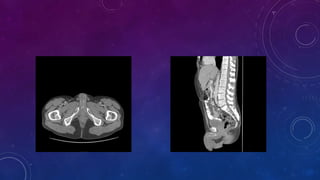
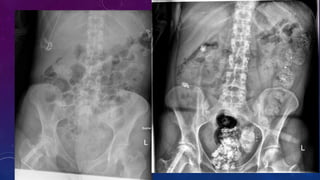
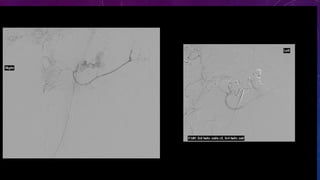
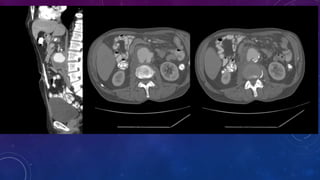
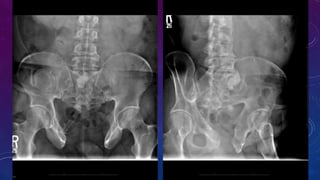
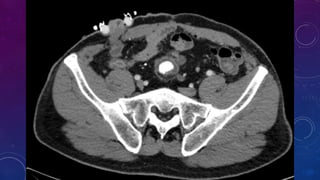
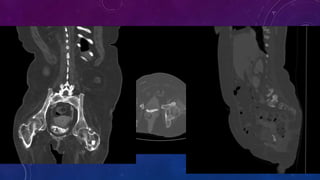
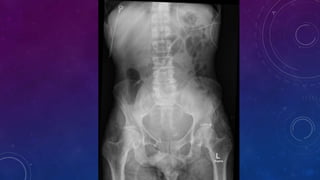
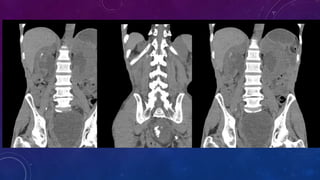
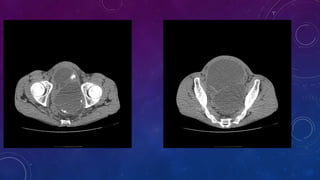
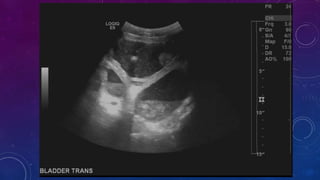
- Case 2 shows seminal vesicle/vas deferens calcification in a patient undergoing pre-transplant evaluation who had failed bilateral renal transplants.
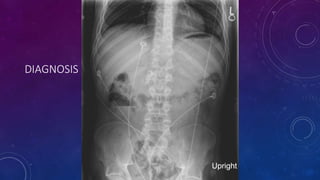
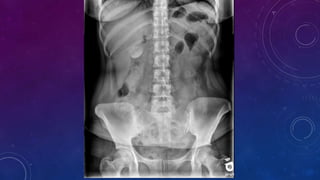
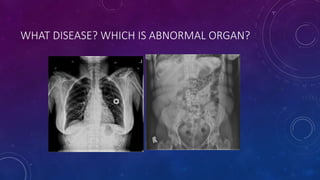
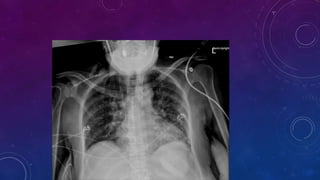
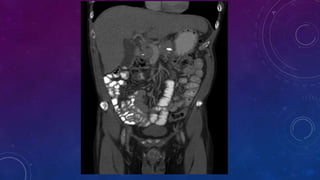
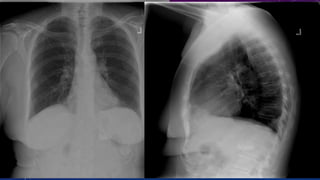
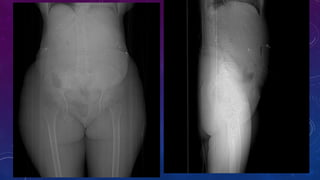
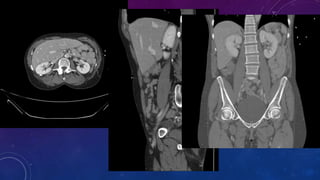
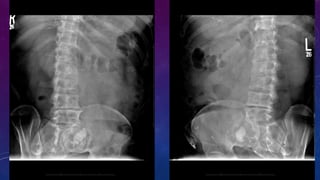
- Other cases discussed include prostatic calcification, left adrenal calcification from old trauma, and fecoliths before and after treatment.