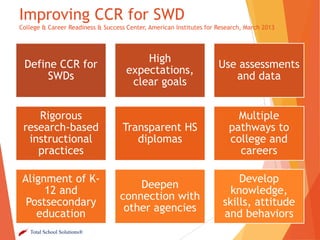
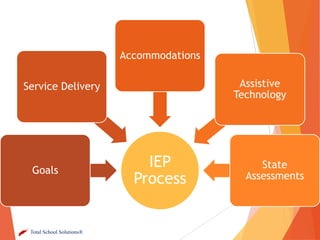
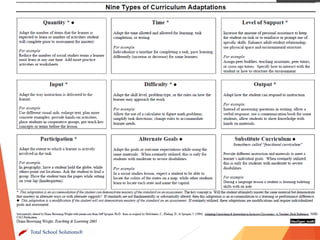
This document provides an overview of a presentation on implementing Common Core State Standards for special education students. The objectives covered include connecting special education to Common Core, factors to consider in developing a strategic plan, and sharing tools and resources. The presentation addresses key topics such as writing IEP goals using grade-level Common Core standards, providing access to the general education curriculum, and differentiating instruction for special education students. It emphasizes building on the general education implementation plan and involving special education staff in professional development. Group activities have attendees discuss changes to service delivery models and support needed by related service providers to help special needs students meet Common Core standards.