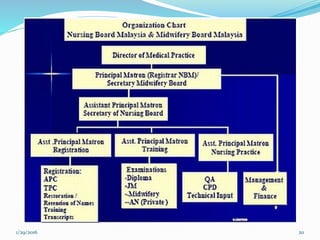
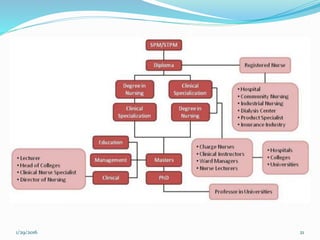
Nursing began developing as a profession in Malaysia in the 1800s through services provided by members of the East India Company and Catholic nuns. The first nursing school was established in 1946 in Johor Bahru. Throughout the 20th century, legislation was passed to regulate nursing practice and training programs, and the first nursing college and university programs were established. Currently there are over 100 nursing education institutions in Malaysia offering diploma through doctoral degrees, with over 80,000 registered nurses in the country as of 2009.