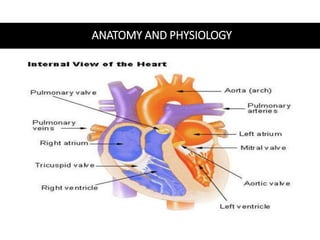
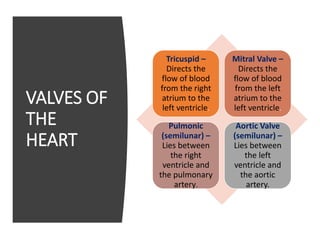
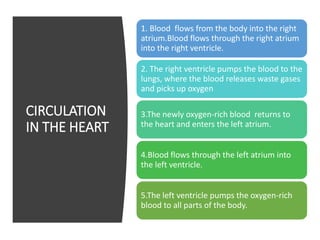
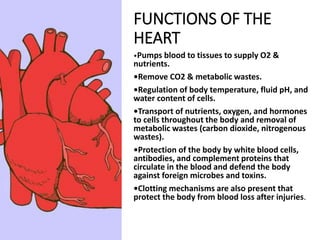
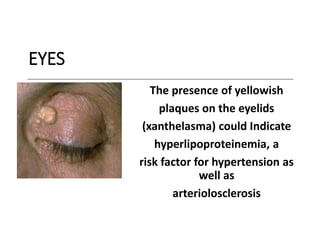
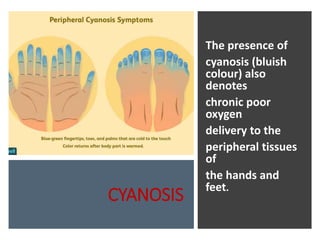
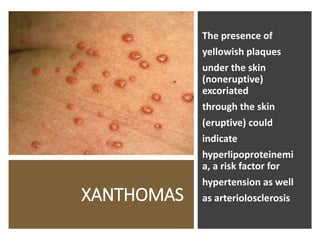
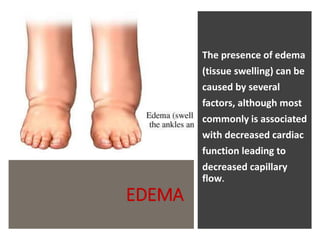
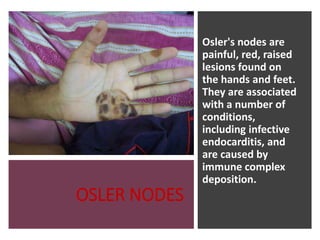
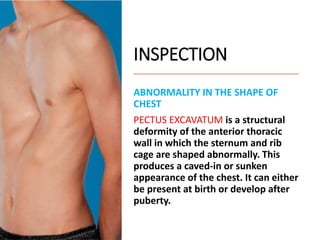
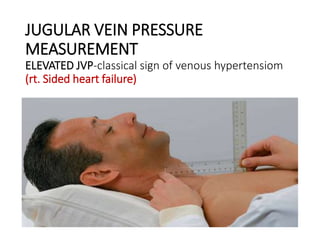
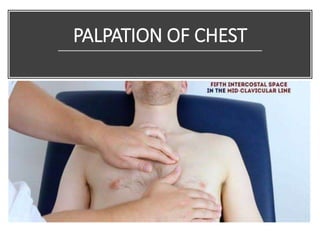
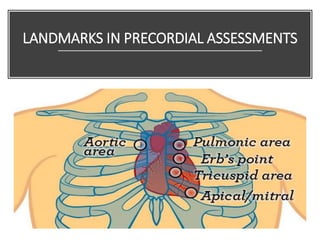
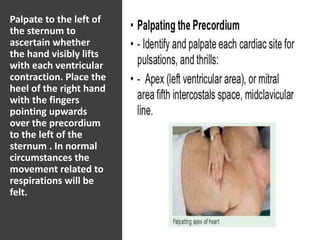
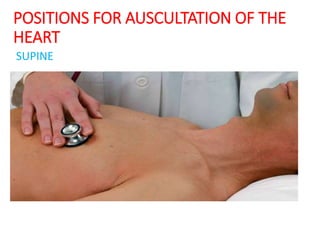
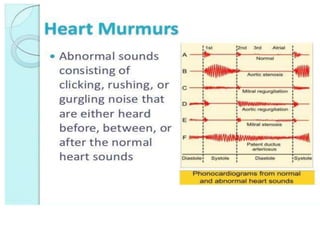
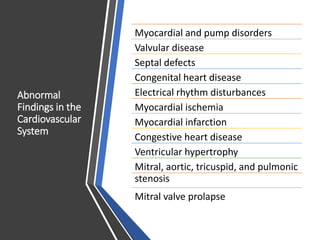
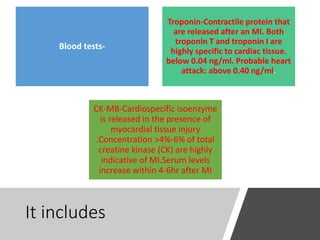
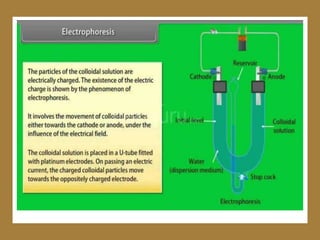
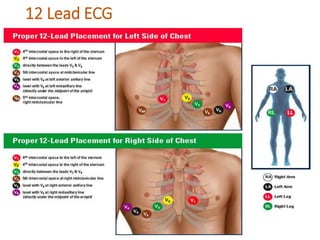
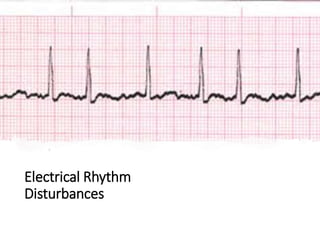
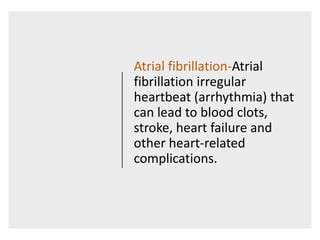
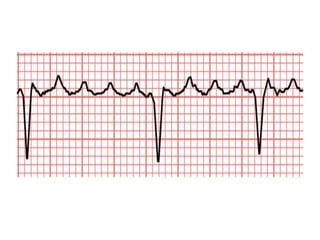
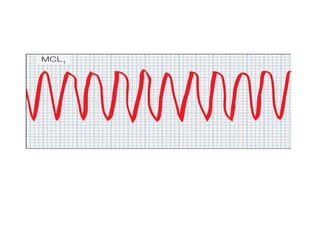
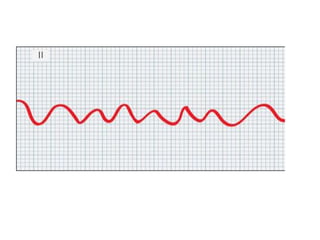
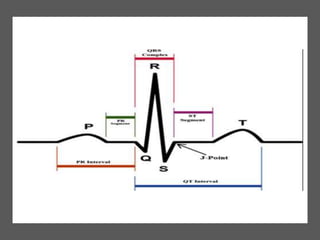
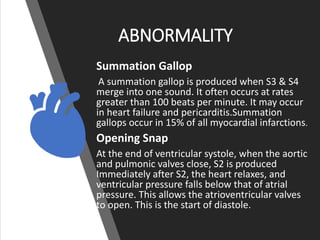
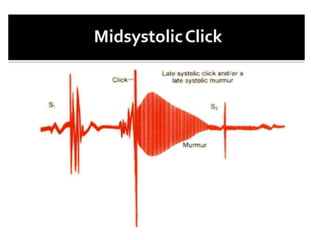
This document provides information on assessing the cardiovascular system. It begins with an introduction on the importance of cardiovascular assessment by nurses. It then covers anatomy and physiology of the heart, including the valves and blood circulation. Physical examination techniques are outlined, including inspection, palpation, percussion and auscultation. Common abnormalities that may be found on assessment are listed. Finally, additional investigation methods are mentioned, such as electrocardiograms, blood tests and cardiac imaging.