Embed presentation
Download to read offline

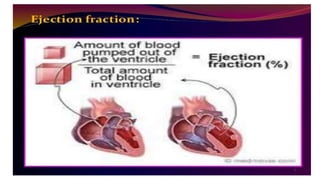
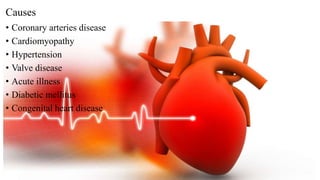
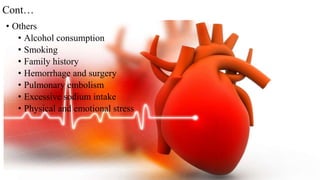

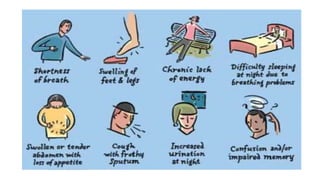















Cardiac failure can be caused by coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathy, hypertension, valve disease, acute illness, diabetes, congenital heart disease, alcohol consumption, smoking, family history, hemorrhage and surgery, pulmonary embolism, excessive sodium intake, and physical or emotional stress. Diagnosis involves echocardiograms, electrocardiograms, and chest x-rays. Nursing diagnoses include decreased cardiac output, excess fluid volume, impaired gas exchange, risk for activity intolerance, and risk of anxiety. Nursing interventions focus on monitoring for edema, distention, and pain; following diet and fluid restrictions; checking vital signs; encouraging breathing exercises; monitoring skin; limiting activity; and providing a calm environment.
























