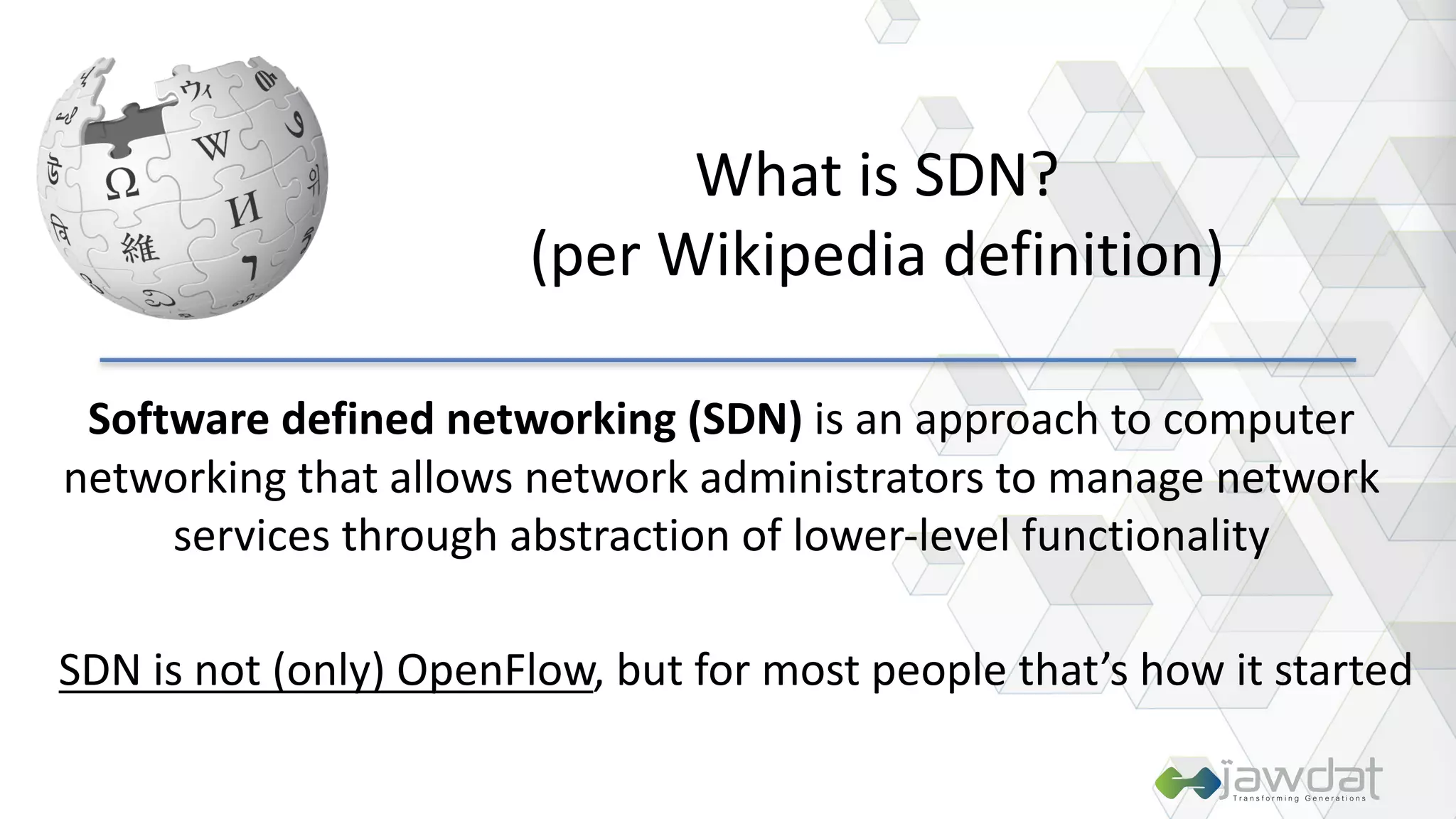
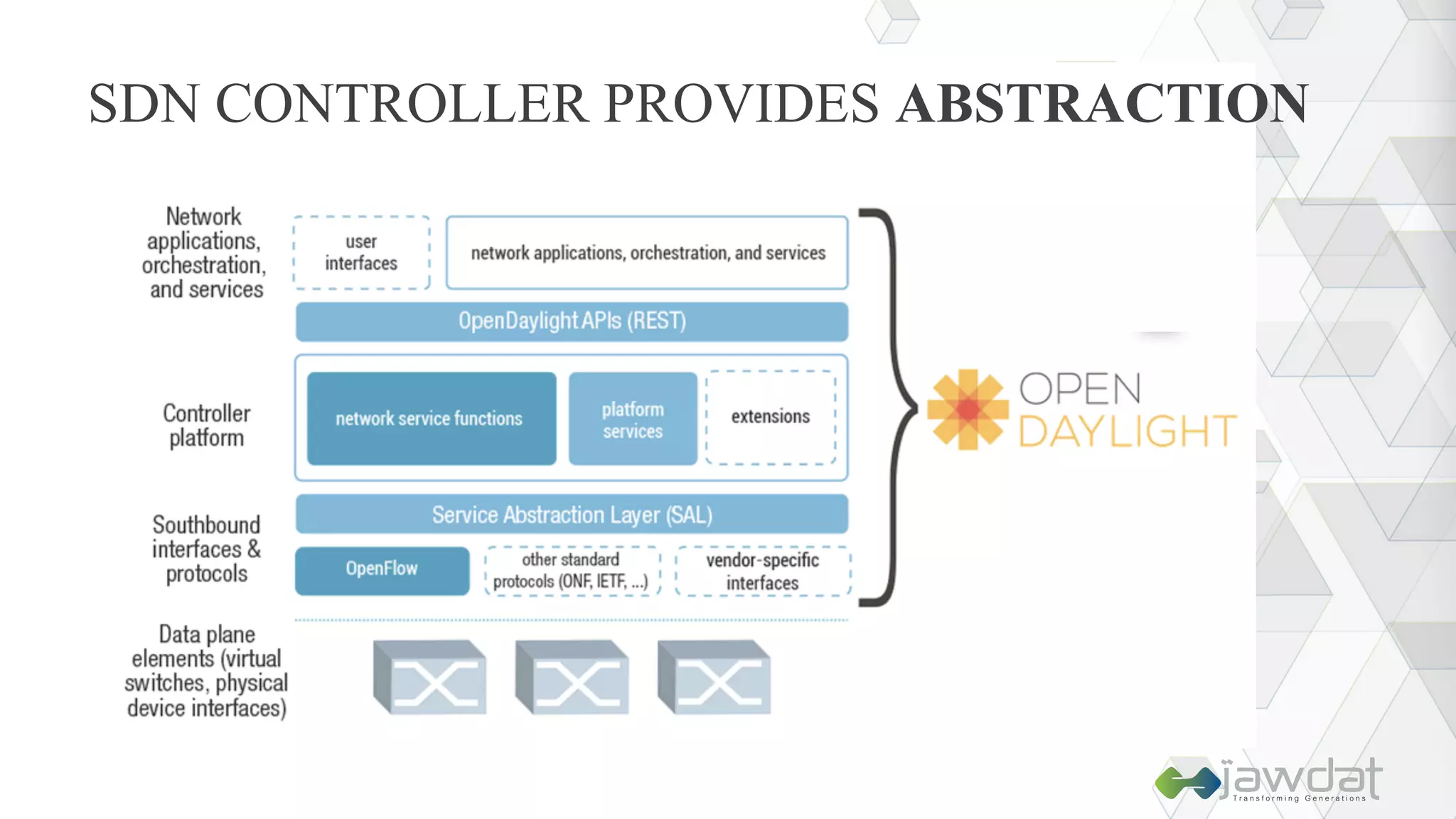
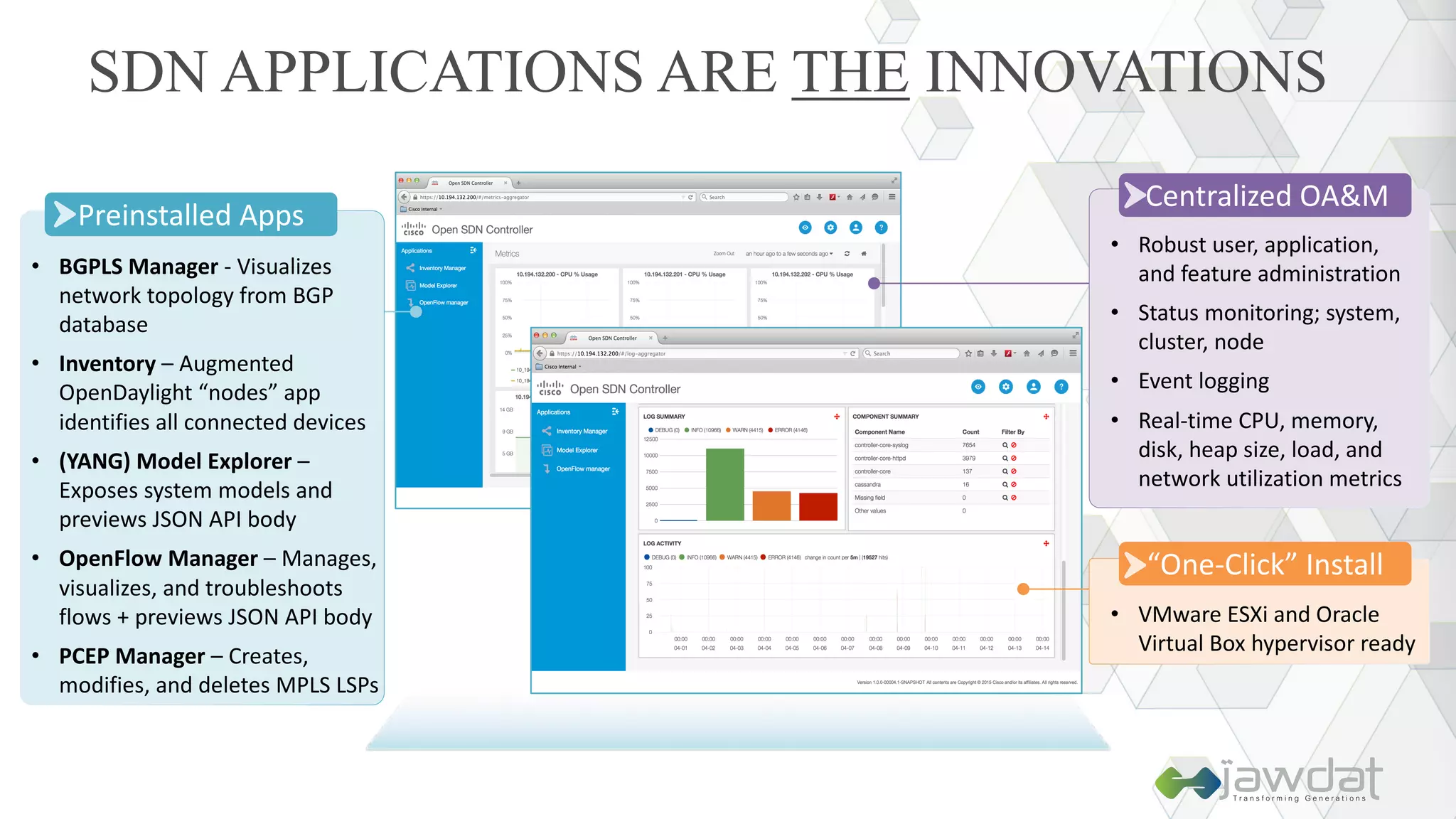
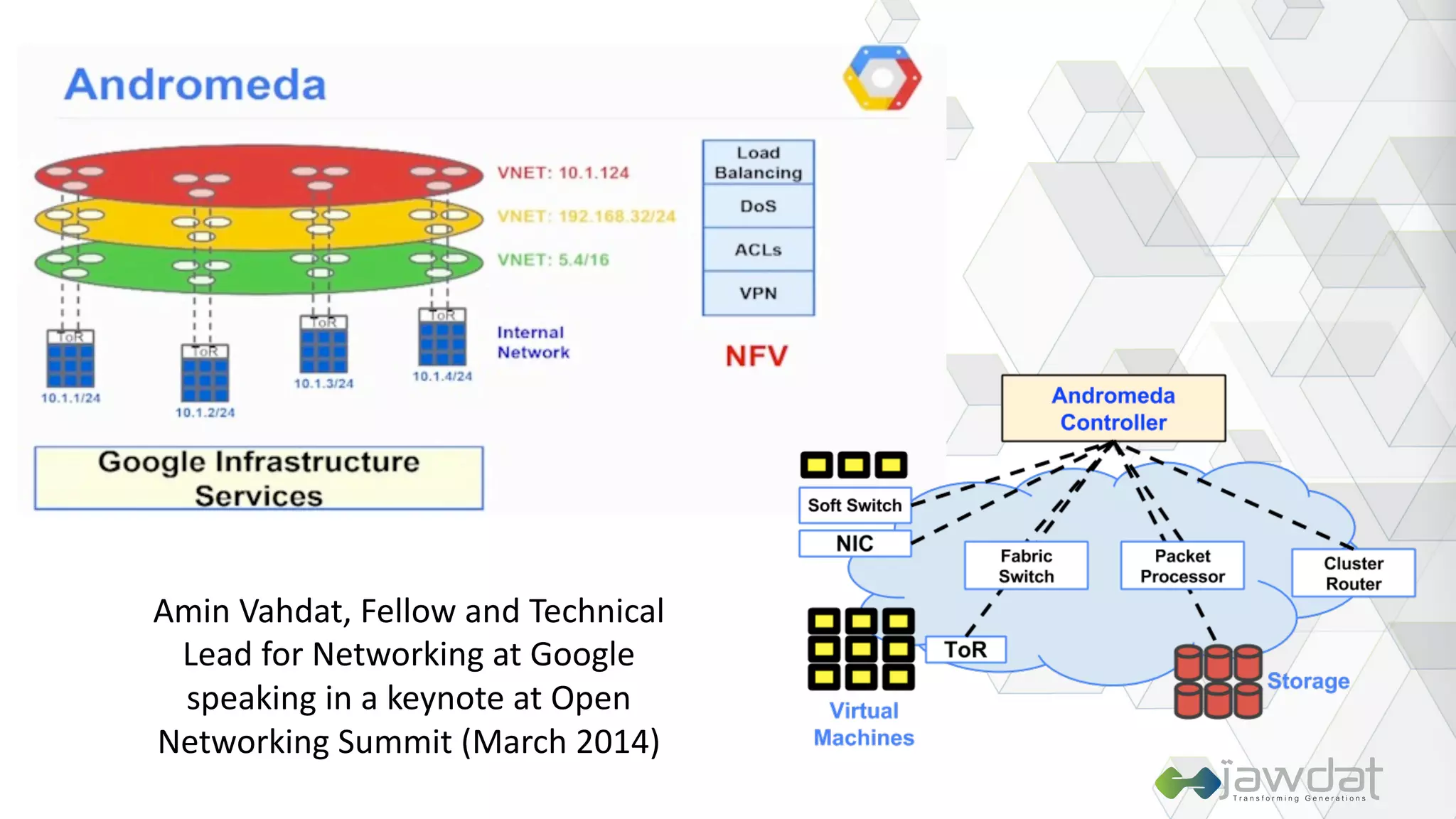
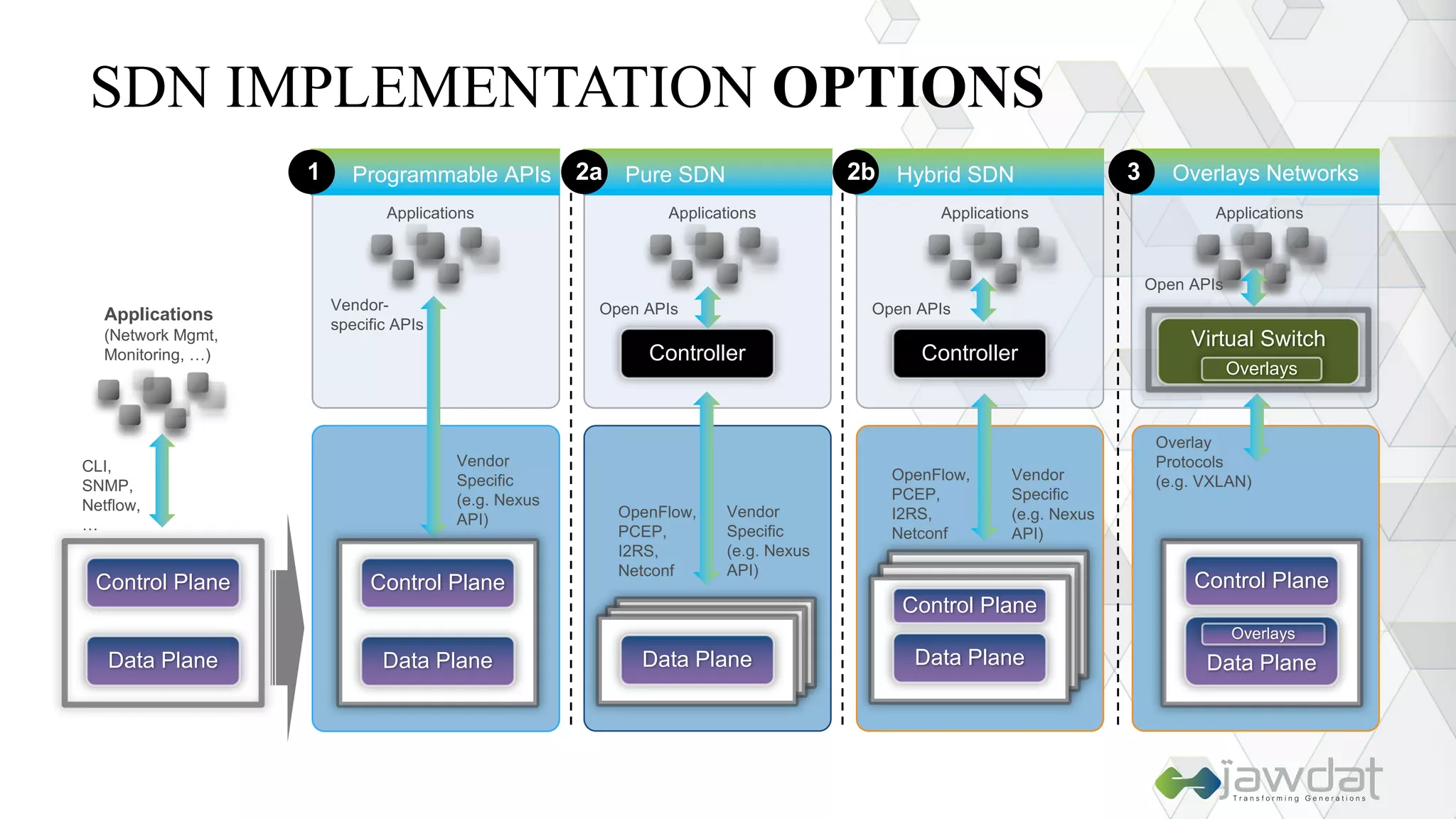
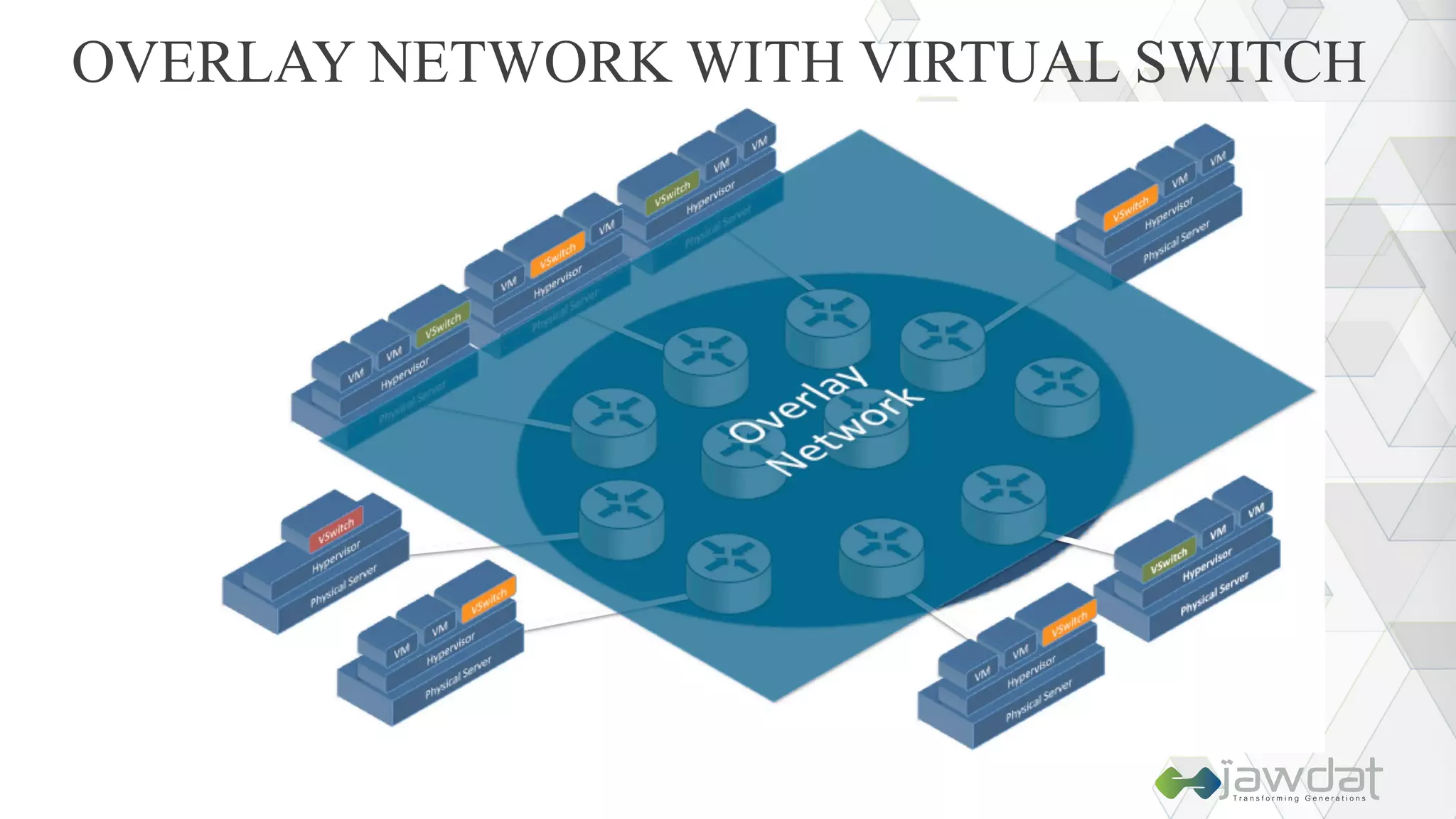
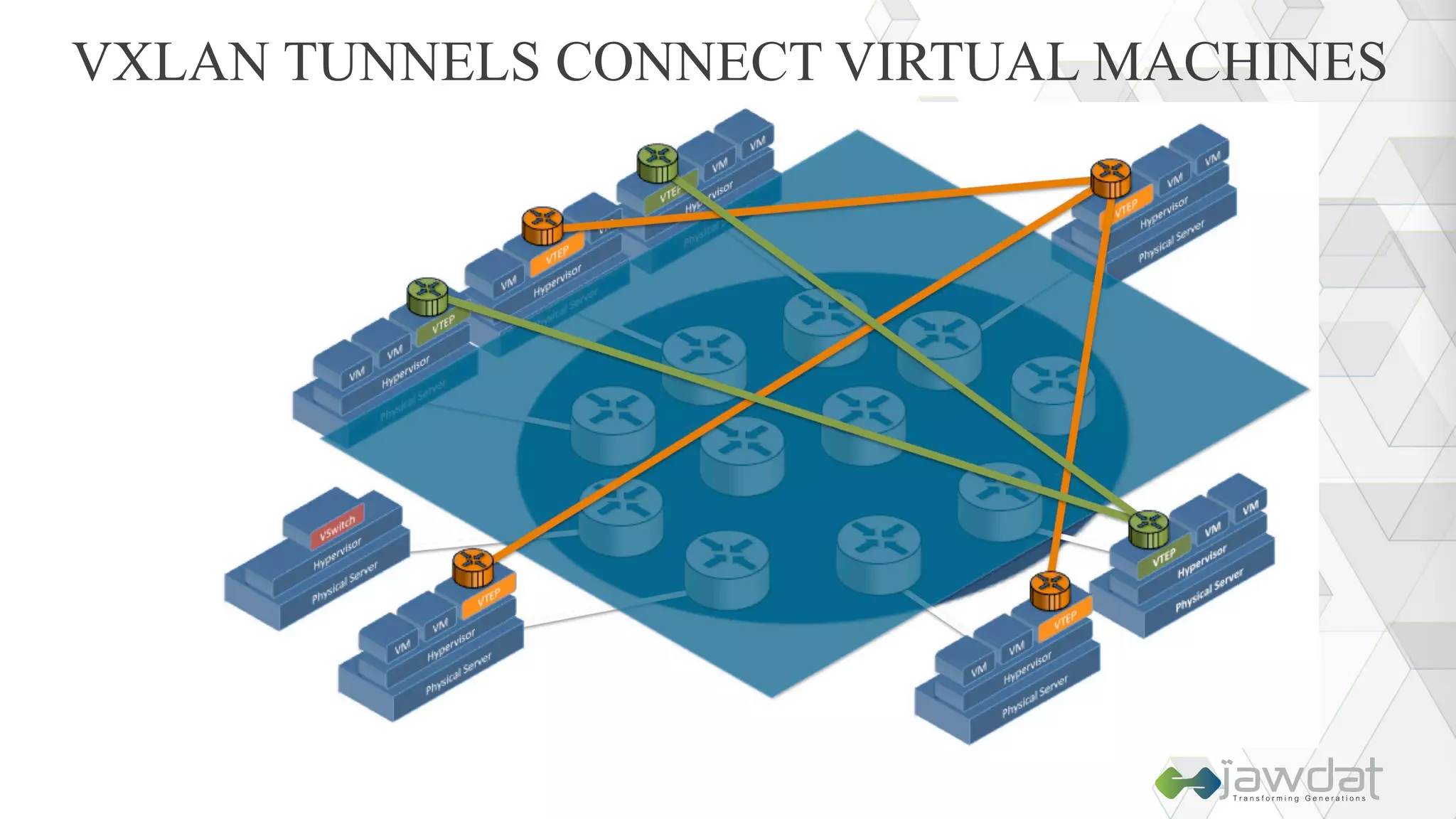
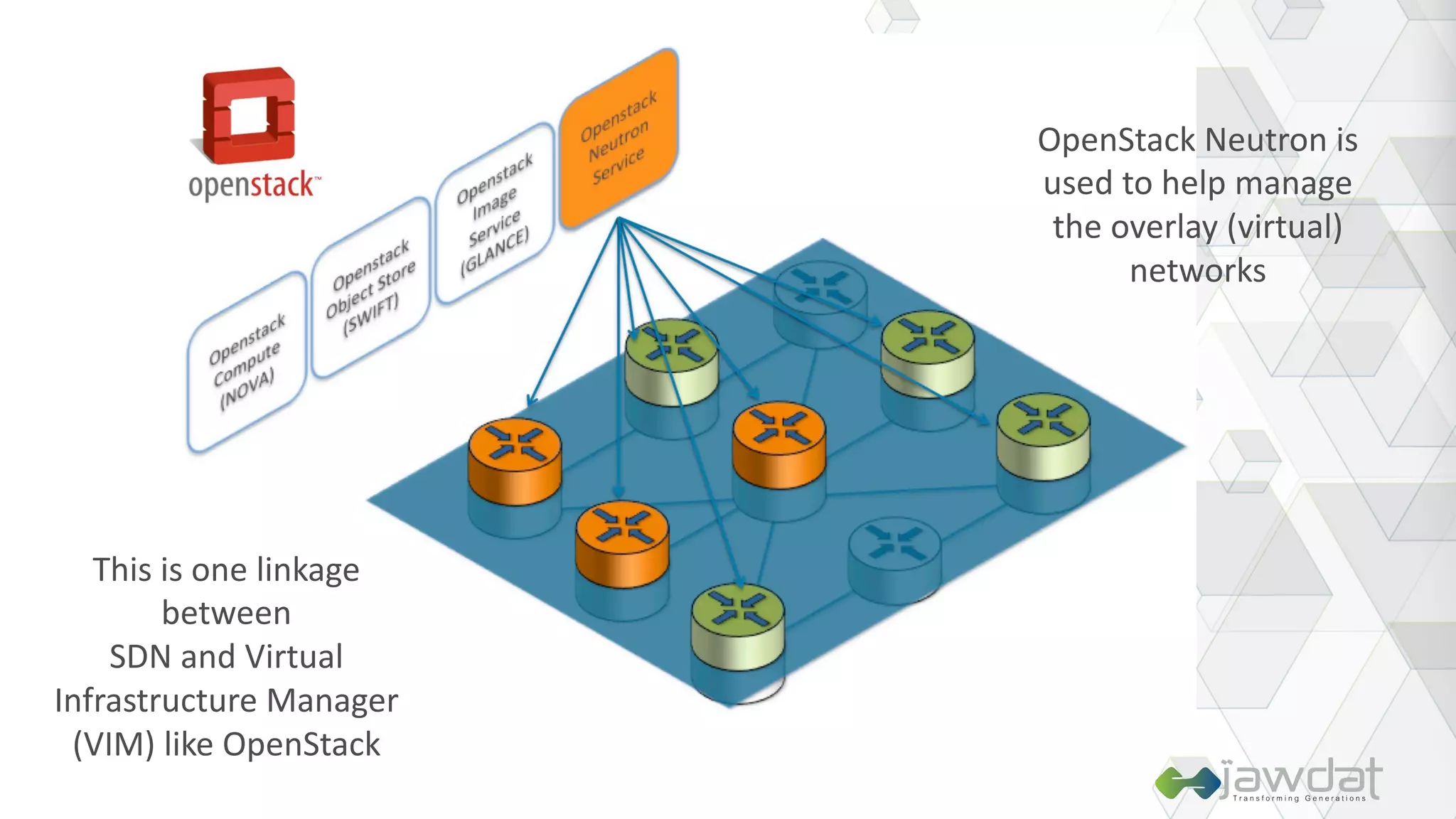
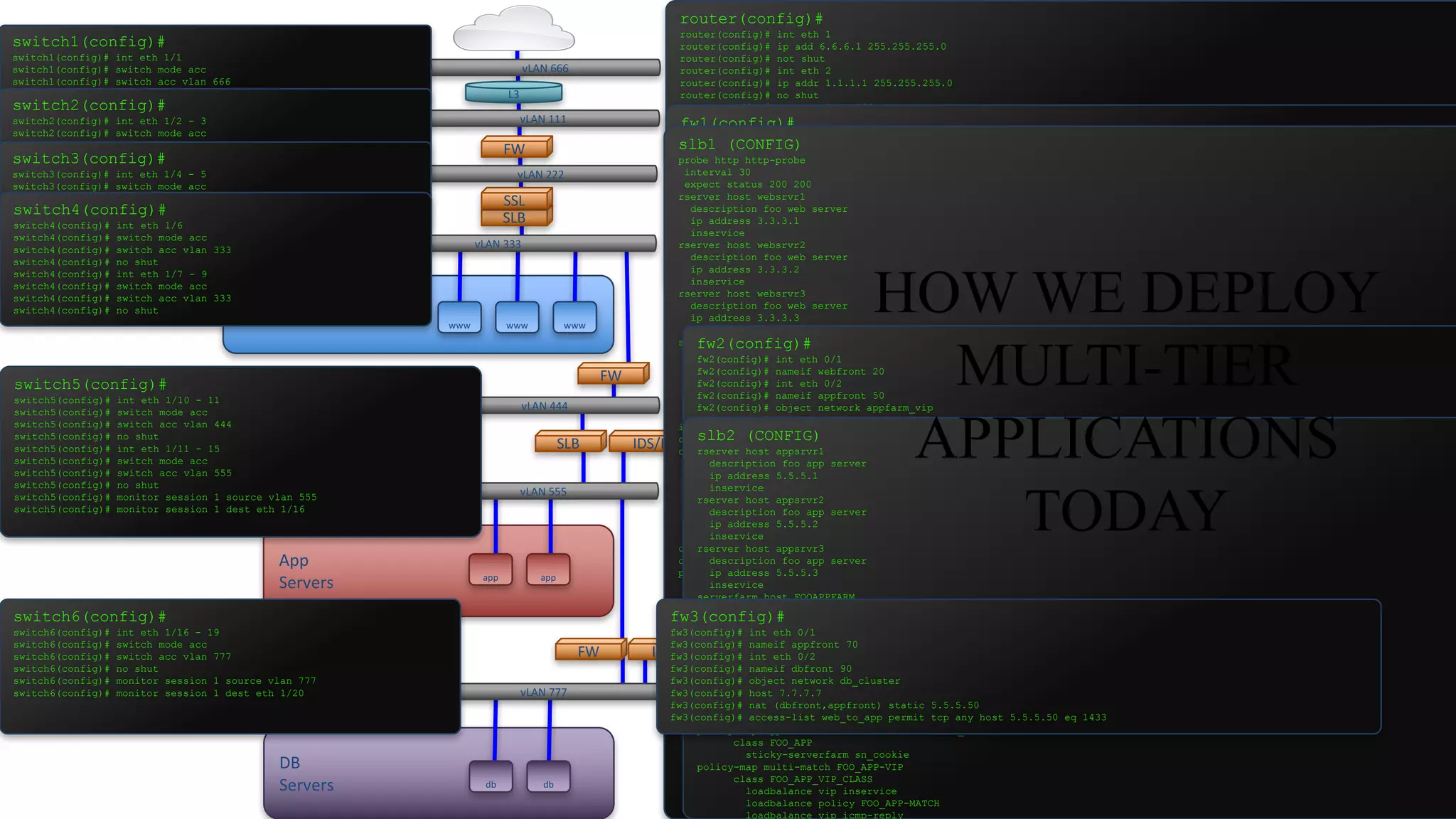
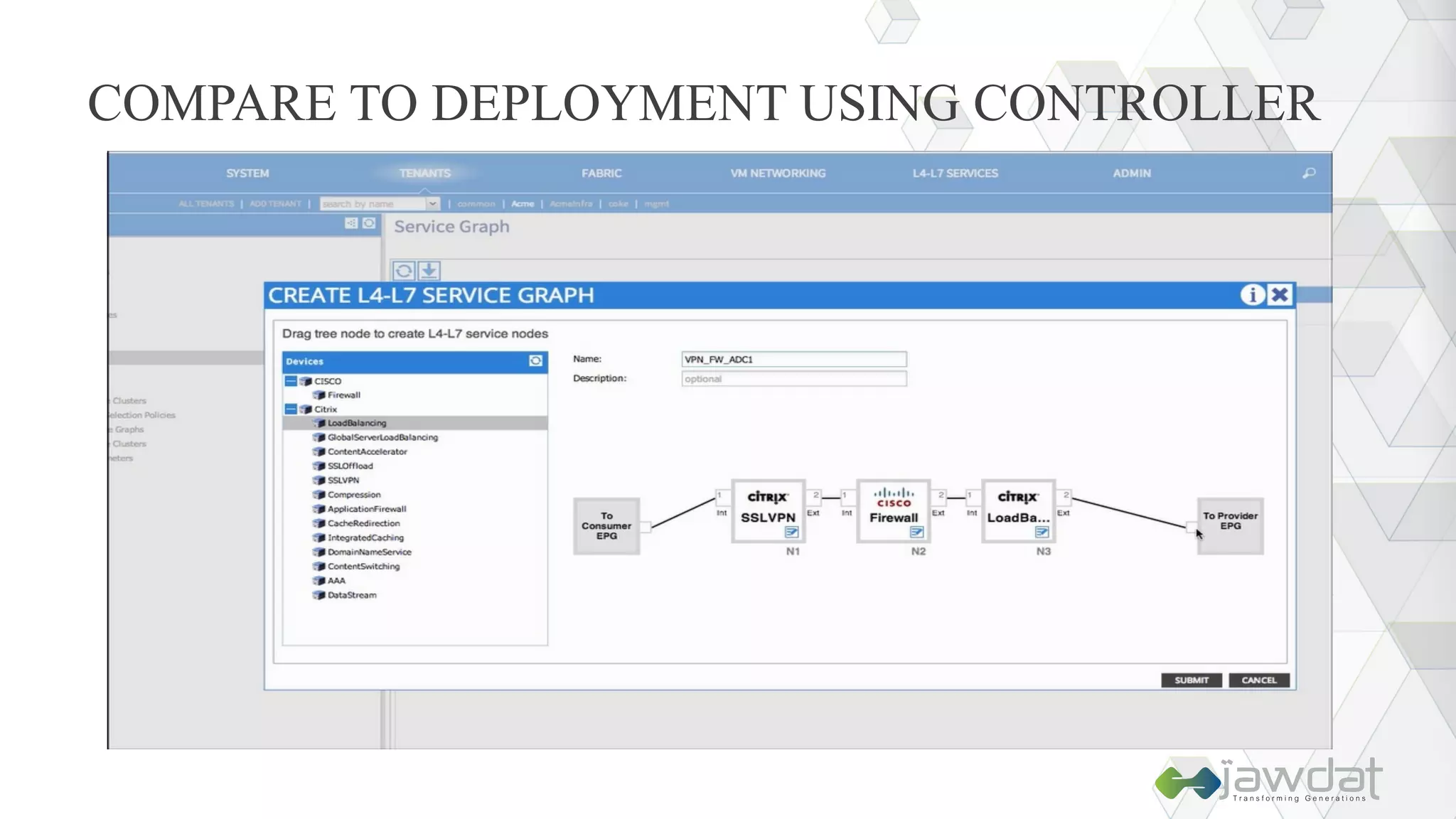
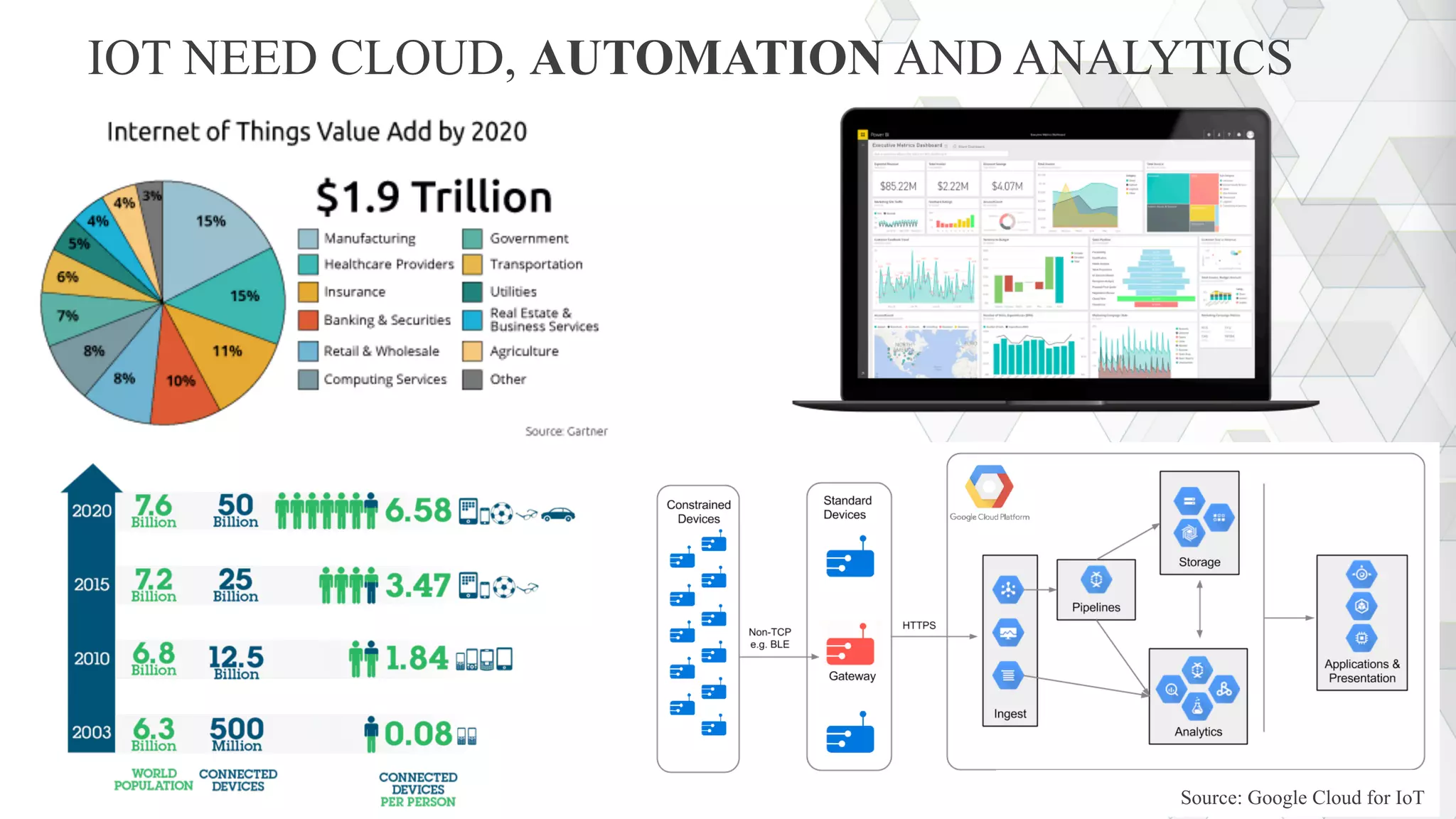
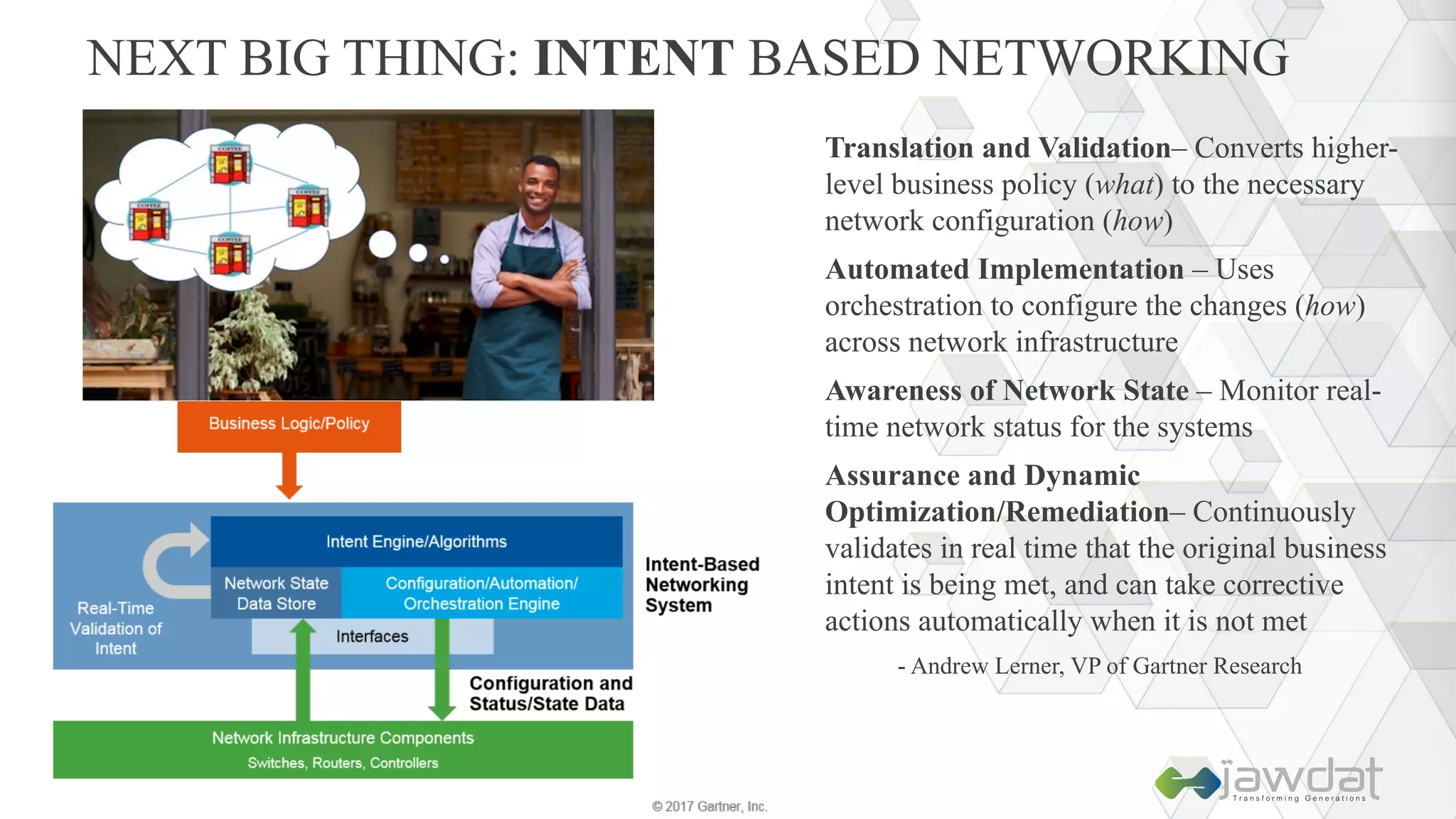
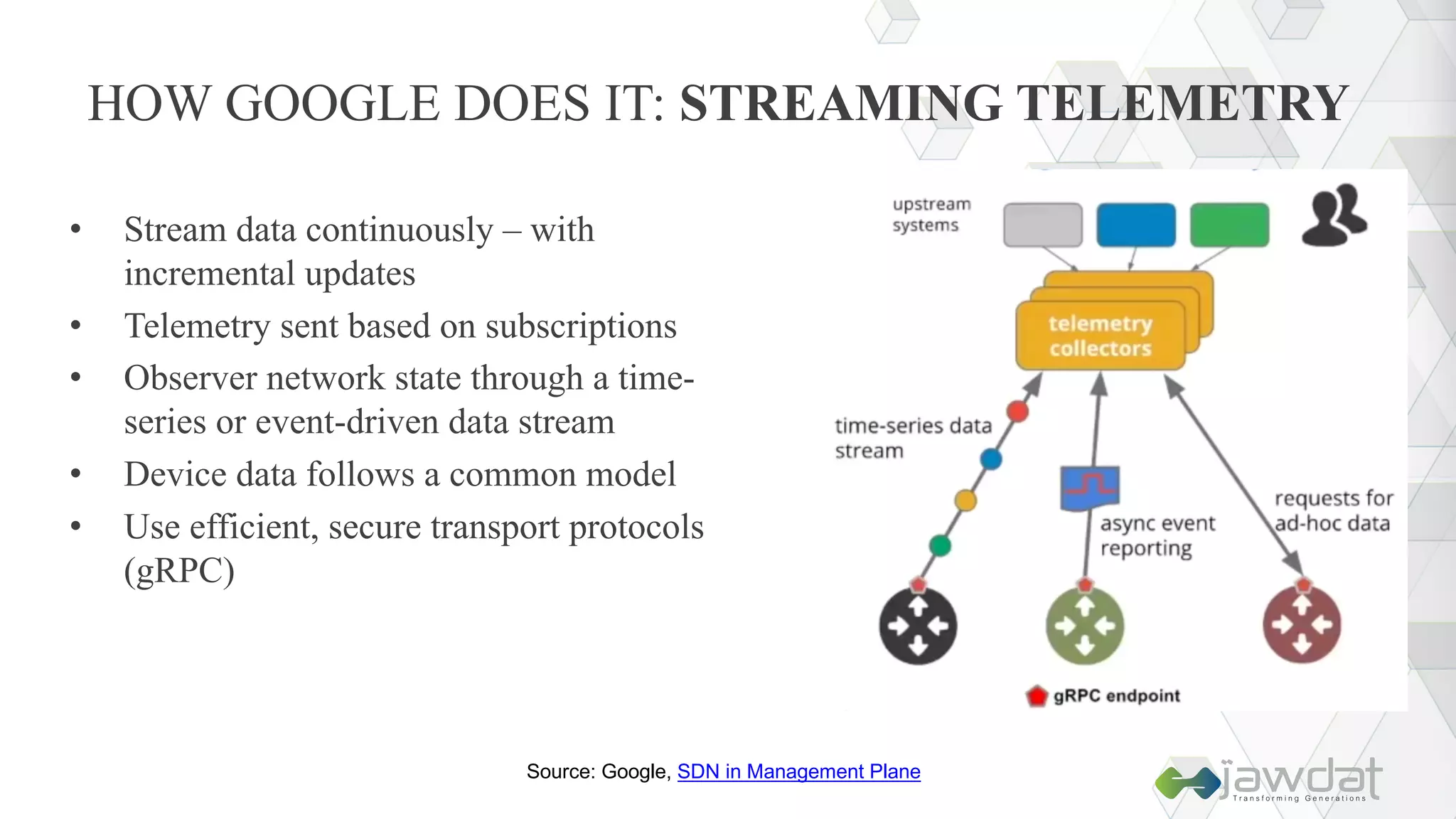
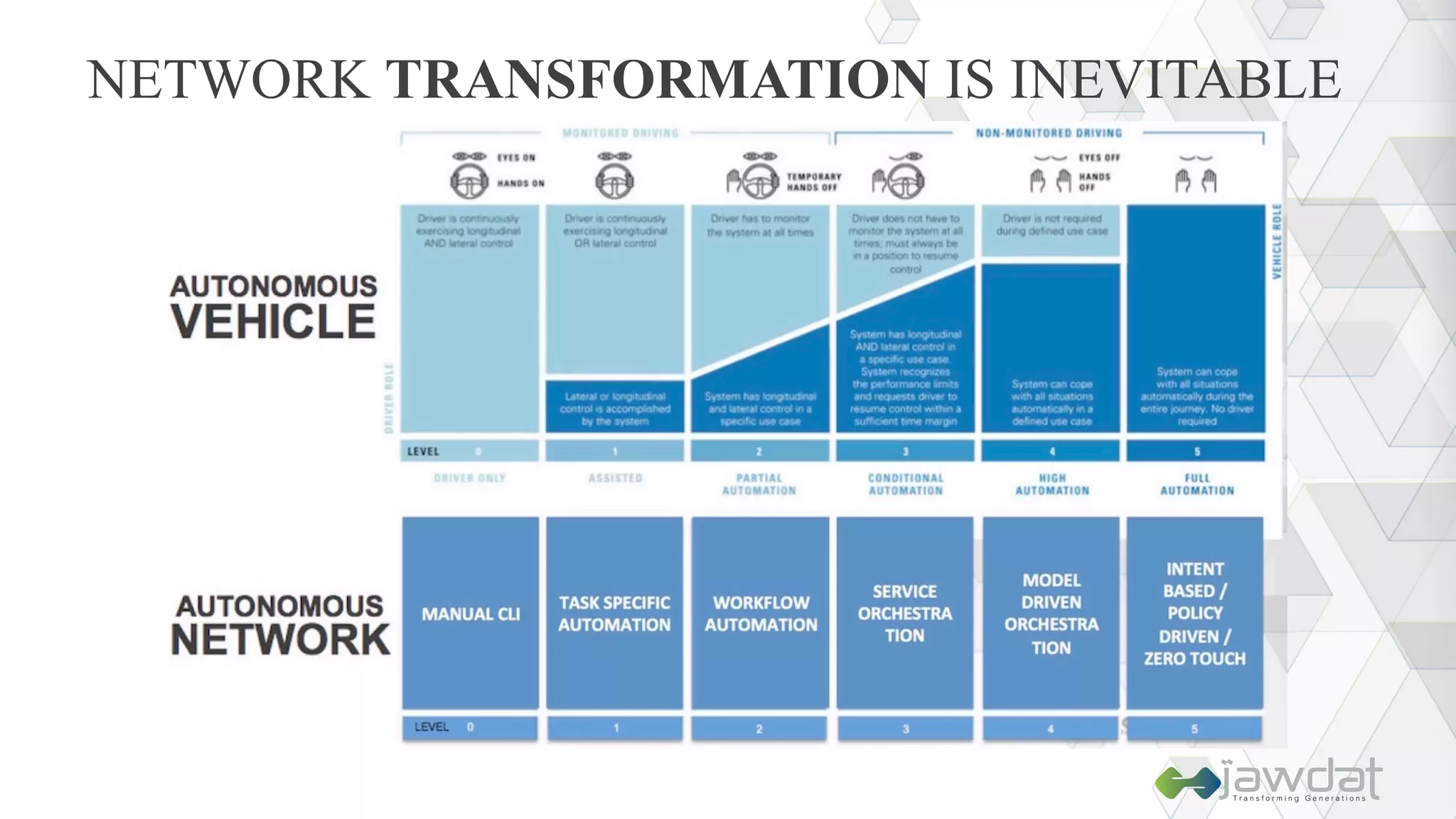
The document discusses the evolution and fundamental concepts of Software Defined Networking (SDN), emphasizing its separation of control and data planes to enhance network management. It details the architecture involving OpenFlow, the roles of controllers, agents, and various applications, as well as the implementation of Network Functions Virtualization (NFV). Additionally, it explores future trends such as intent-based networking and the adoption of cloud, automation, and analytics in SDN transformation.