1. The document describes an experiment to determine the amount of caffeine in different tea samples.
2. The procedure involves boiling tea leaves, filtering, precipitating with lead acetate, extracting caffeine using chloroform, evaporating the chloroform, and weighing the remaining caffeine.
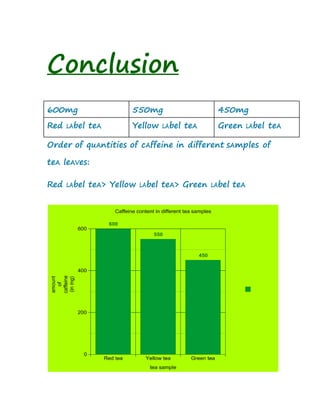
3. Observations show the red label tea contains the most caffeine (0.6g), followed by yellow label tea (0.55g), and then green label tea (0.45g).