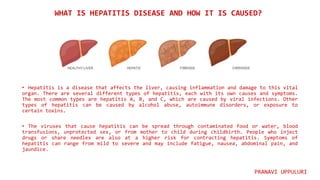
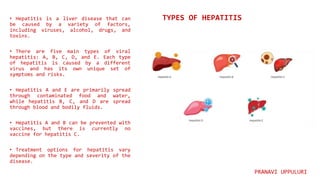
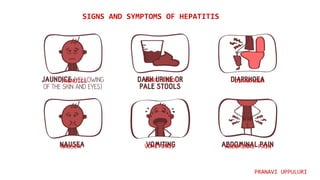
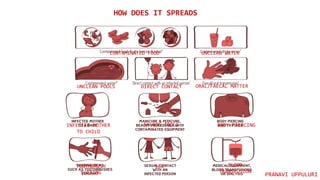
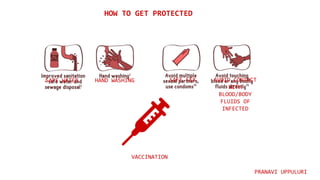
Hepatitis is a disease that causes inflammation of the liver and is caused by several different viruses and other factors. There are five main types of viral hepatitis: A, B, C, D, and E. Hepatitis A and E are primarily spread through contaminated food and water, while hepatitis B, C, and D are spread through blood and bodily fluids. Hepatitis is a major global health concern, affecting millions worldwide, with the highest burden in low and middle income countries where access to testing and treatment is limited.