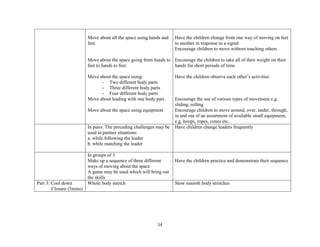
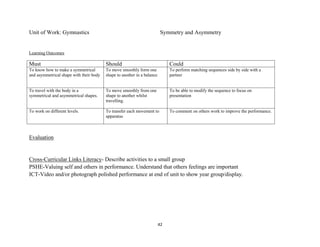
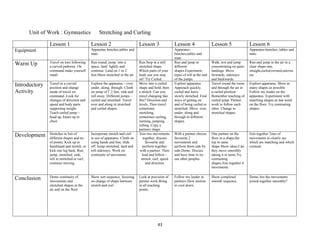
Stand side on to target
Ball: Hold ball in one hand at side of body
Throw: Step forward with opposite foot, swing arm forward and release ball
Partner: (10mins) - Practice
underhand throw to partner
Thrower: Aim at partner's hands
Catcher: Watch ball into hands, give feedback
Small groups: (10mins) - Throw
into hoops/targets
Thrower: Aim for target, follow through arm swing
Others: Give feedback, collect balls
Part 3: Closure (5mins)
Review key points of underhand throw
Cool down activity: Jogging on spot
Assessment: Observe students' ability to