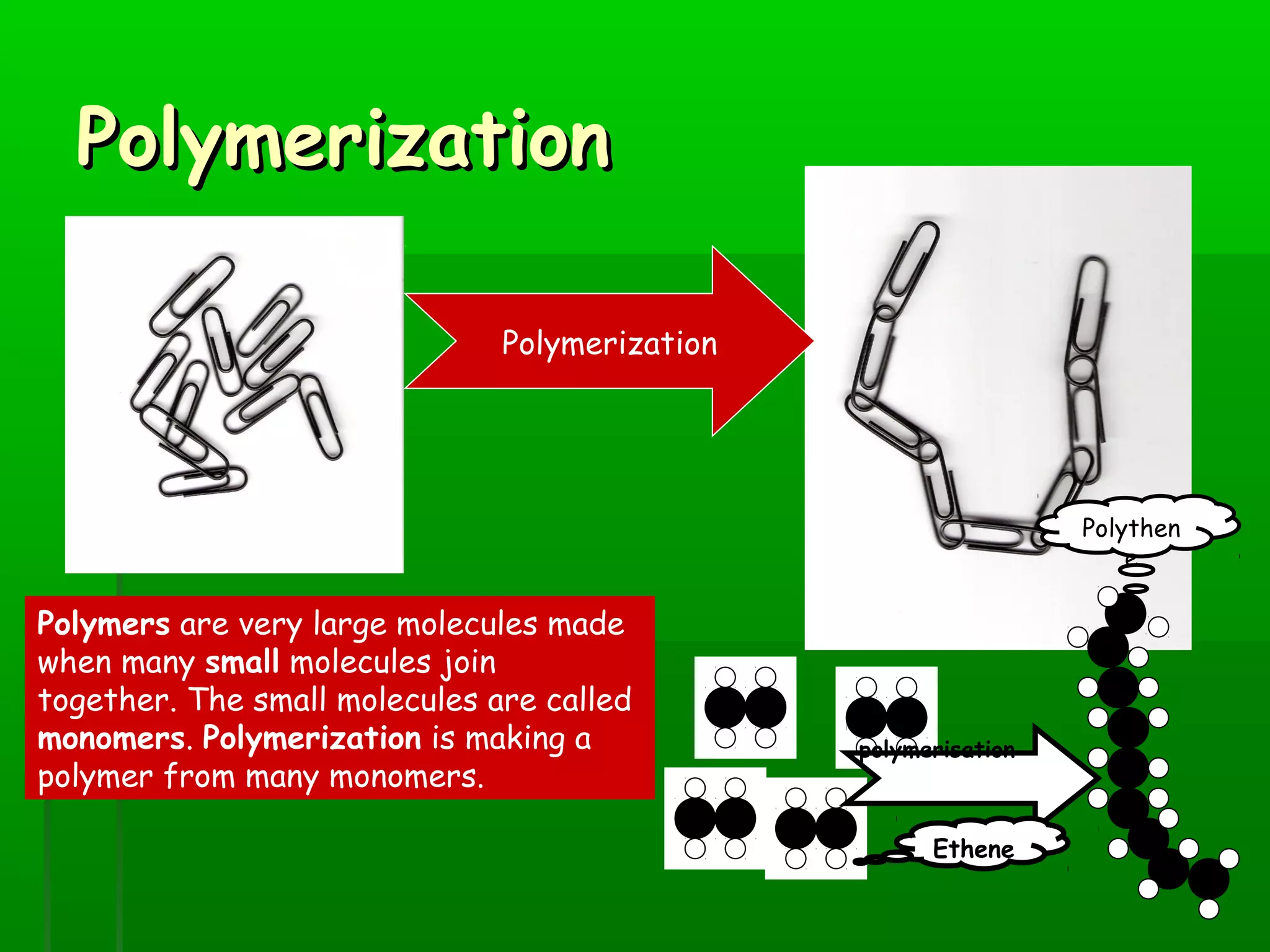
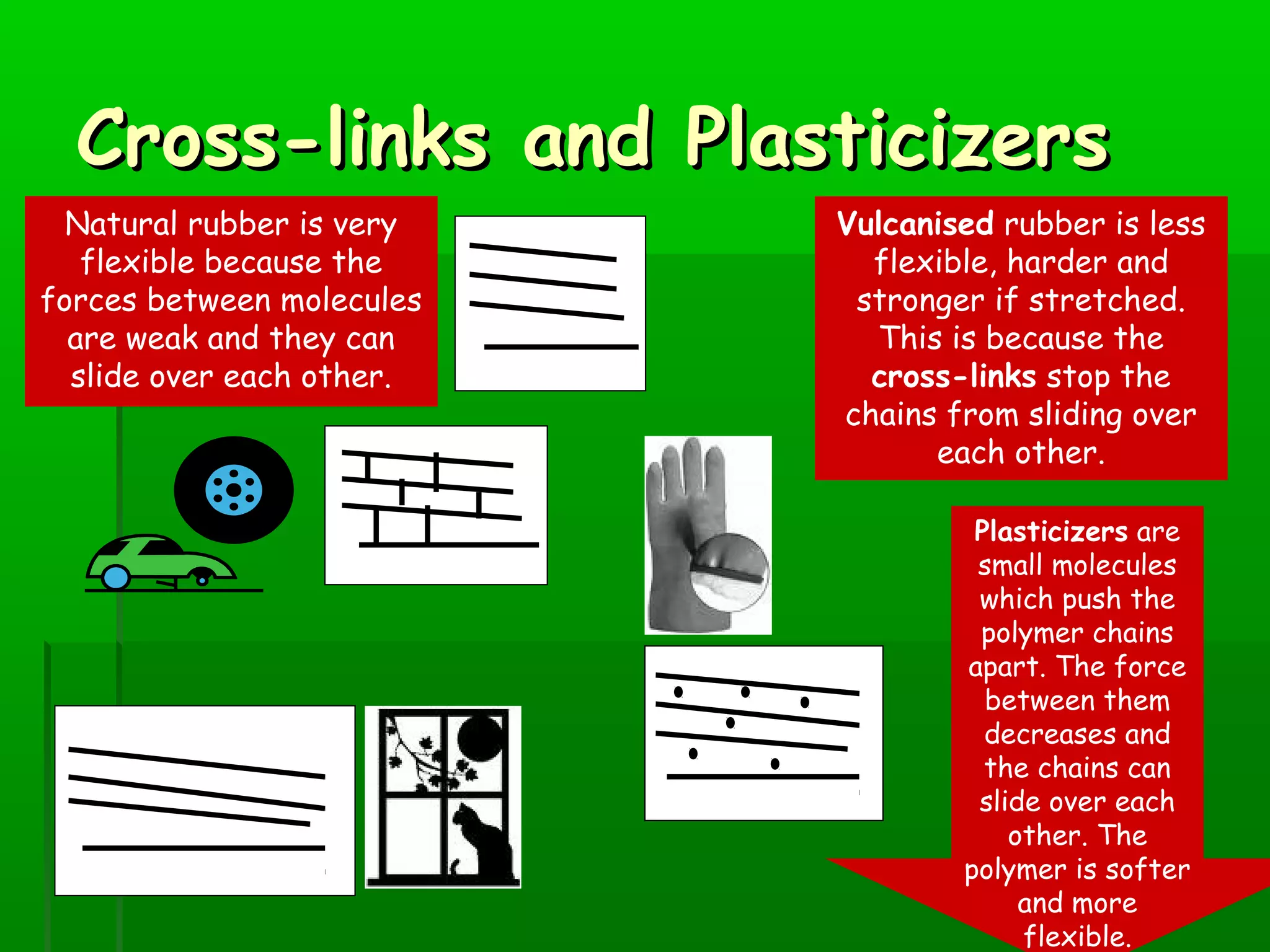
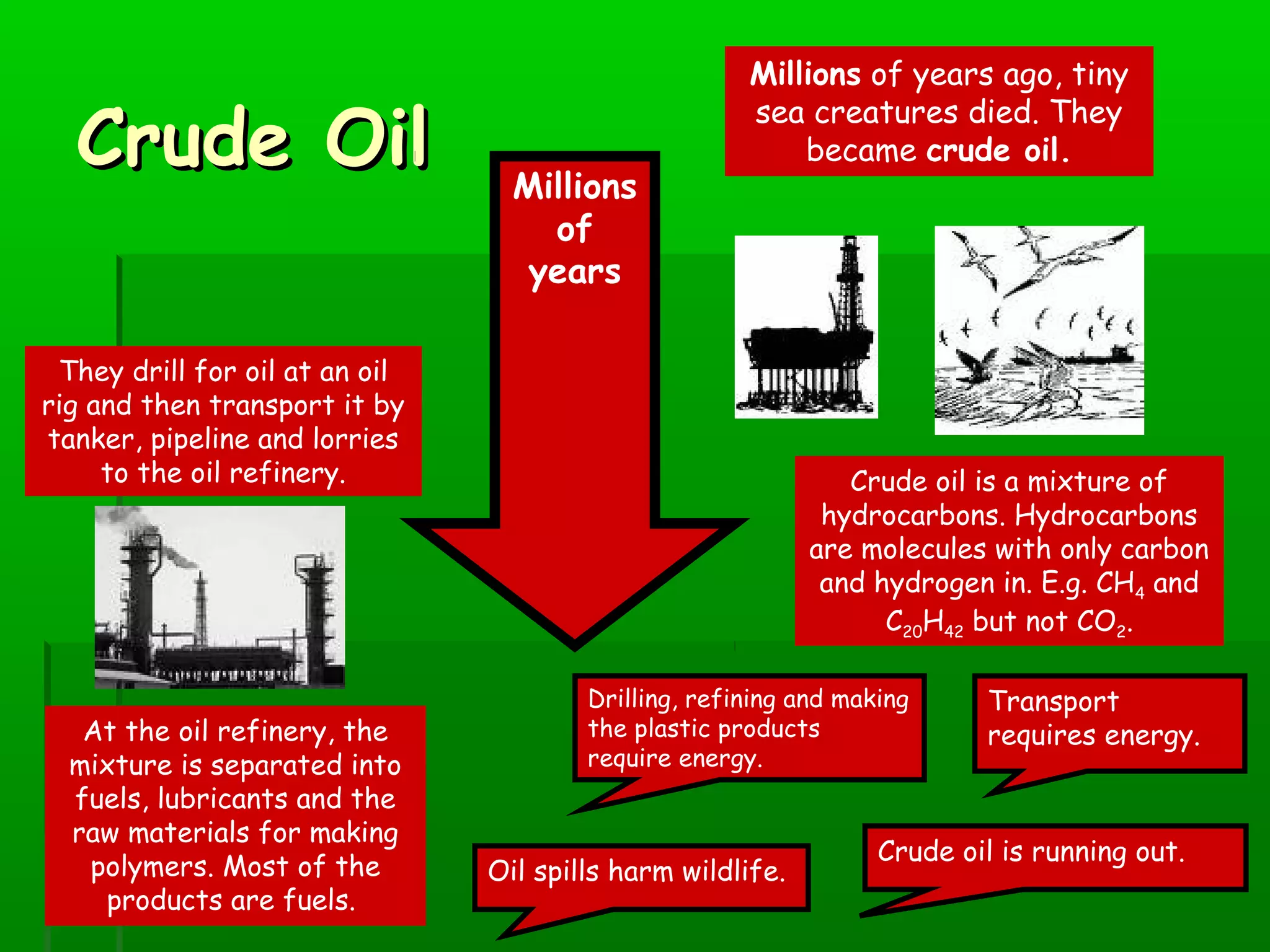
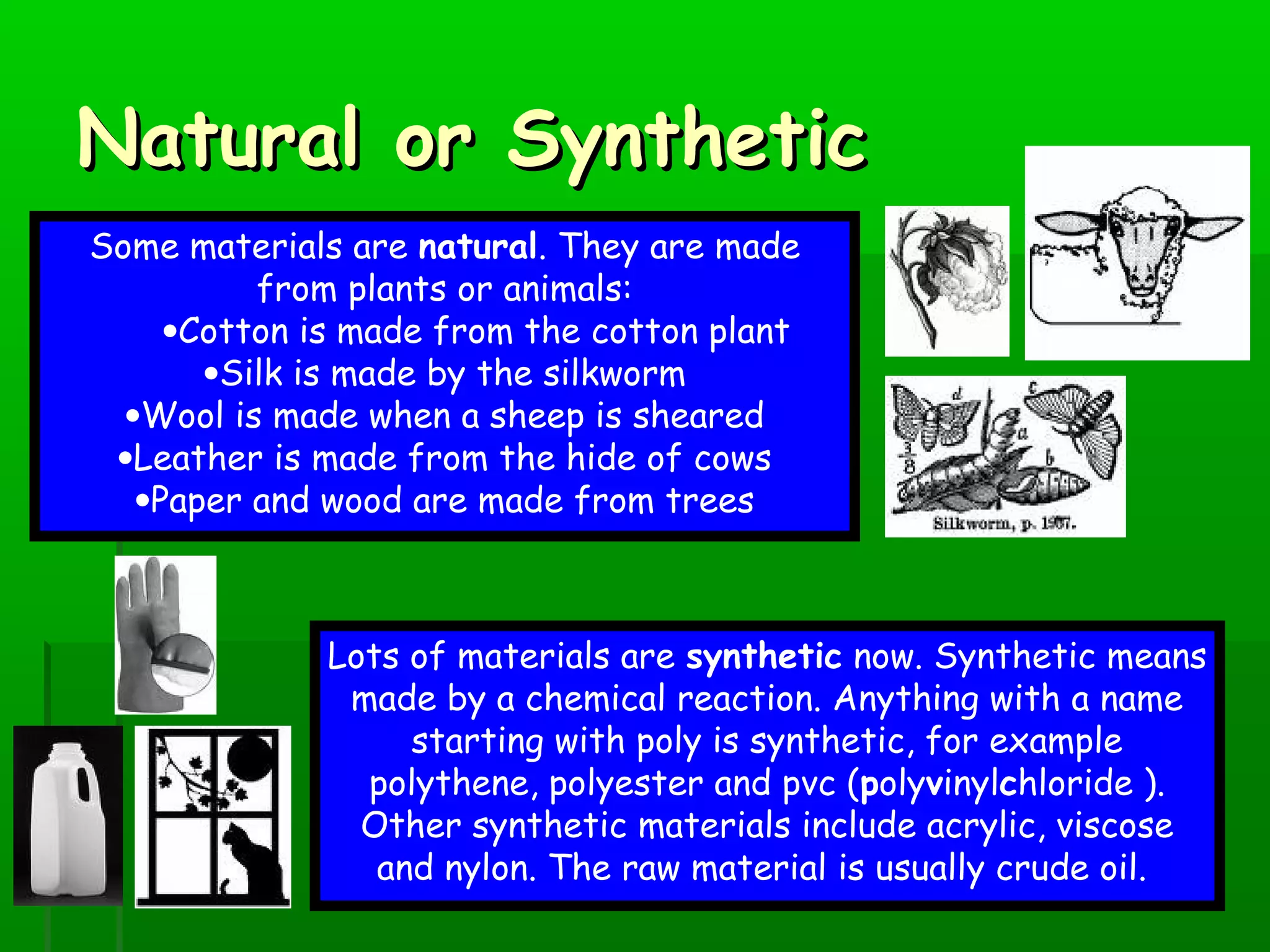
Materials are chosen based on their properties, such as polystyrene being used for hot drink containers because it is waterproof, low density, and a poor thermal conductor. Polymers are large molecules formed from monomers joining together through polymerization. The strength and flexibility of materials depends on the forces between polymer chains and whether they are crystalline or allow for movement. Most materials are now synthetic, derived from crude oil through extraction and refining, rather than natural sources. When selecting materials, a life cycle assessment considers impacts from raw material extraction through product use and disposal.