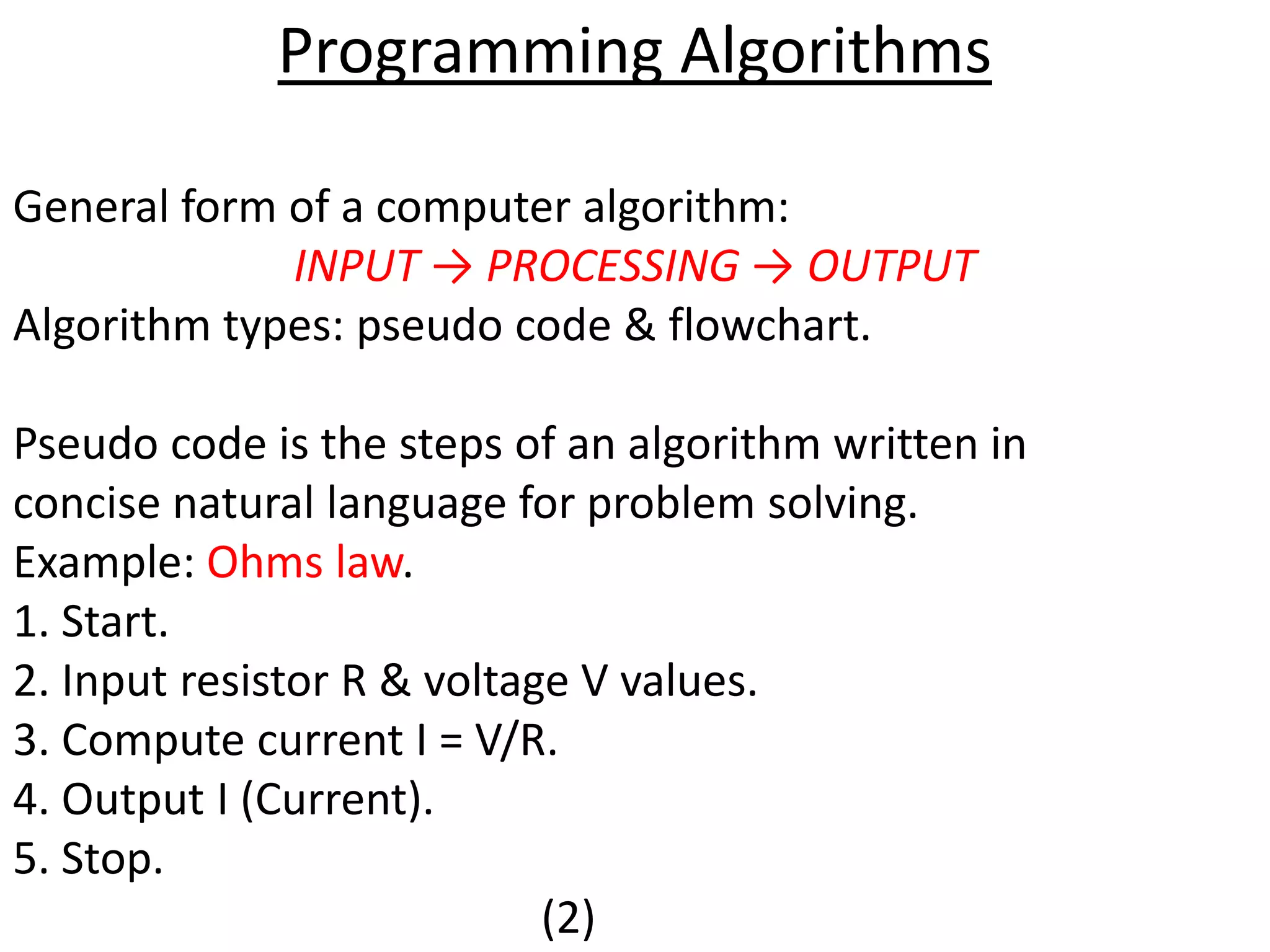
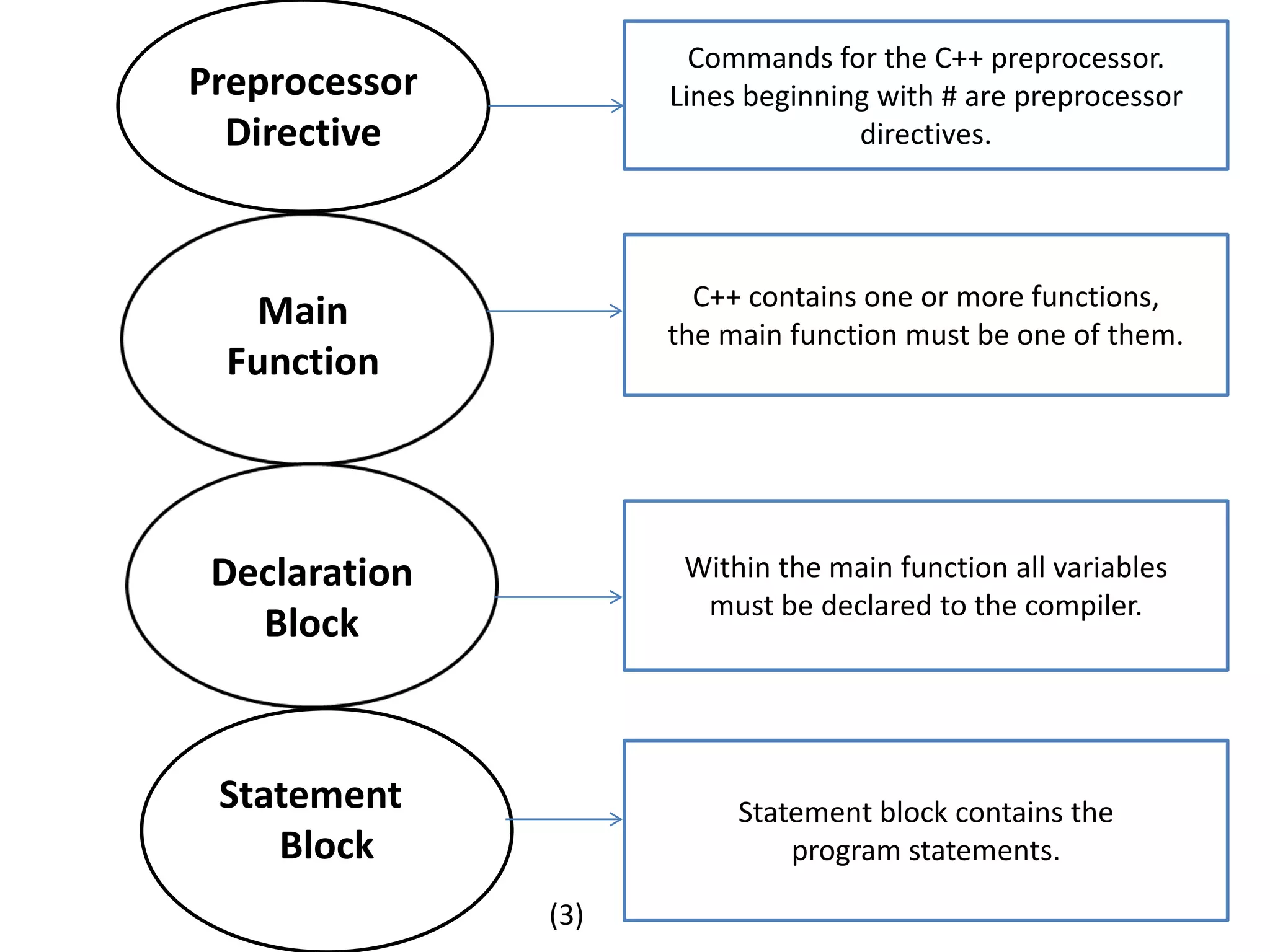
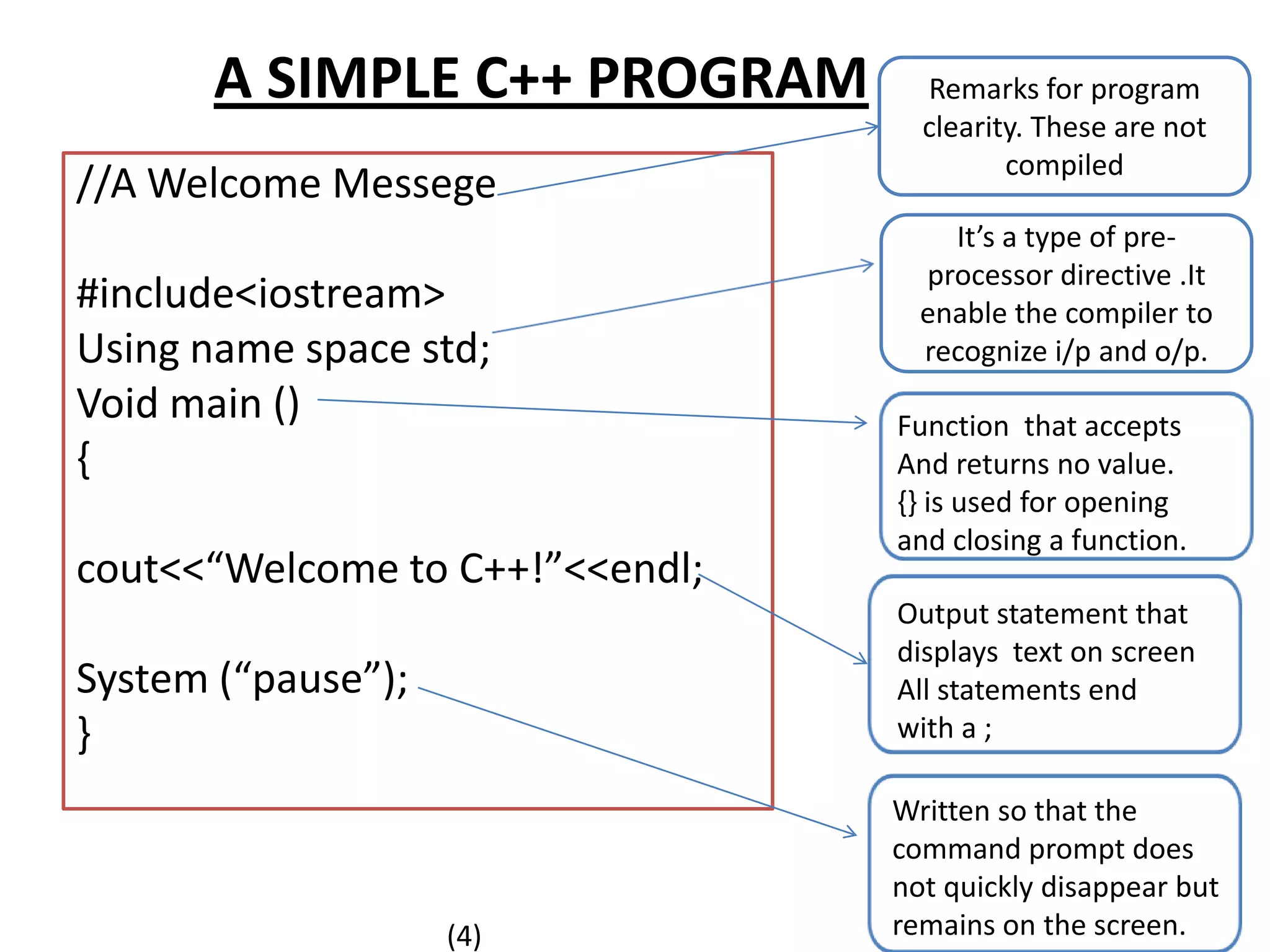
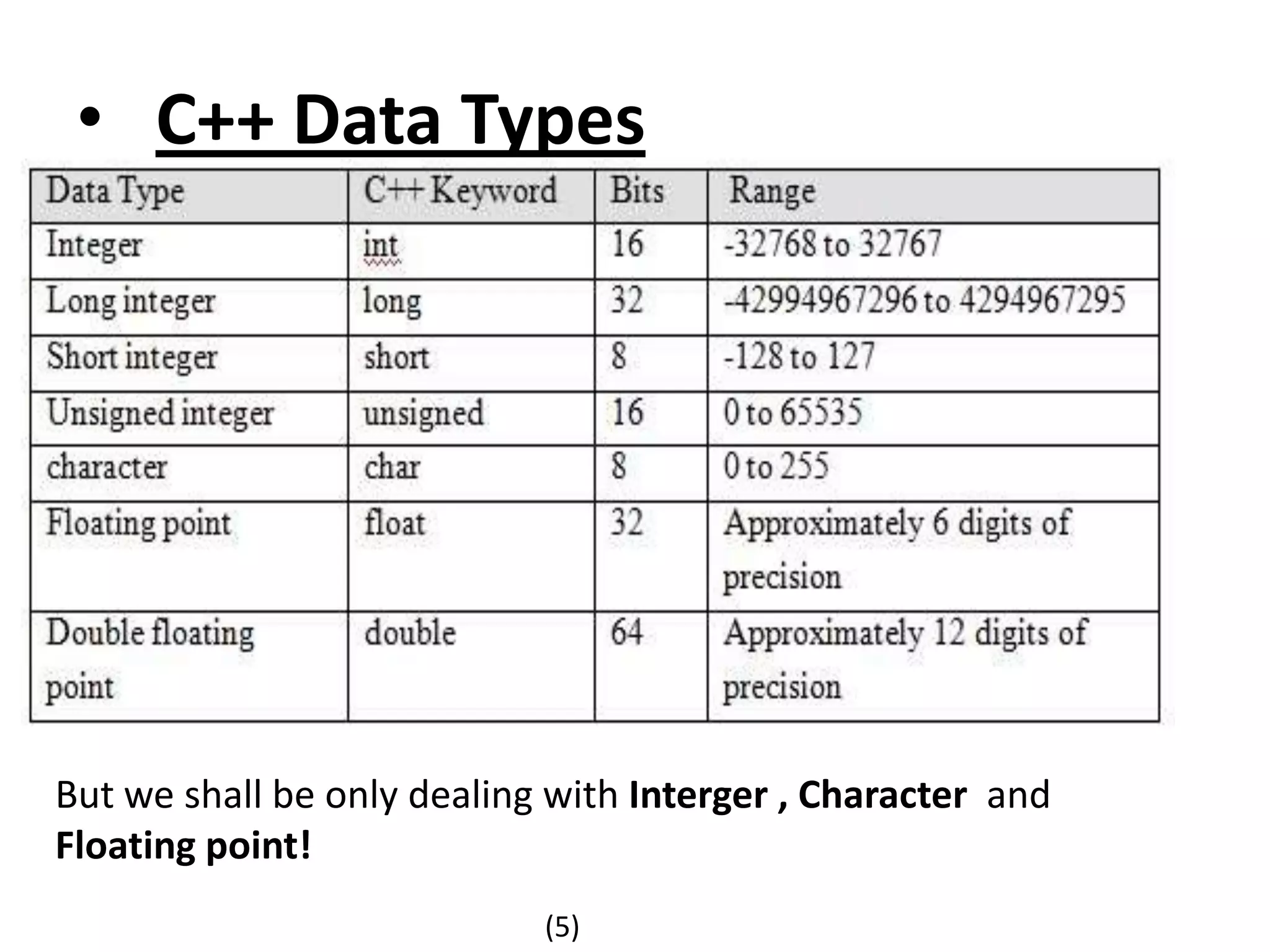
The document outlines the steps to solve programming problems in C++, including problem definition, algorithm development, coding, testing, and debugging. It introduces basic algorithm types, C++ preprocessor commands, and a simple C++ program structure, along with examples for finding force and homework assignments. Key topics include data types and specific computations such as calculating circumference and temperature conversion.