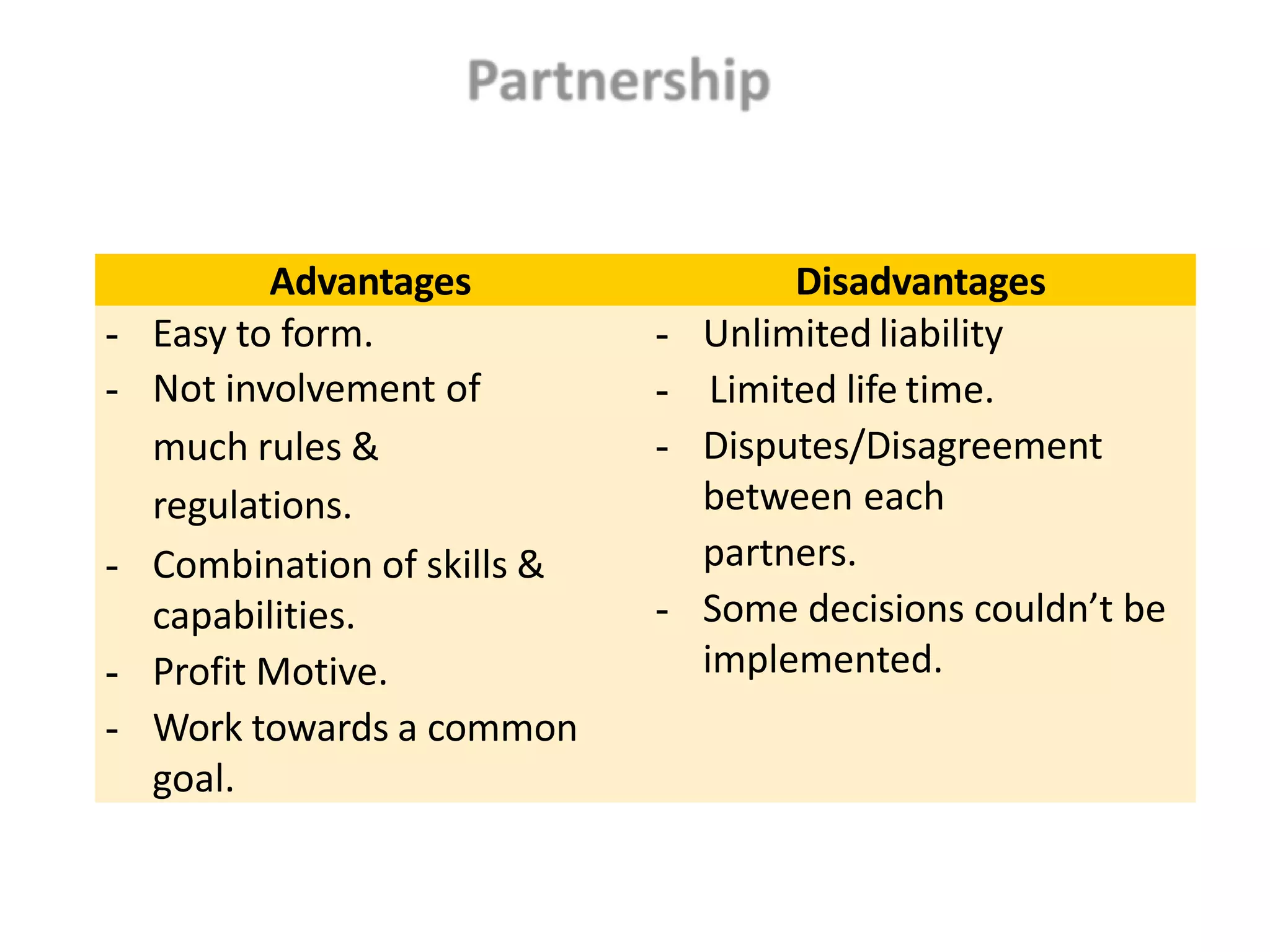
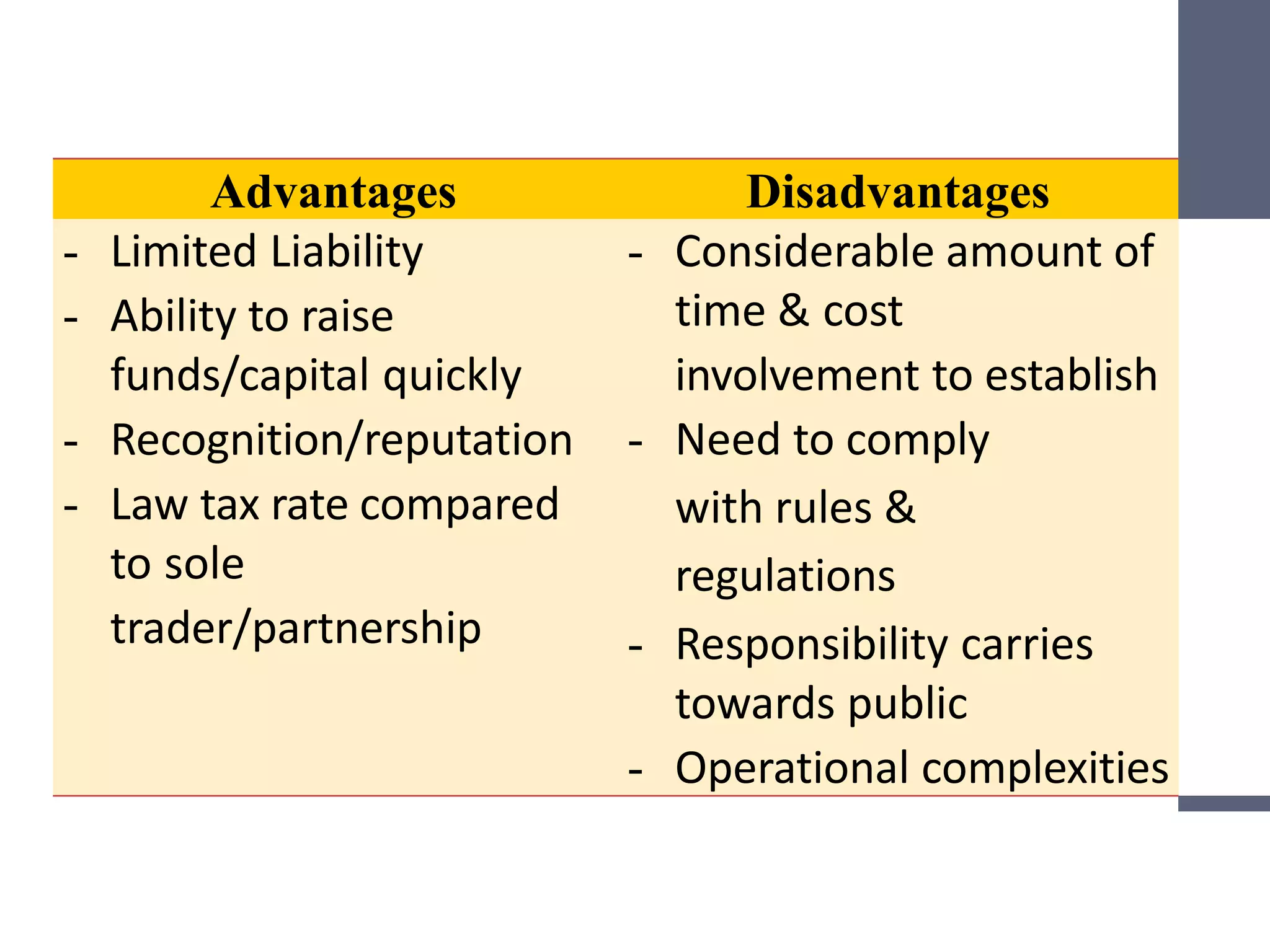
This document discusses different types of business entities including sole proprietorships, partnerships, private companies, public companies, and non-profit organizations. It provides details on their key characteristics such as ownership, capital structure, management, liability, legal status, registration process, profit sharing, and business risks. The types of business entities vary in their complexity, from the simple sole proprietorship to the more complex public company. Financial reporting also differs depending on the applicable rules and regulations for each entity type.