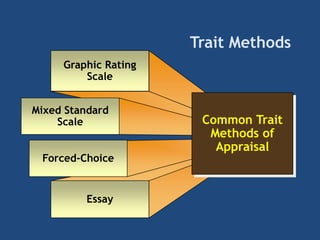
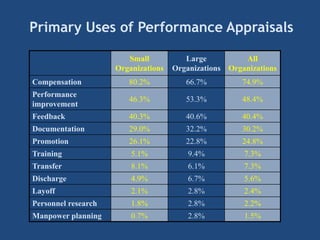
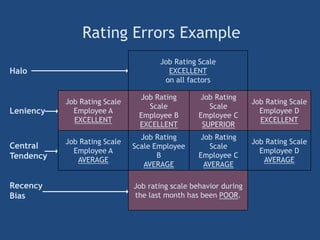
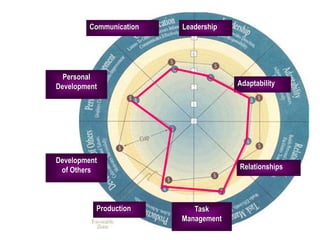
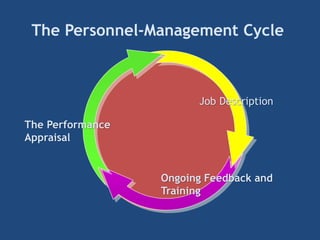
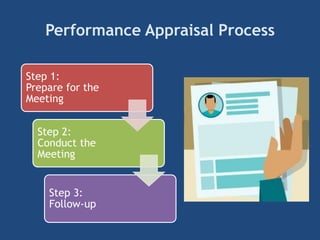
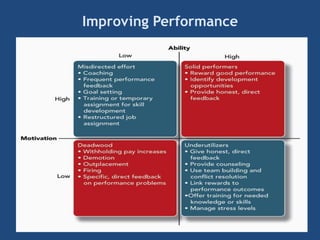
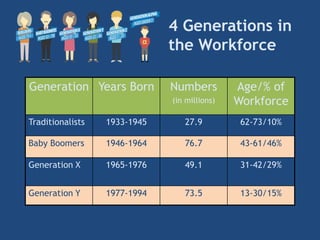
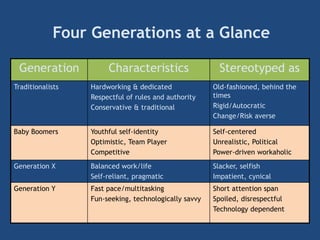
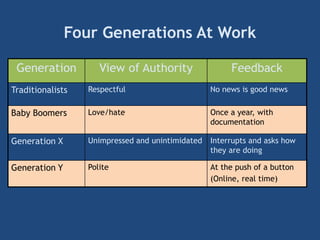
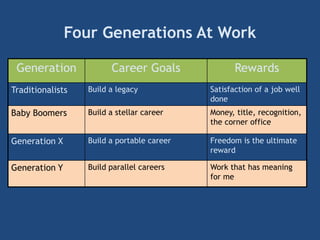
The document provides an overview of performance appraisal processes, including methods, purposes, and common issues. It emphasizes the importance of objective evaluation, feedback, and continuous communication between employees and management. Additionally, it addresses the varying perceptions of different generations in the workforce and their expectations regarding appraisals.