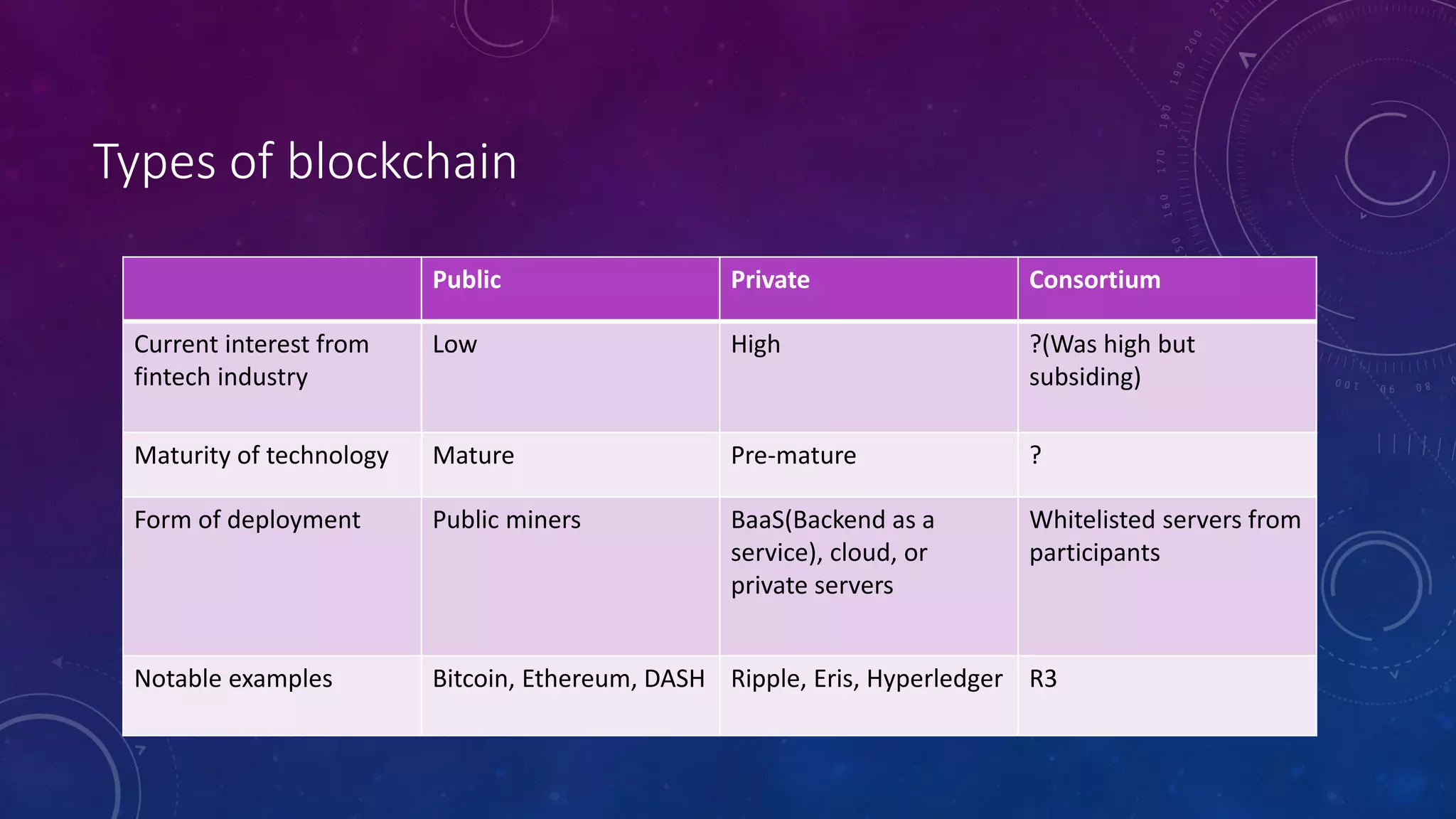
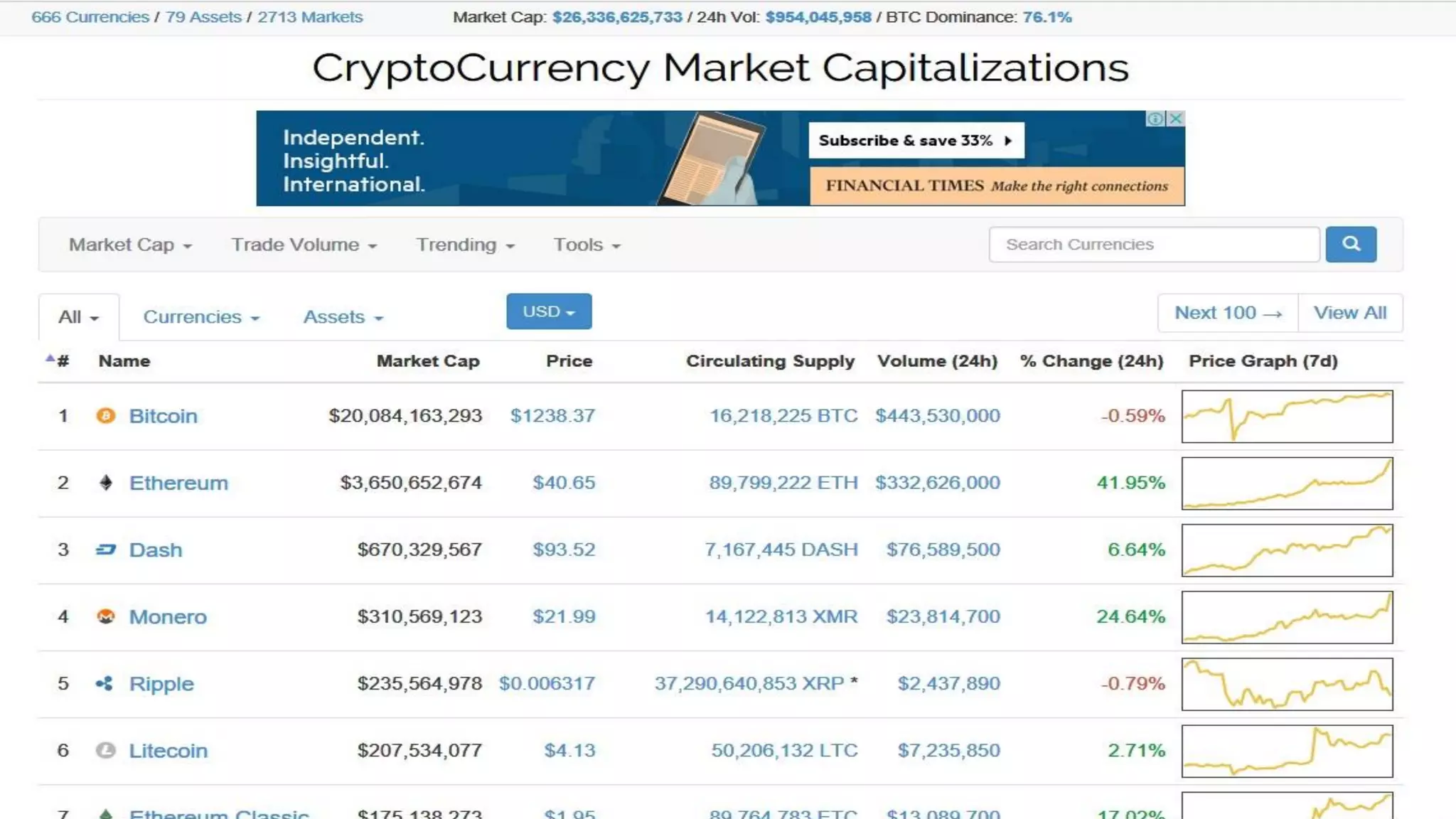
The document discusses the transformative potential of fintech and blockchain technologies in the global financial industry, emphasizing the need for infrastructure overhaul and the benefits of decentralization. It outlines the definition, benefits, and applications of blockchain, along with insights into current and future initiatives in the UAE aimed at adopting blockchain technologies. Key challenges to adoption include regulatory hurdles, the need for skilled resources, and understanding complex vocabulary associated with blockchain.