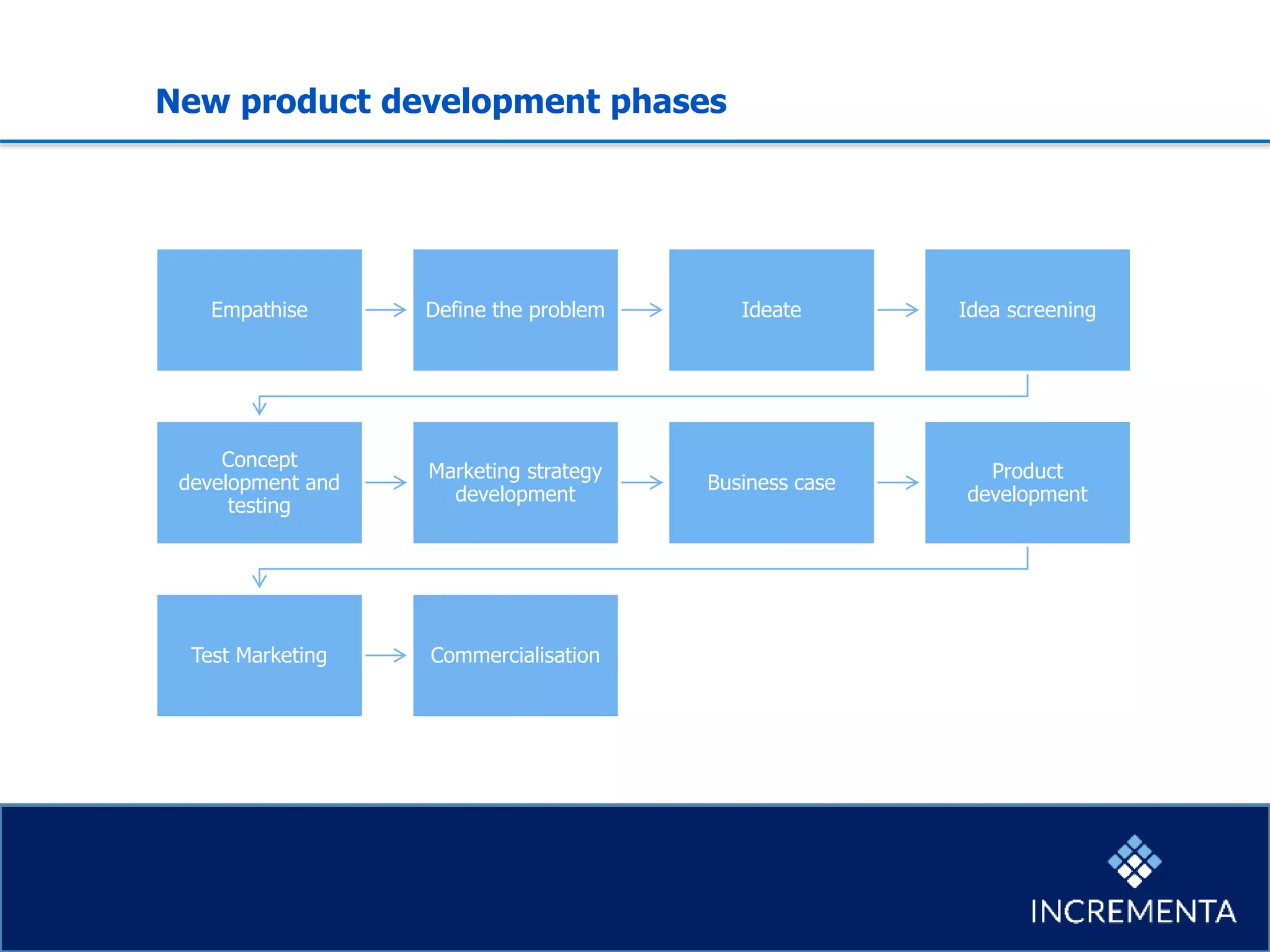
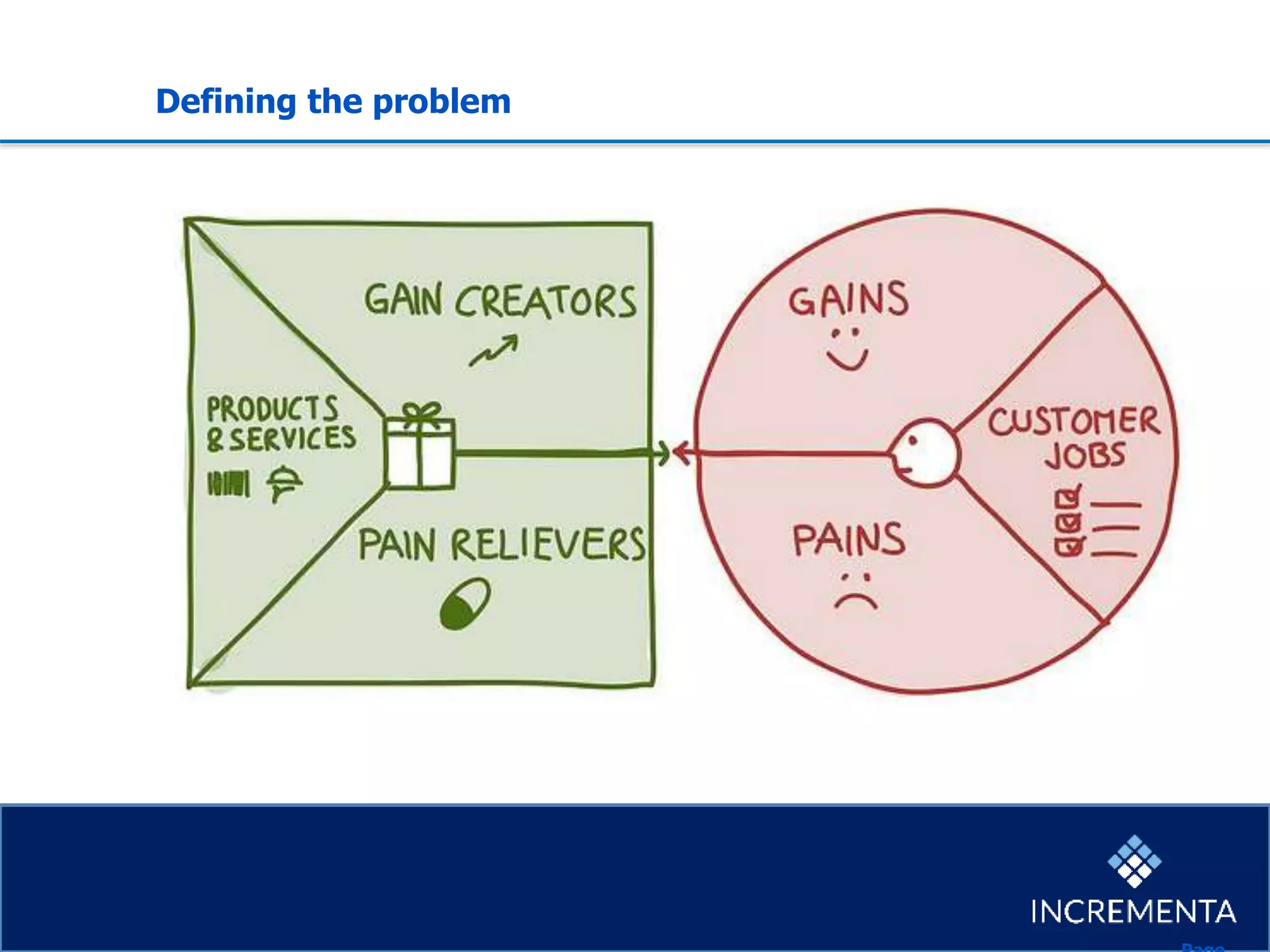
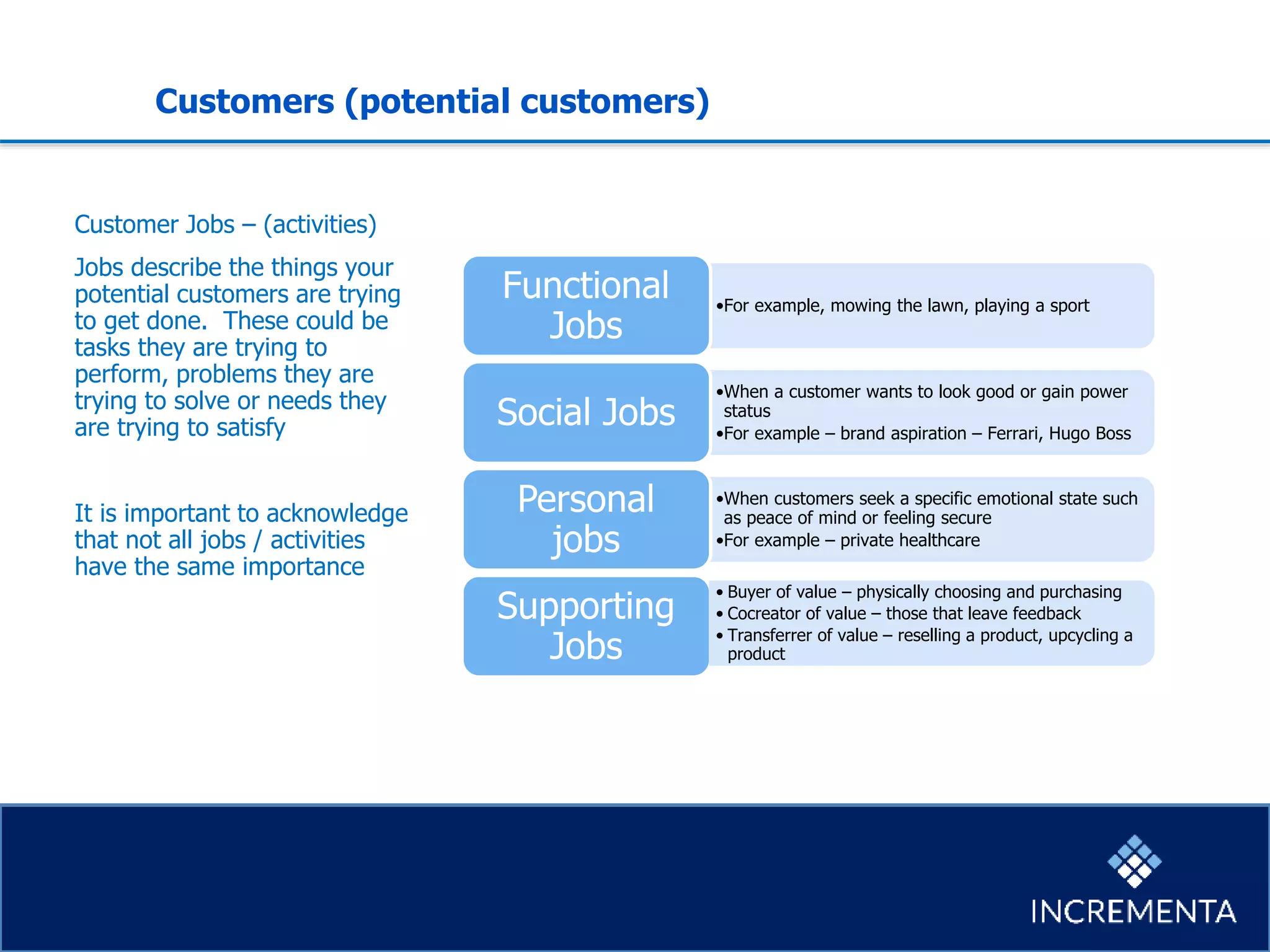
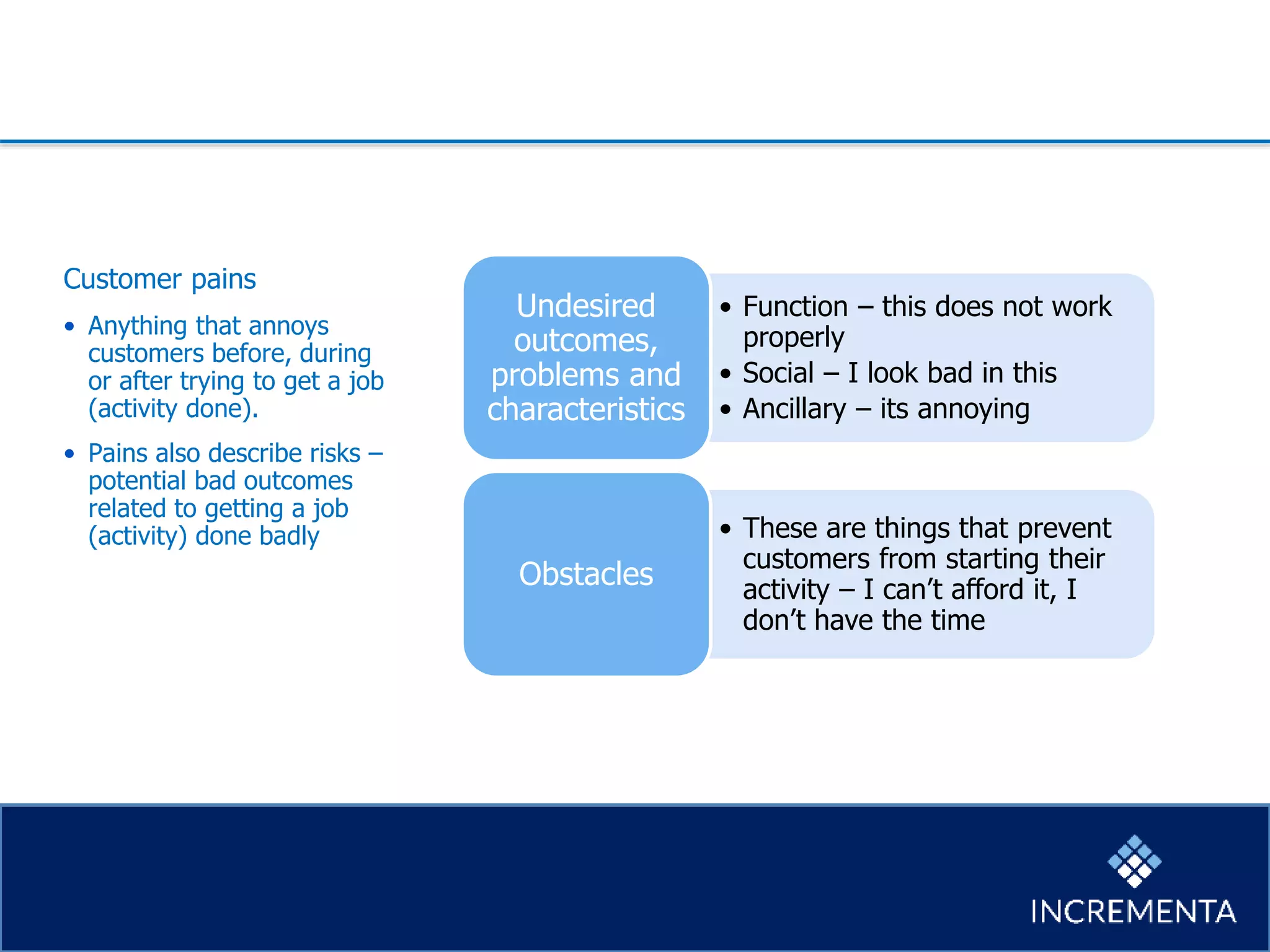
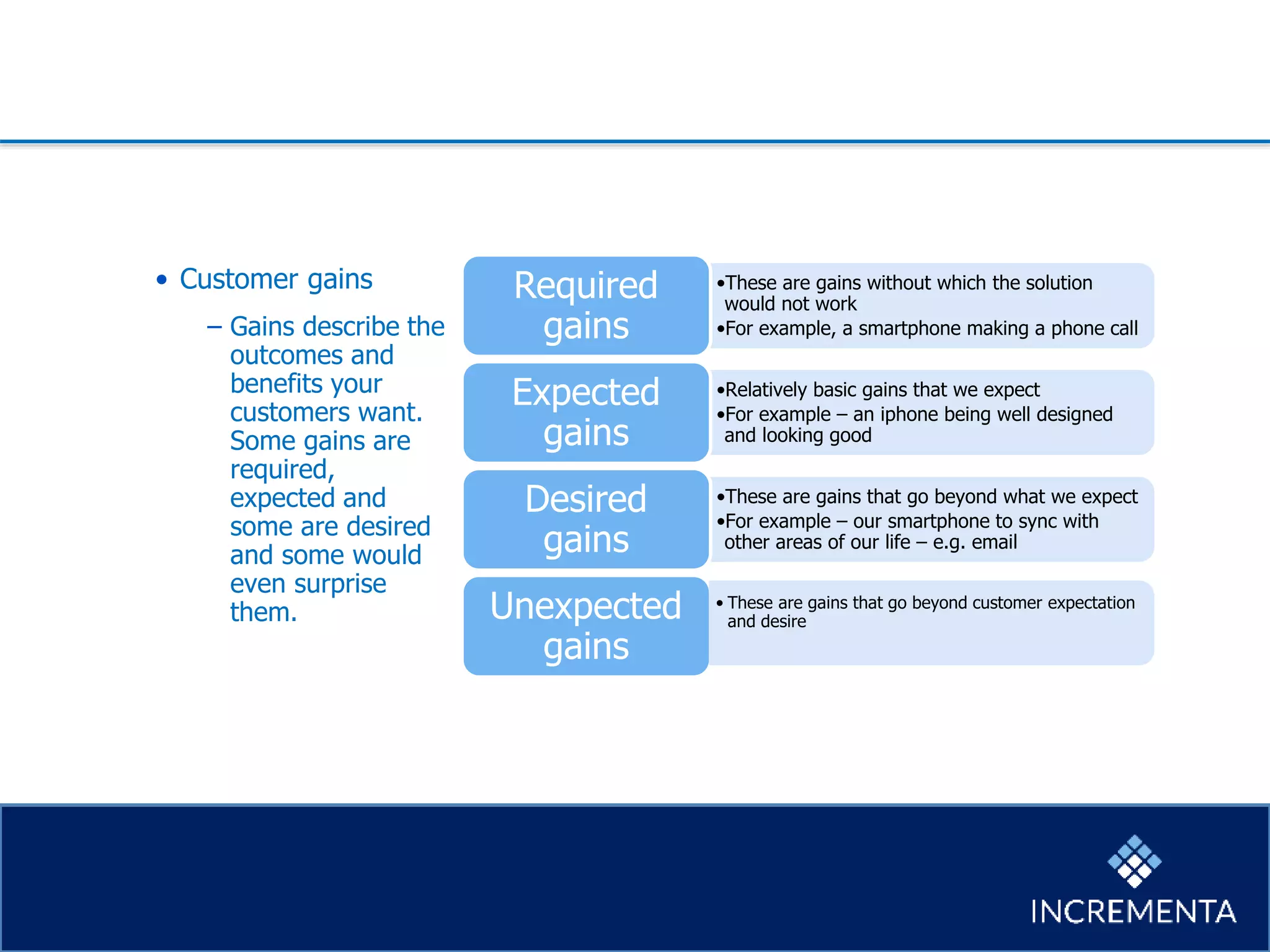
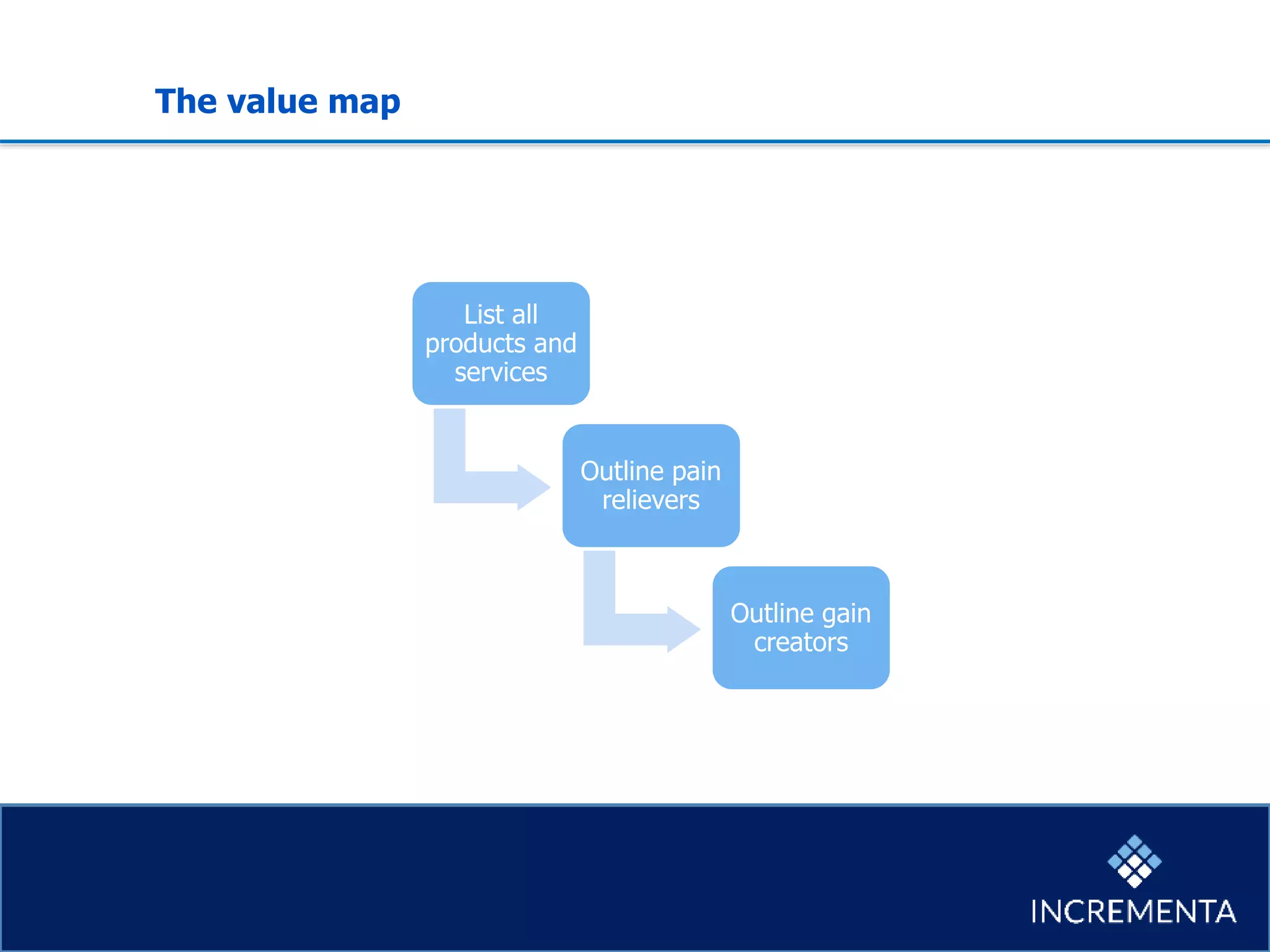
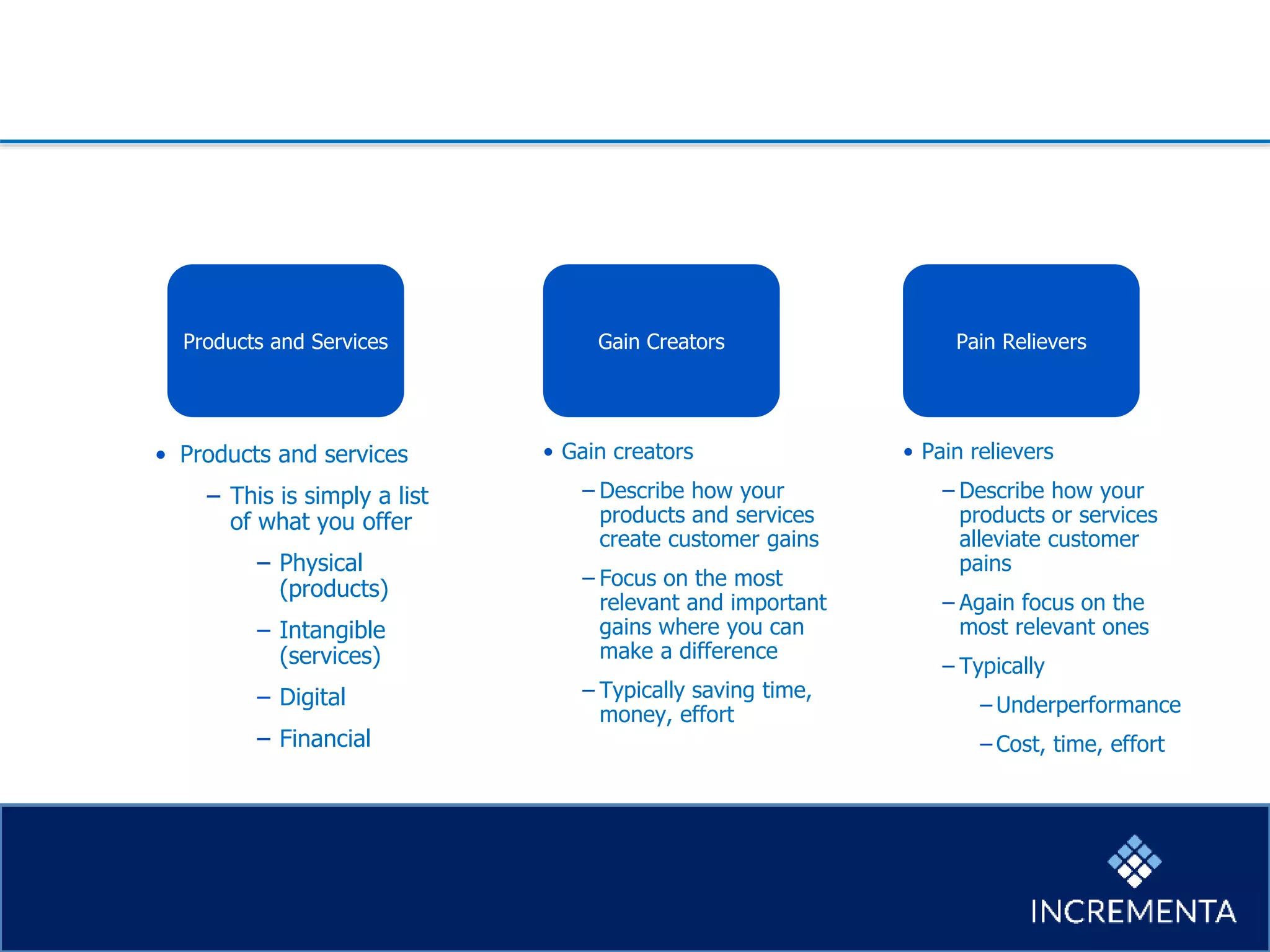
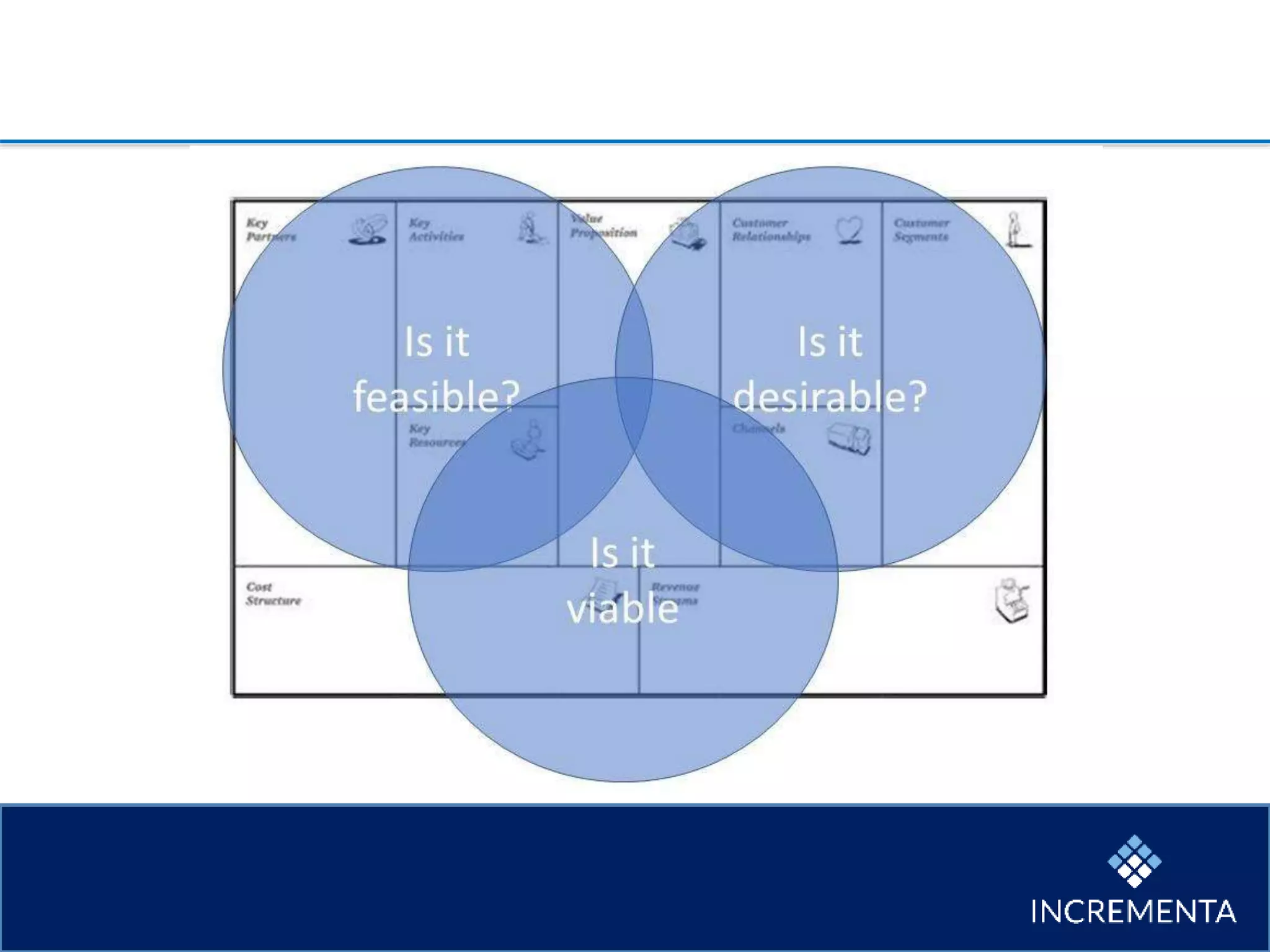
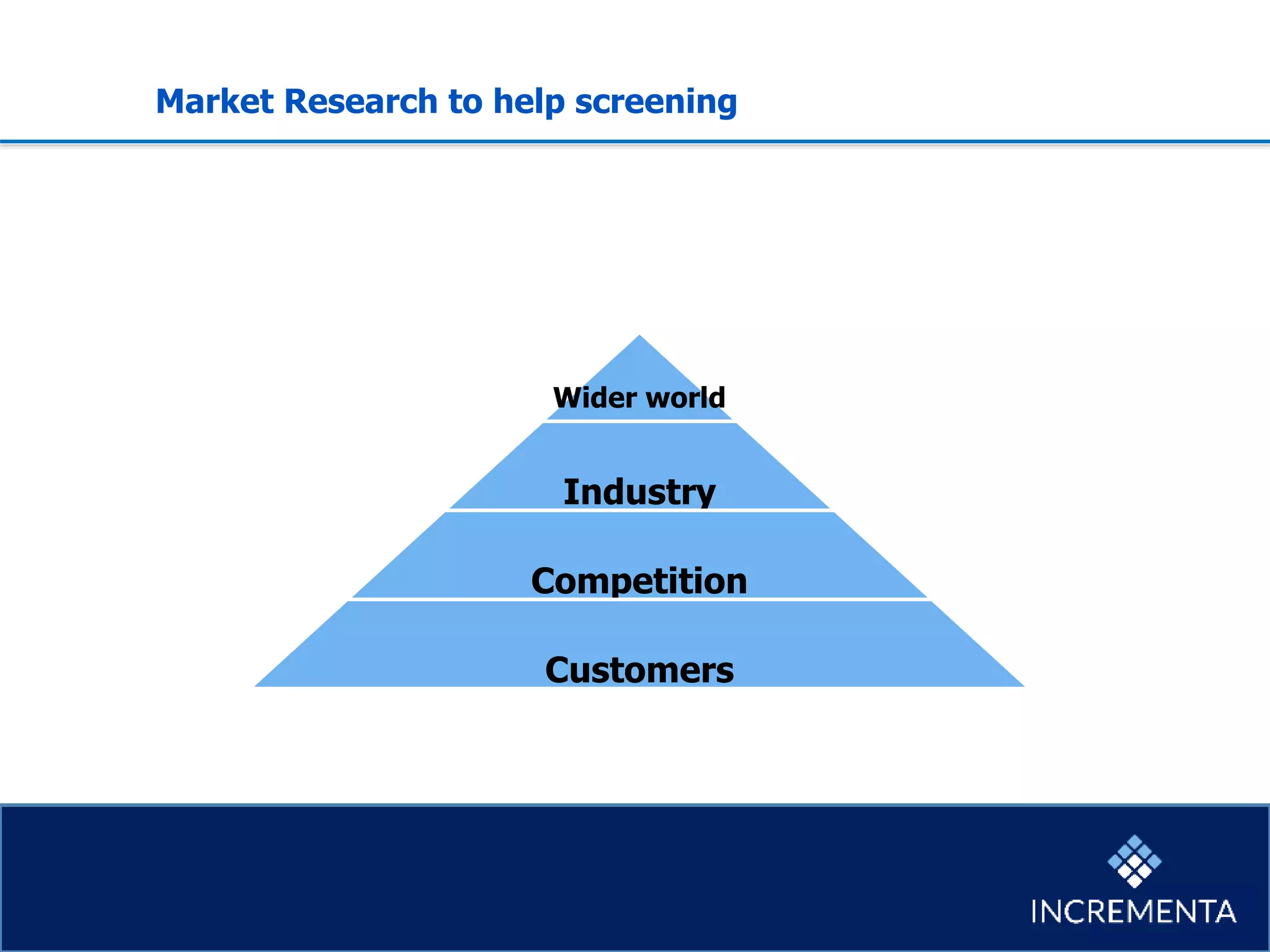
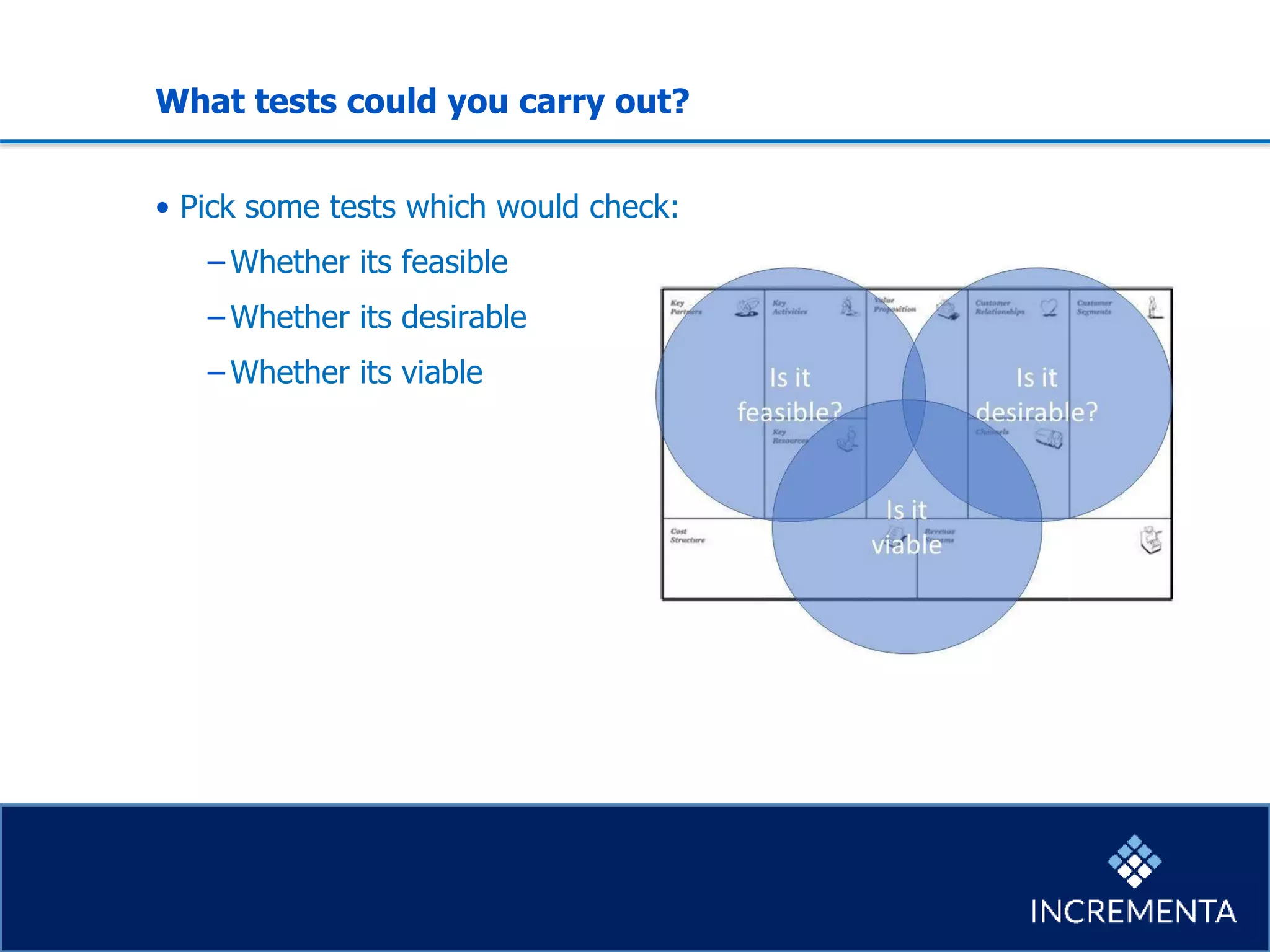
This document provides an overview of the new product development process, including key phases and considerations. It discusses defining problems from the customer perspective by understanding customer jobs, pains, and gains. Various screening and testing methods are presented for evaluating new product concepts, such as focus groups, prototyping, and market testing. Business planning elements like financial forecasts, target setting, and launch checklists are also reviewed. Finally, common causes of new product failures are summarized, emphasizing the importance of understanding customers, markets, and competitors to develop successful new offerings.