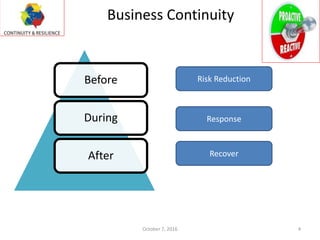
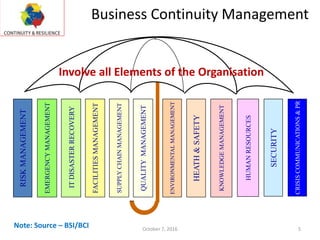
This document contains information about a business continuity consulting firm called Continuity and Resilience (CORE) including their contact details in India and the United Arab Emirates. It also summarizes a presentation given by S. Seshadri of CORE at the 4th India Business & IT Resilience Summit on establishing a business continuity management system based on ISO 22301. The presentation covers why organizations implement BCM, key requirements and elements, and issues to consider when initiating a BCM program such as scope, roles, and obtaining leadership support.