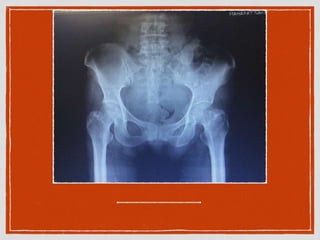
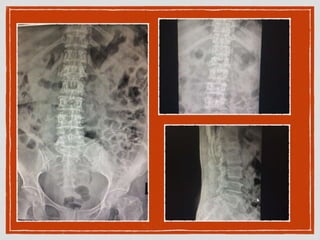
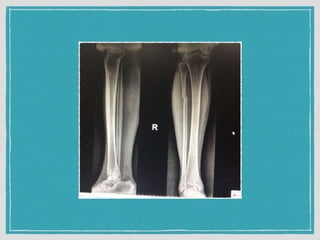
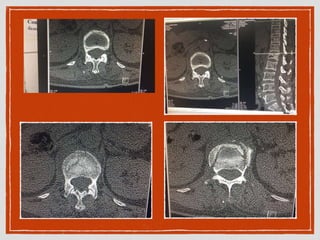
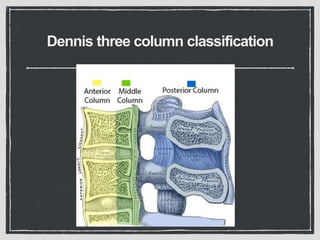
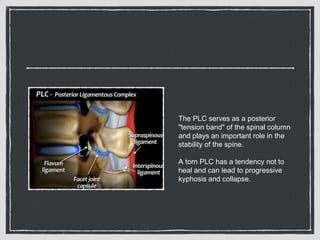
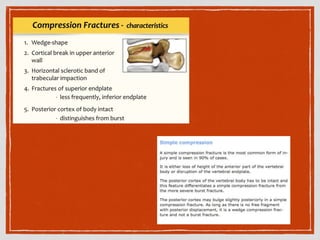
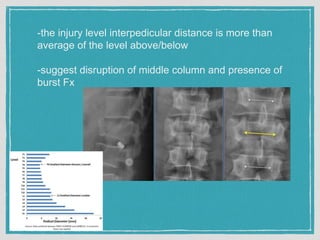
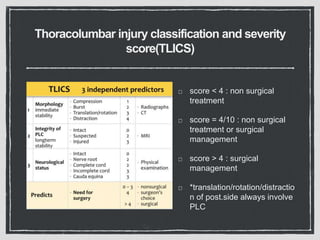
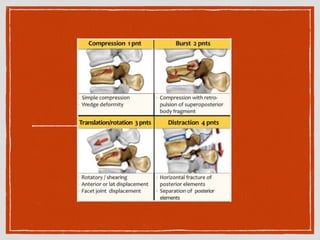
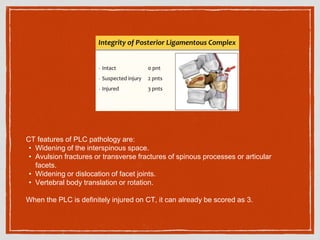
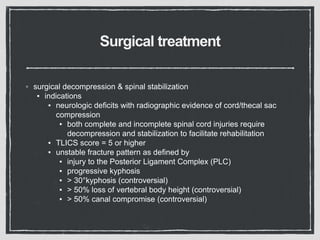
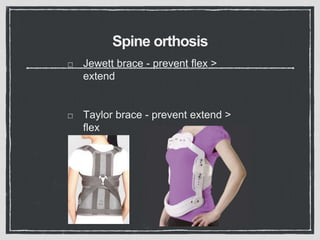
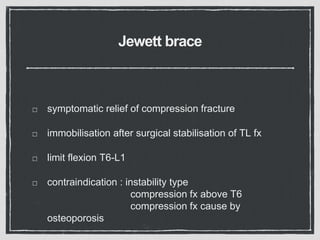
This document summarizes a case conference regarding a 68-year-old Thai woman who presented to the emergency department after being hit by a motorcycle while crossing the street. She sustained a head injury with left temporal laceration and was hemodynamically stable. Imaging showed a left parieto-temporal bone fracture and subarachnoid hemorrhage. She was admitted for observation and later discharged. A subsequent case discussed low back pain after a bicycle accident, with imaging revealing a compression fracture of L1 vertebra. The patient was treated conservatively with bed rest, bracing, and pain management.