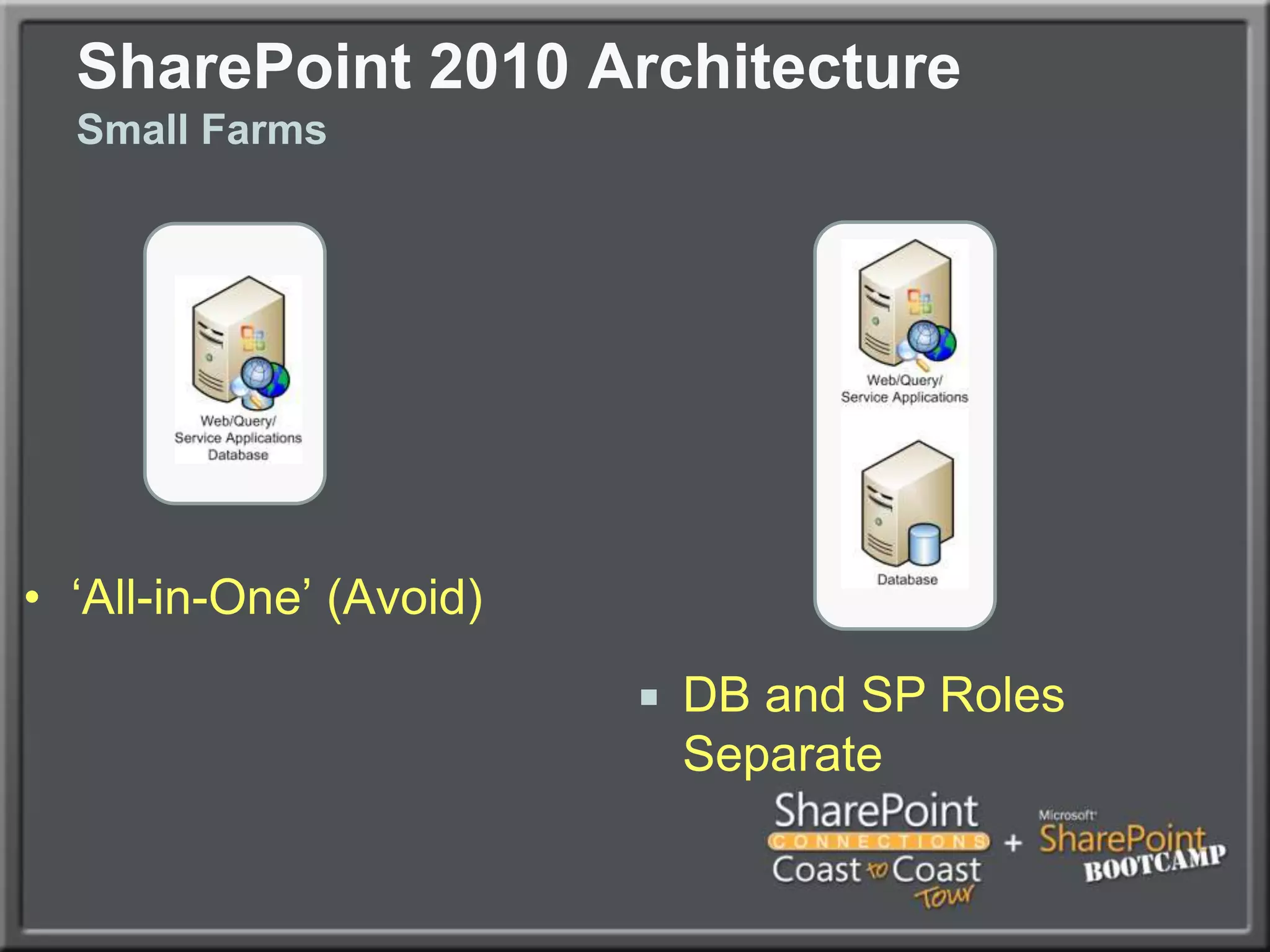
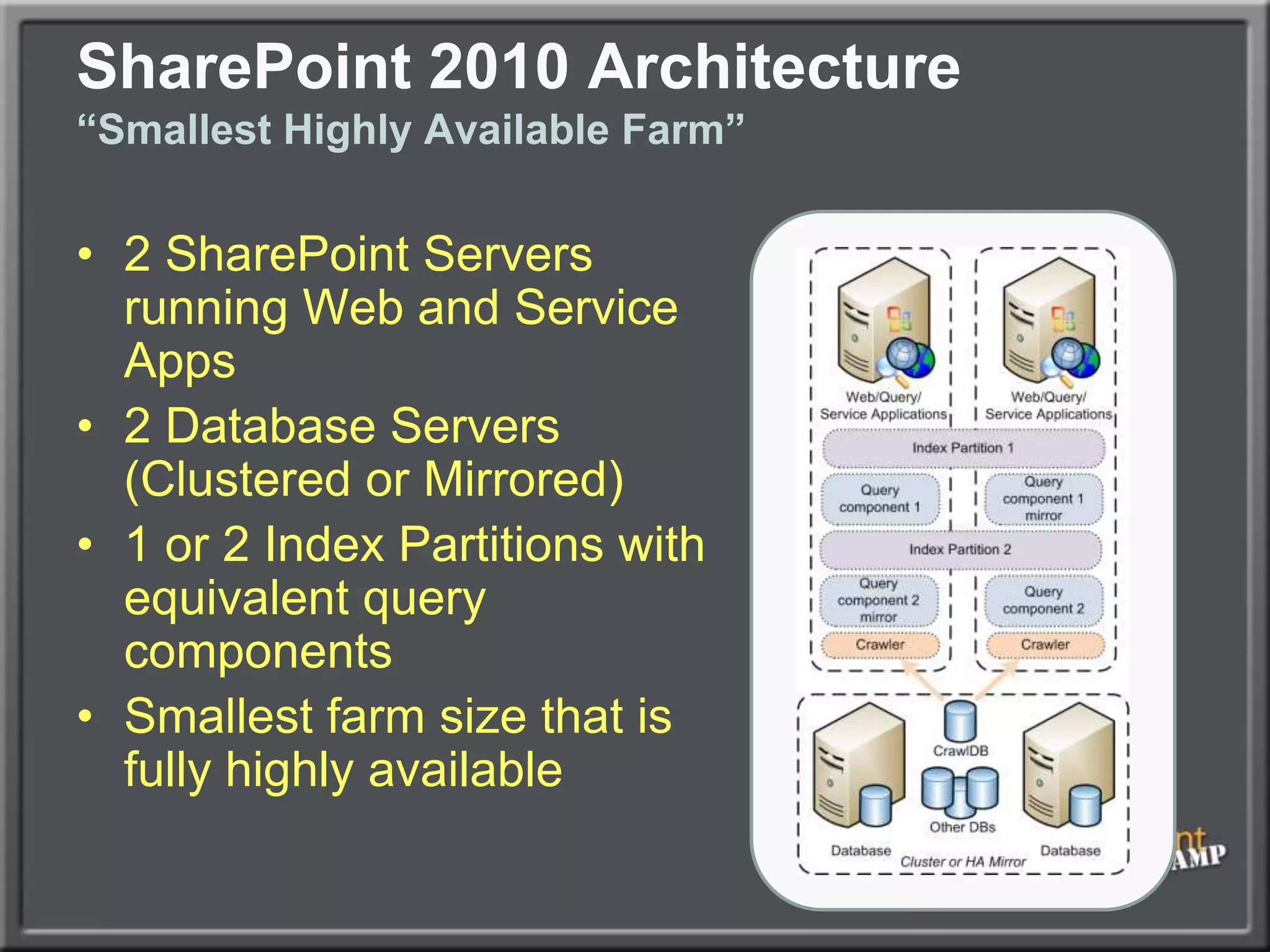
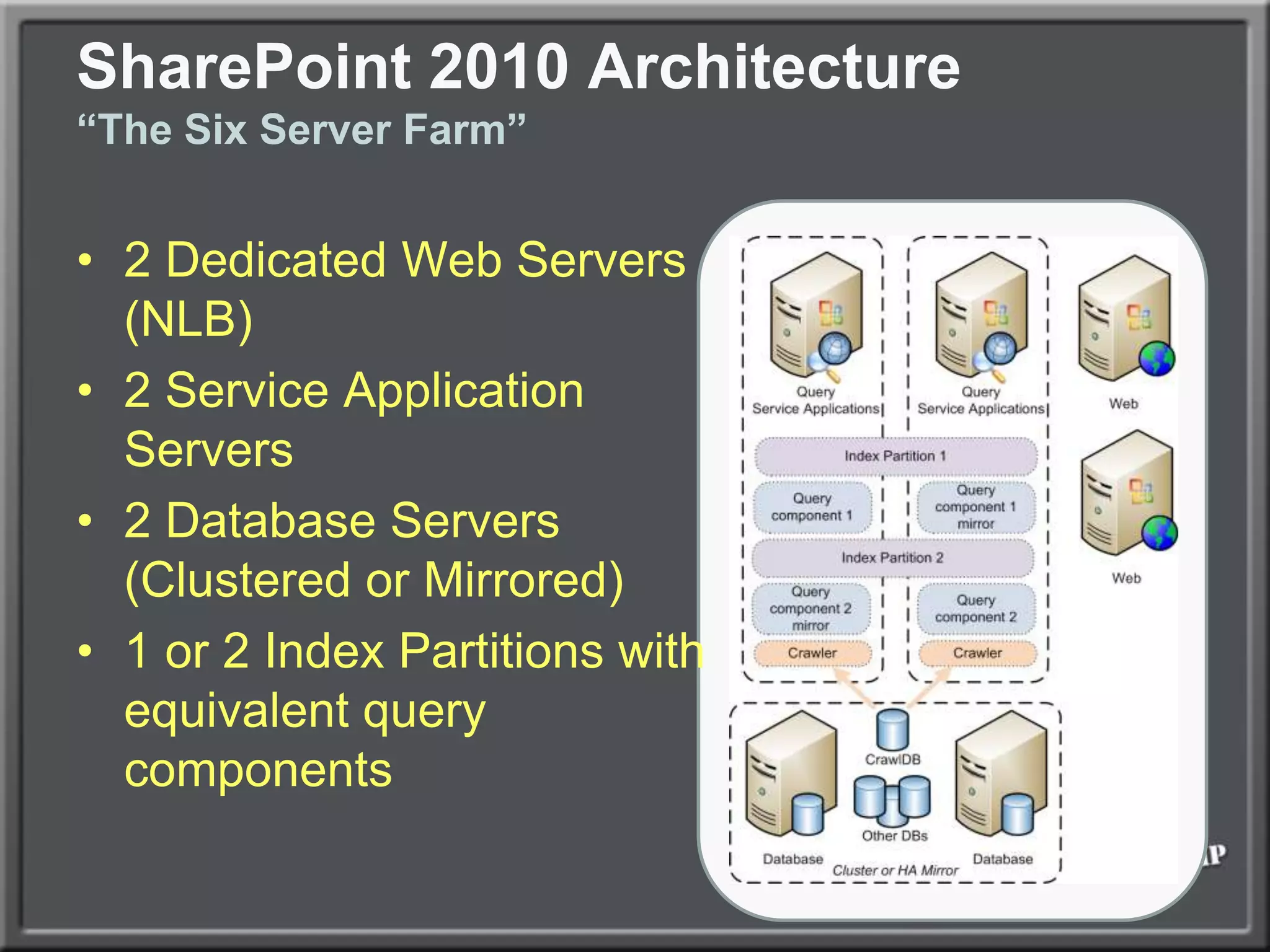
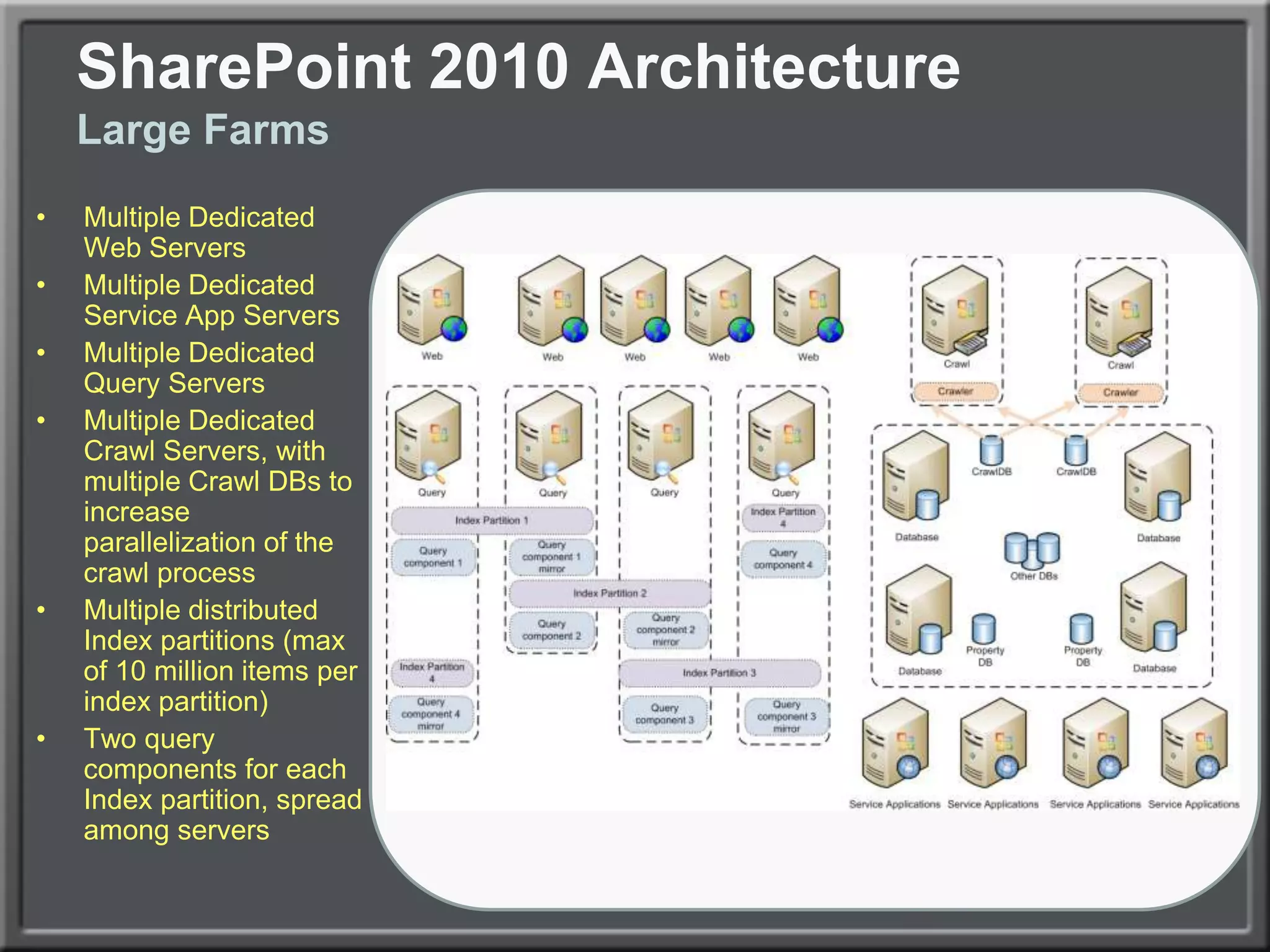
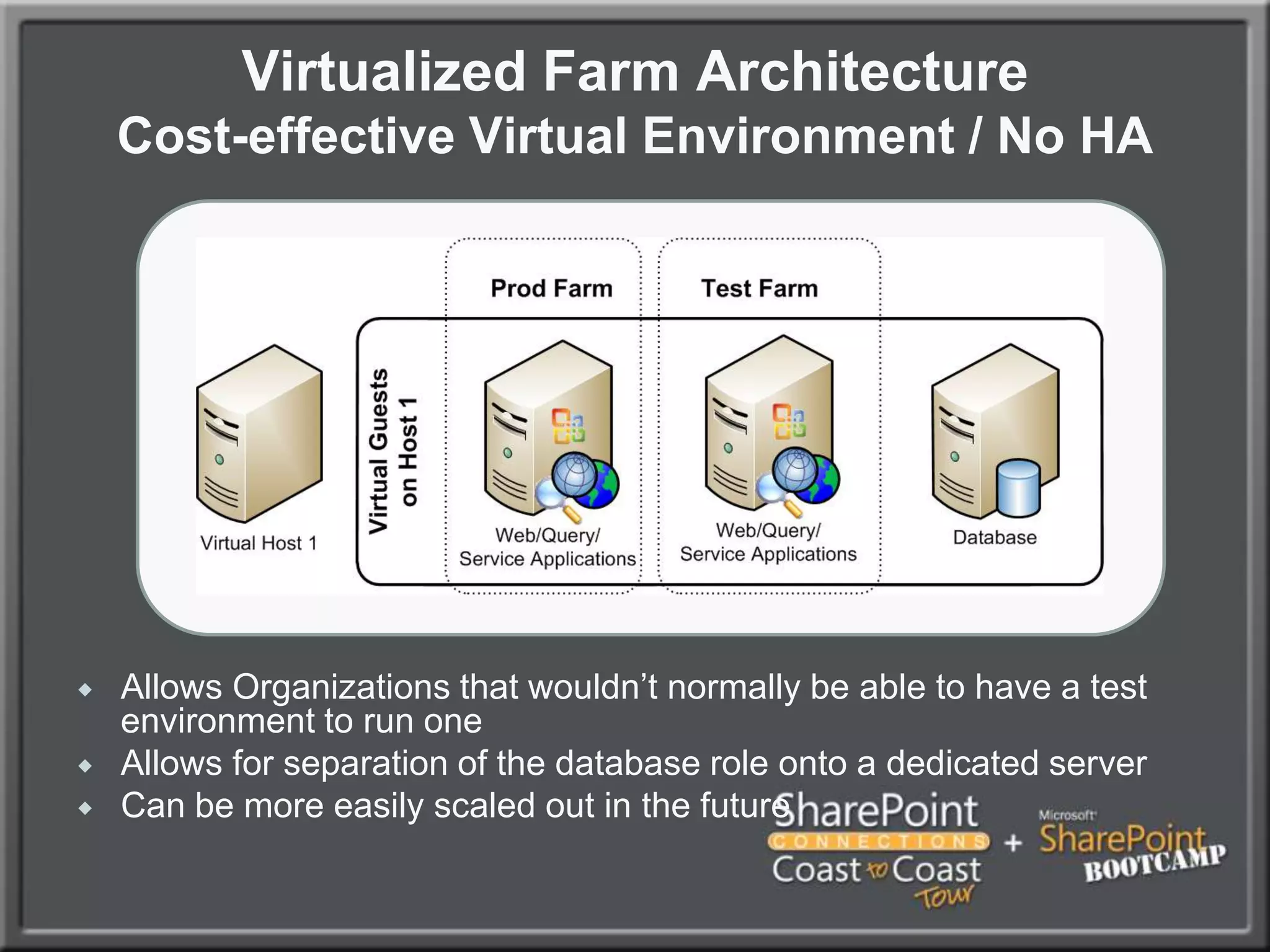
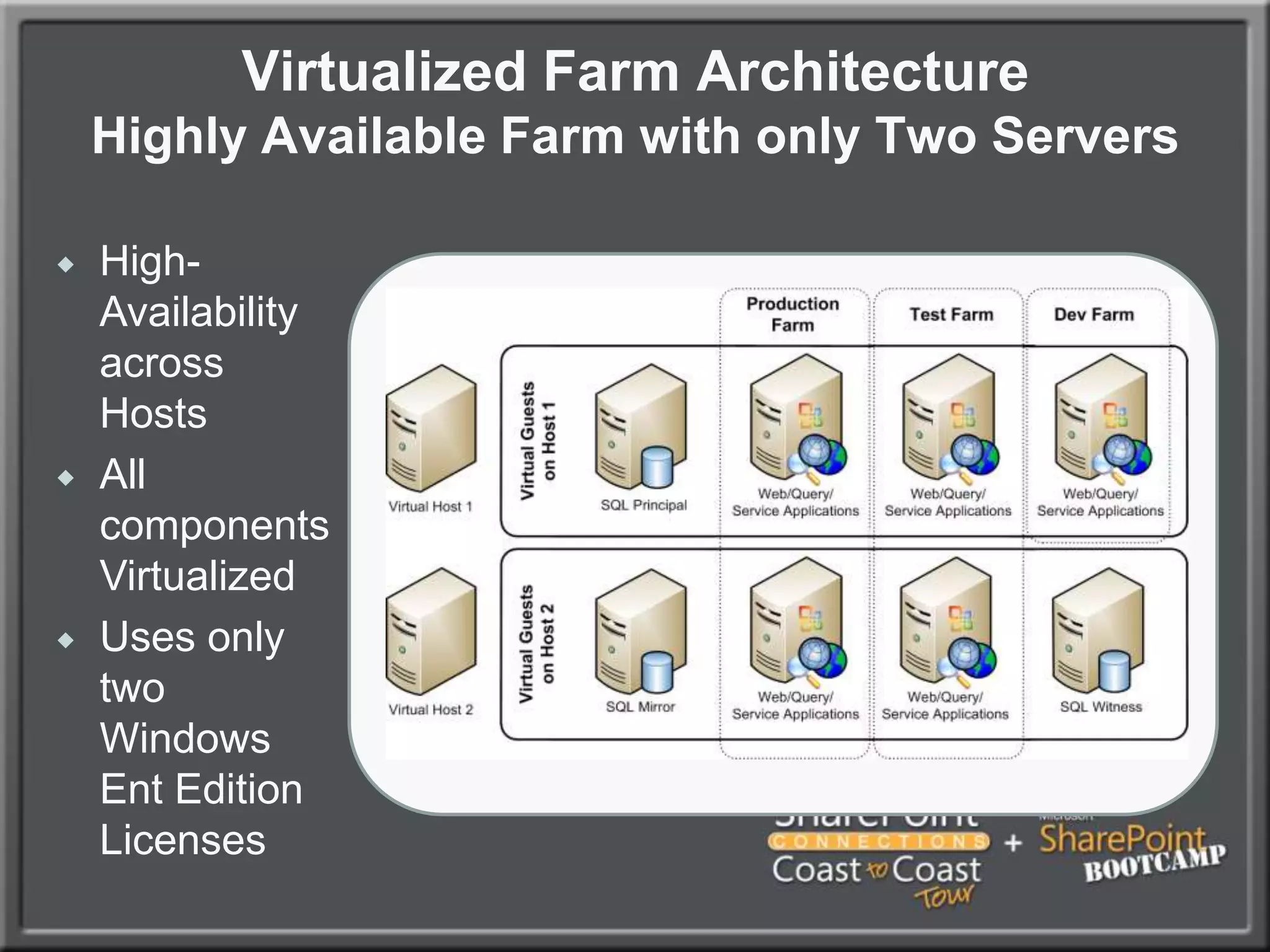
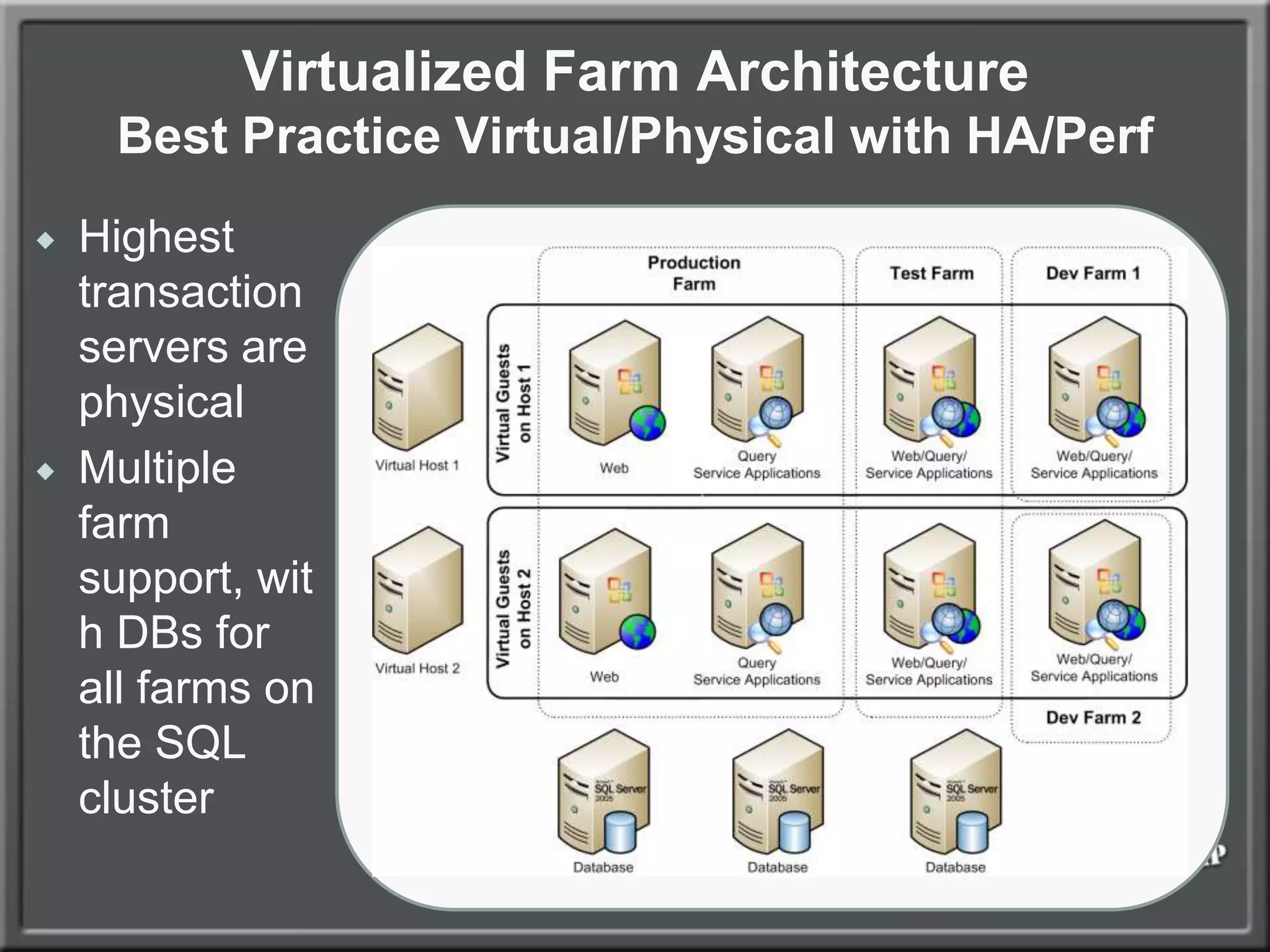
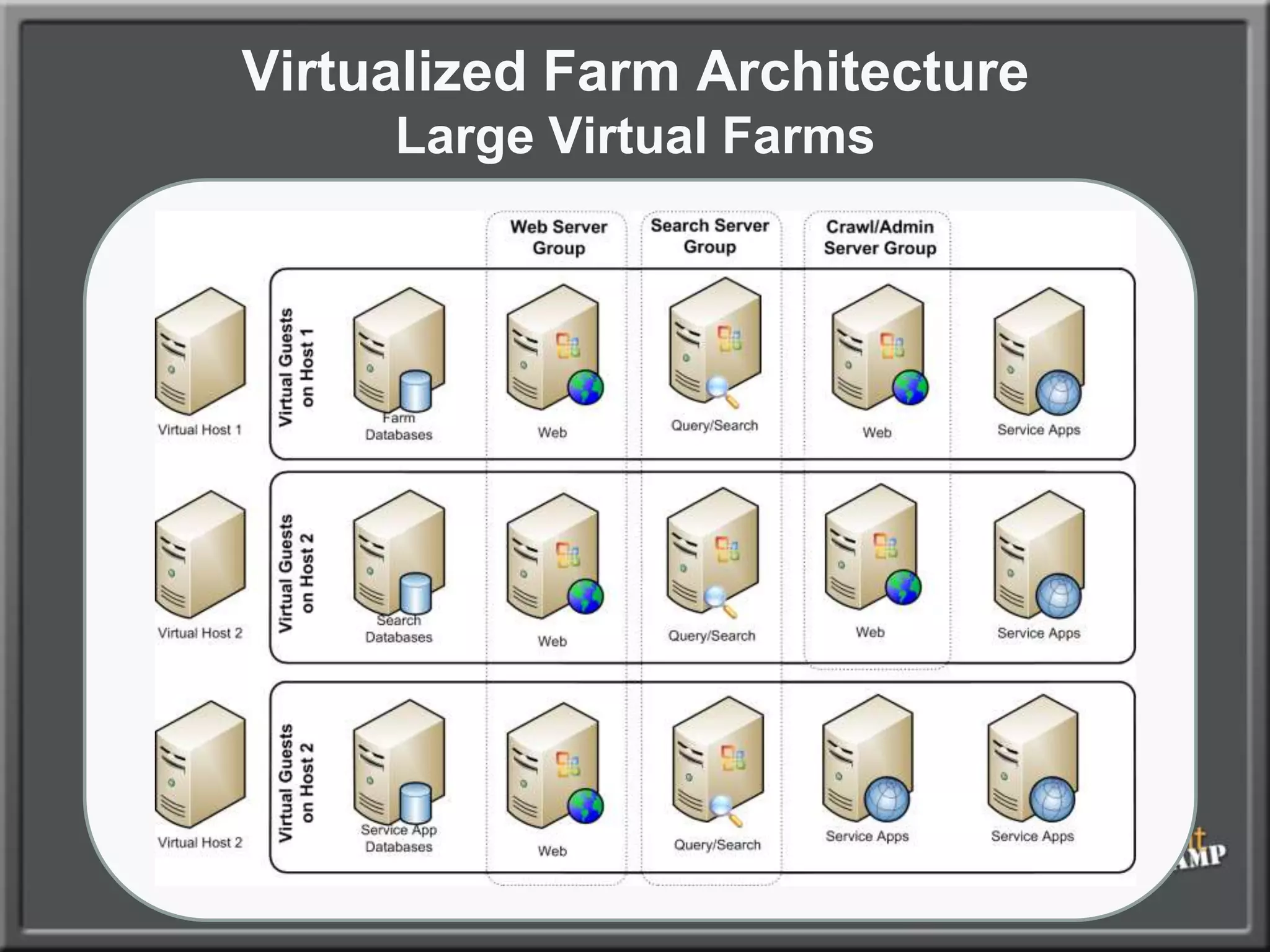
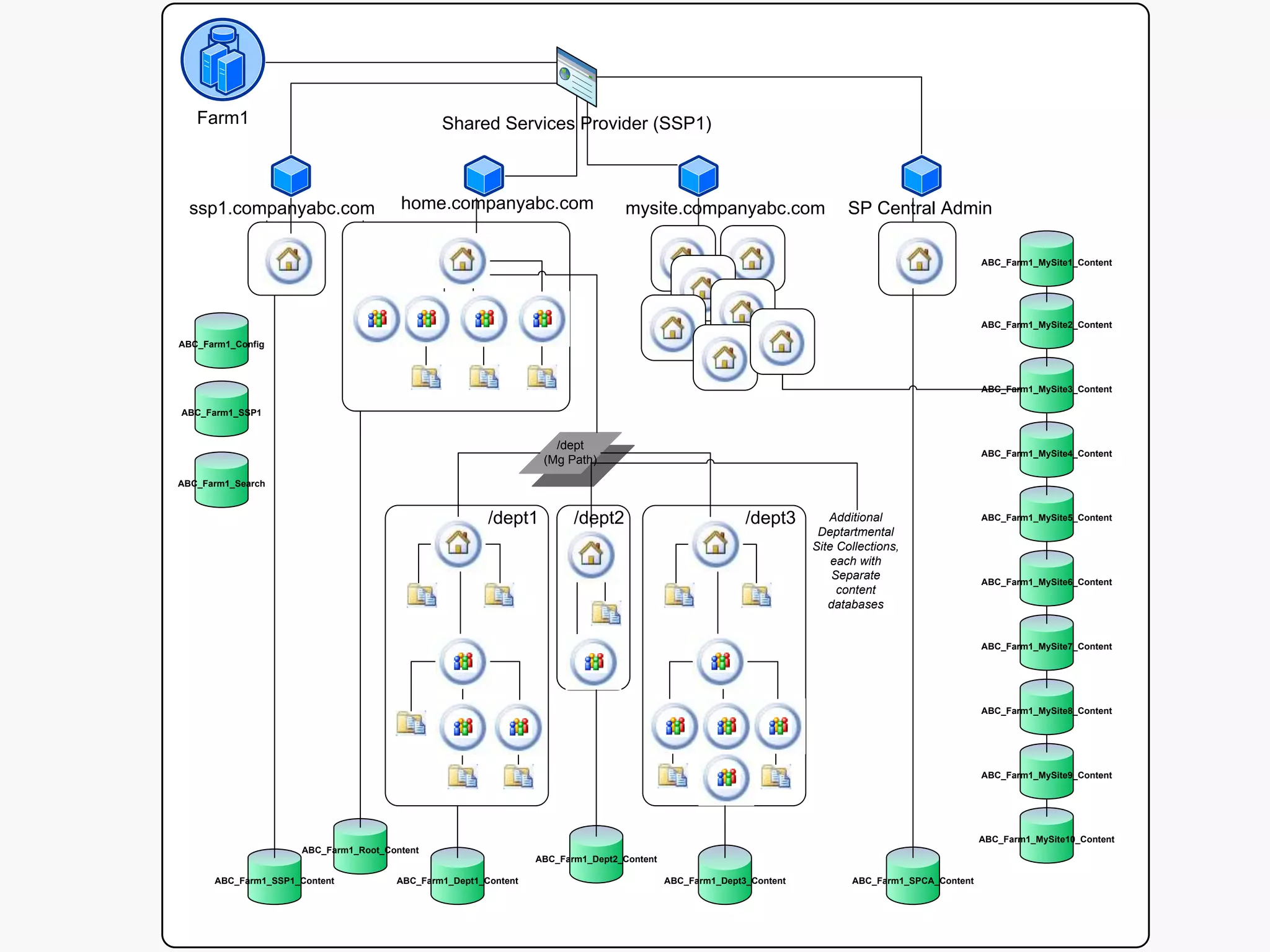
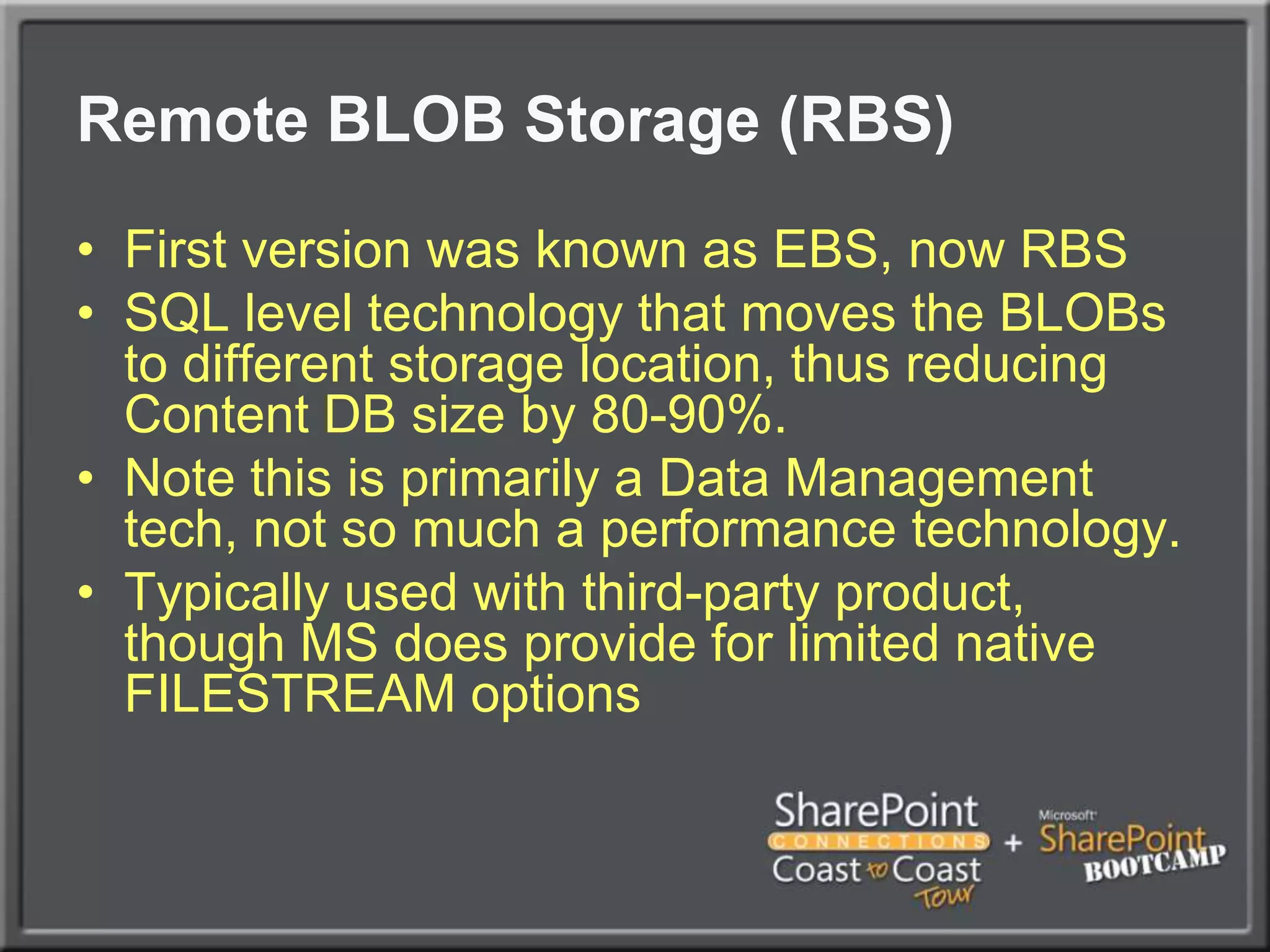
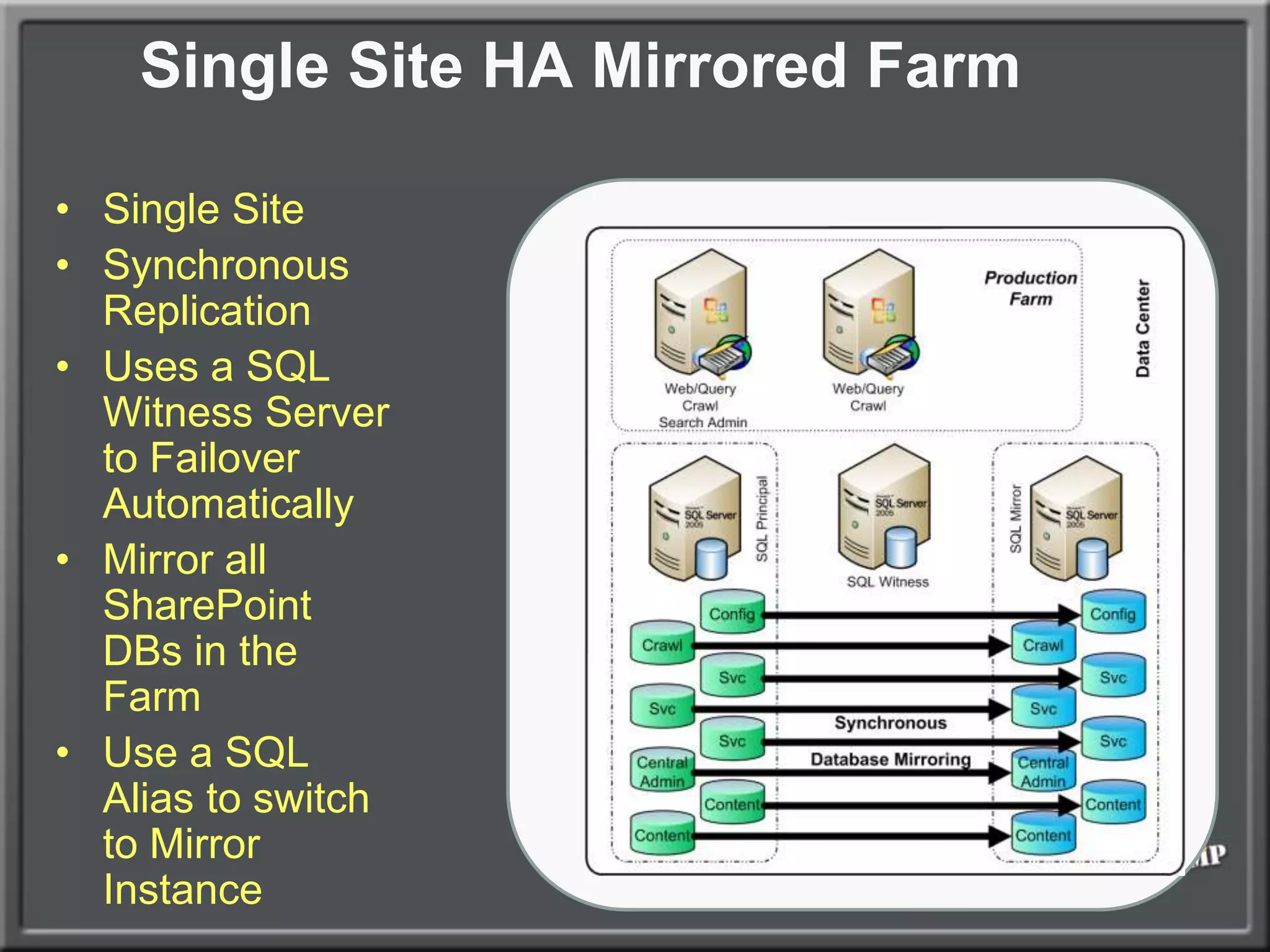
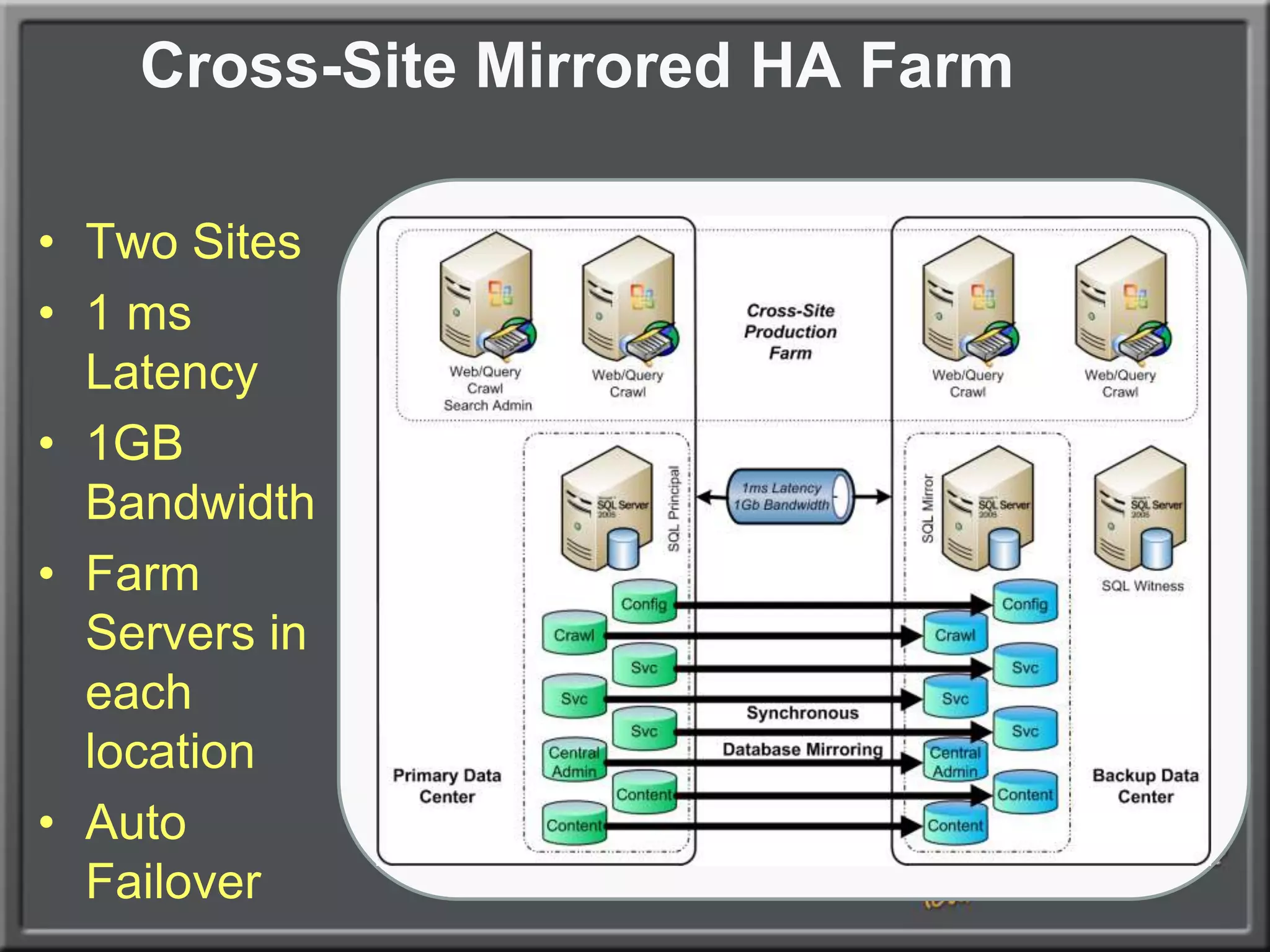
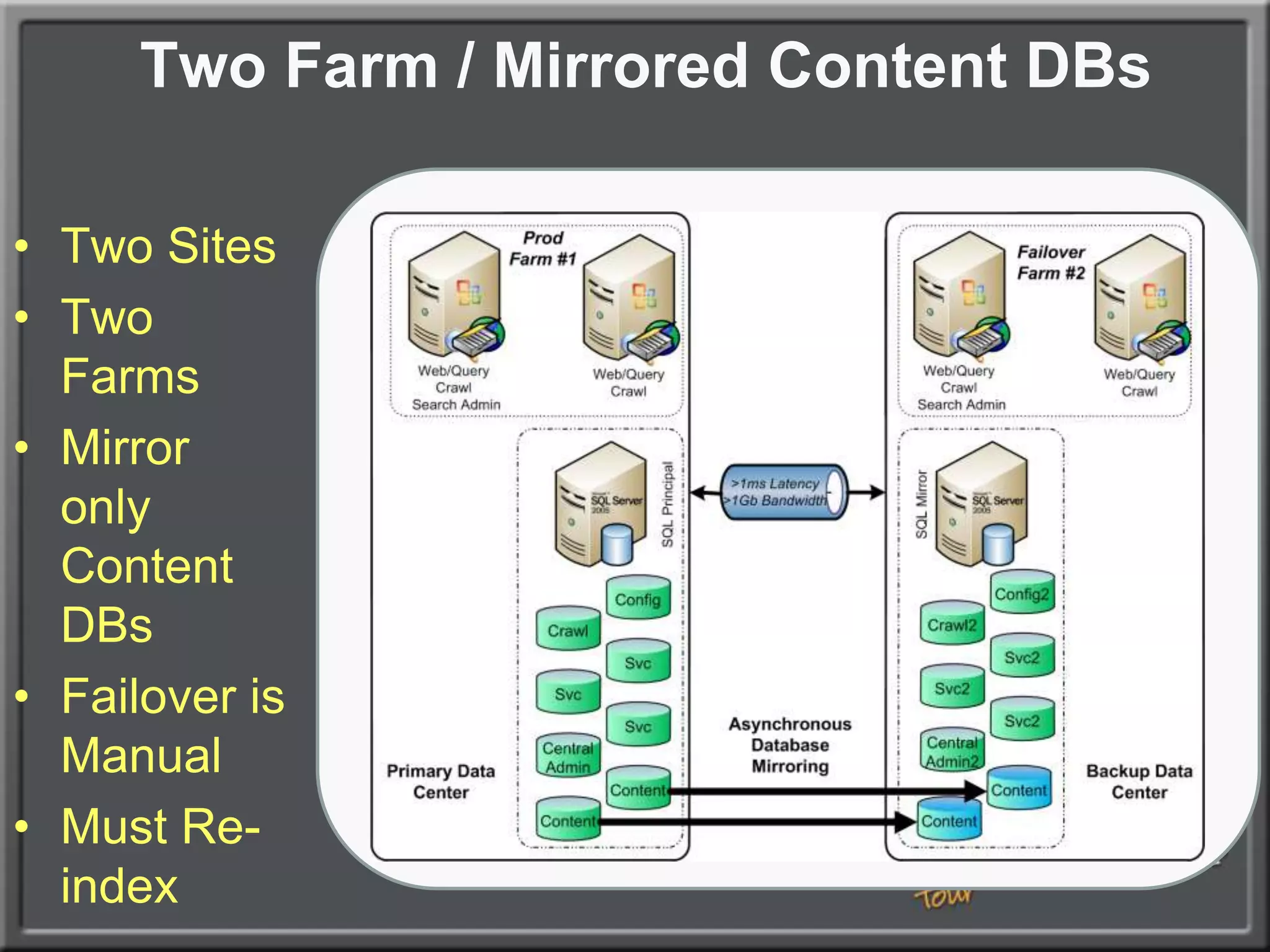
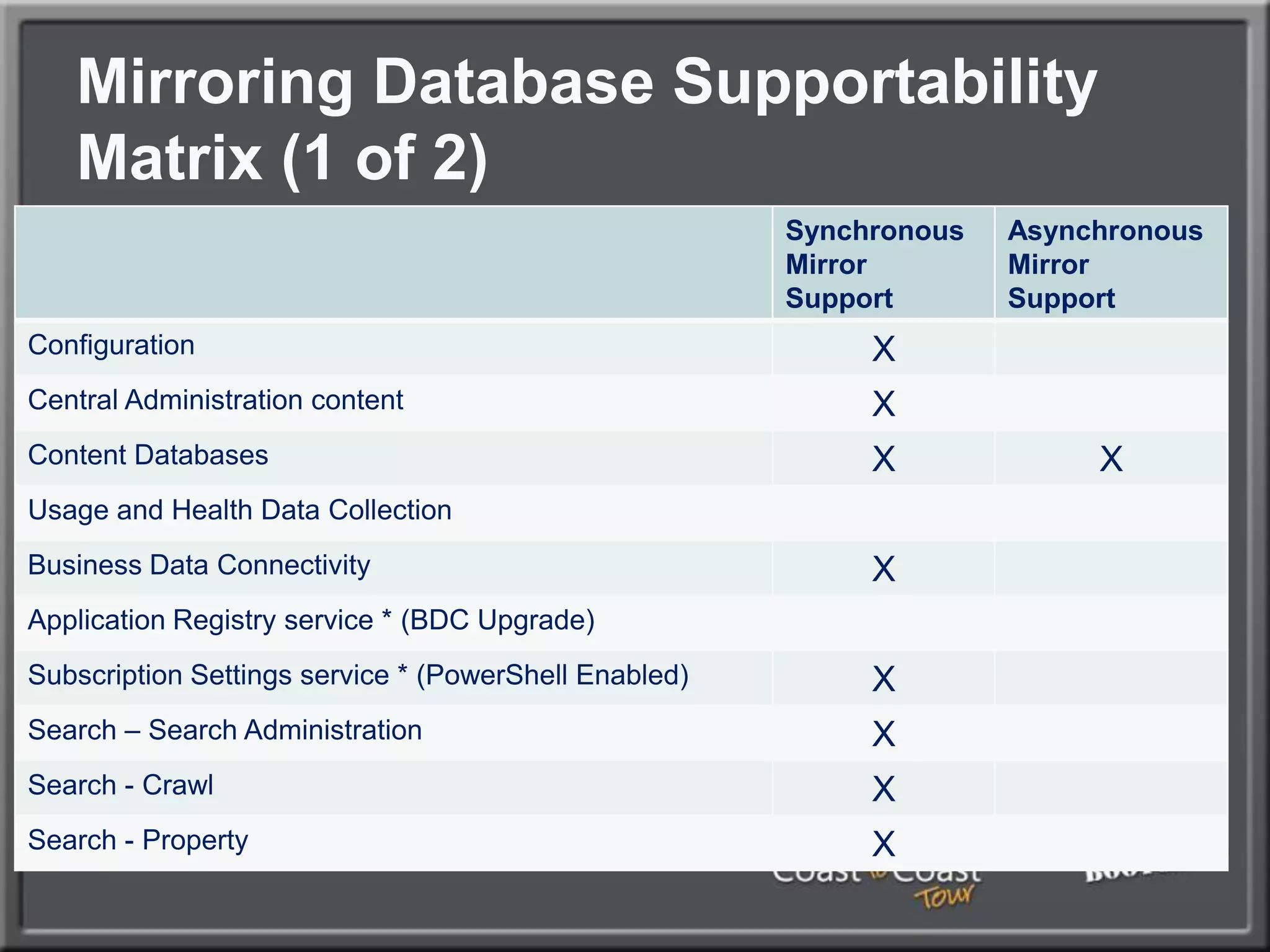
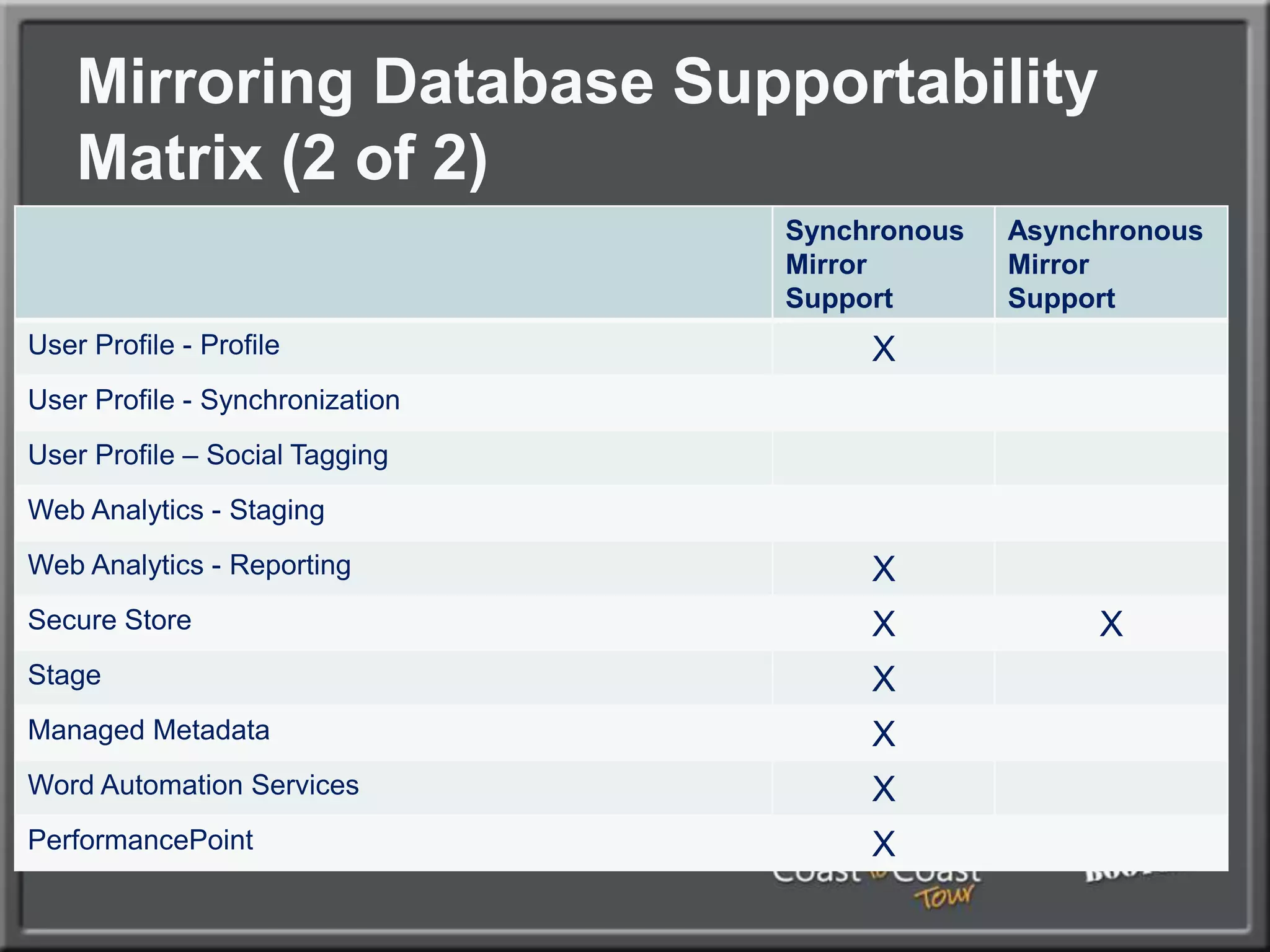
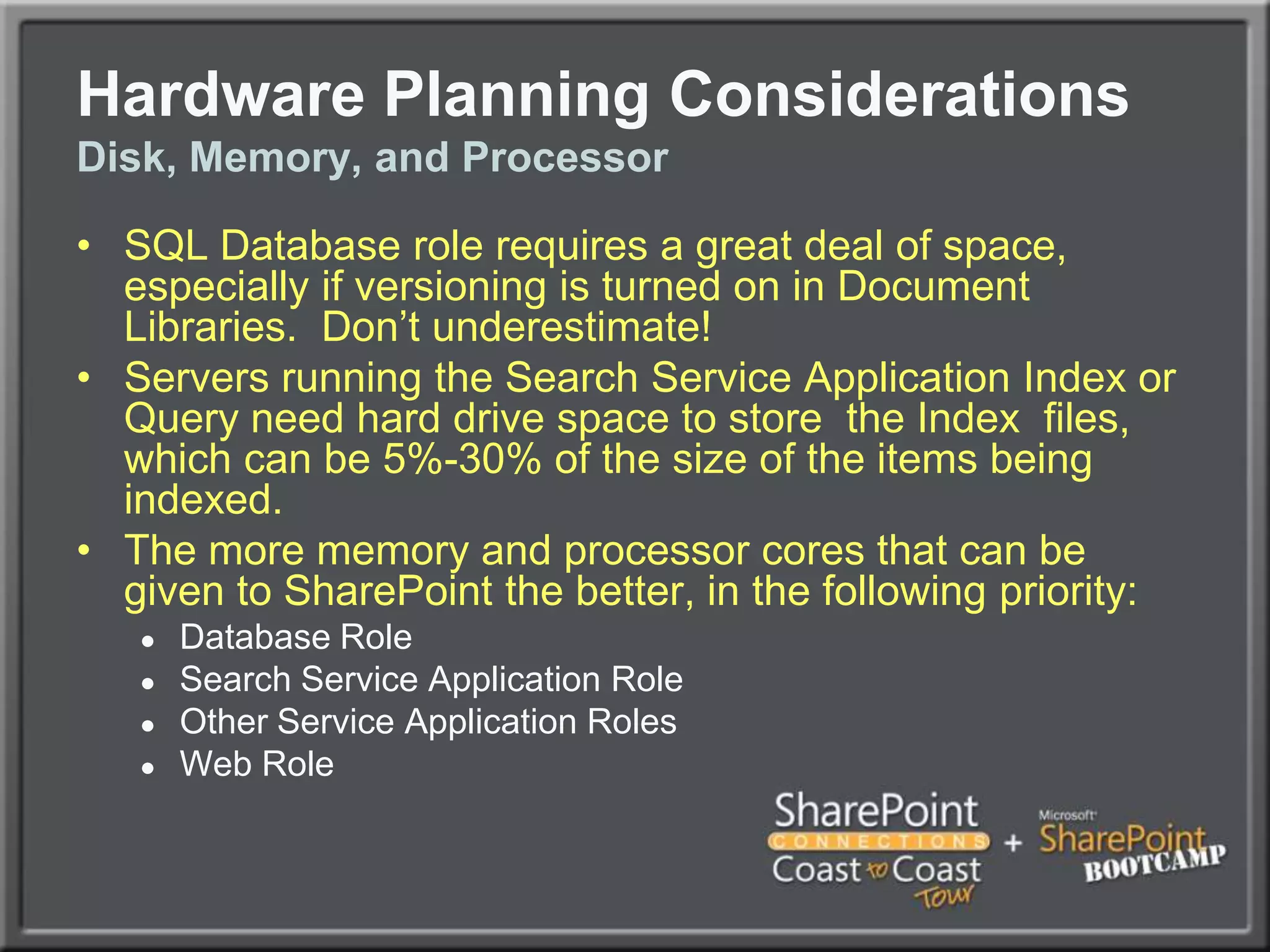
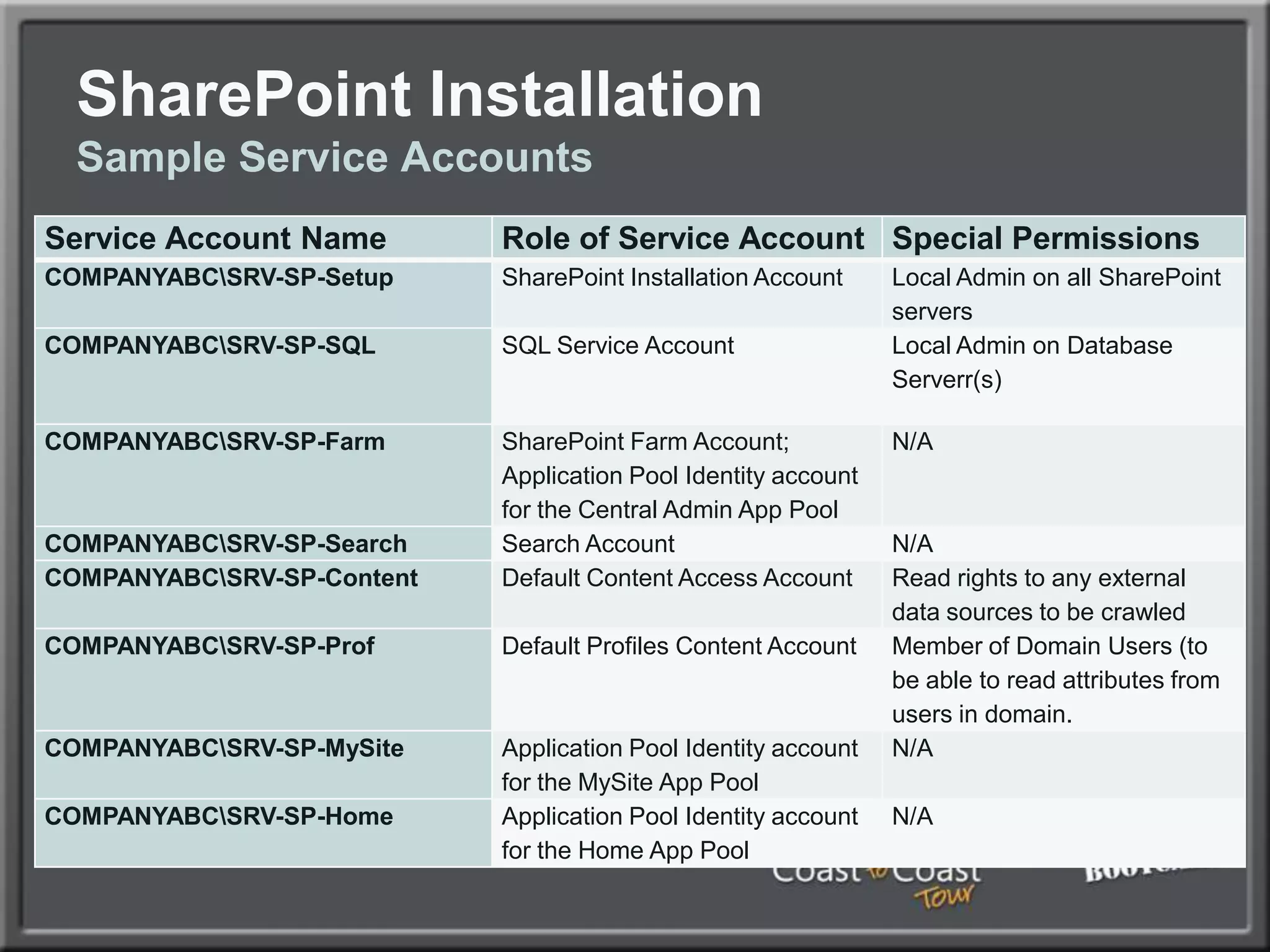
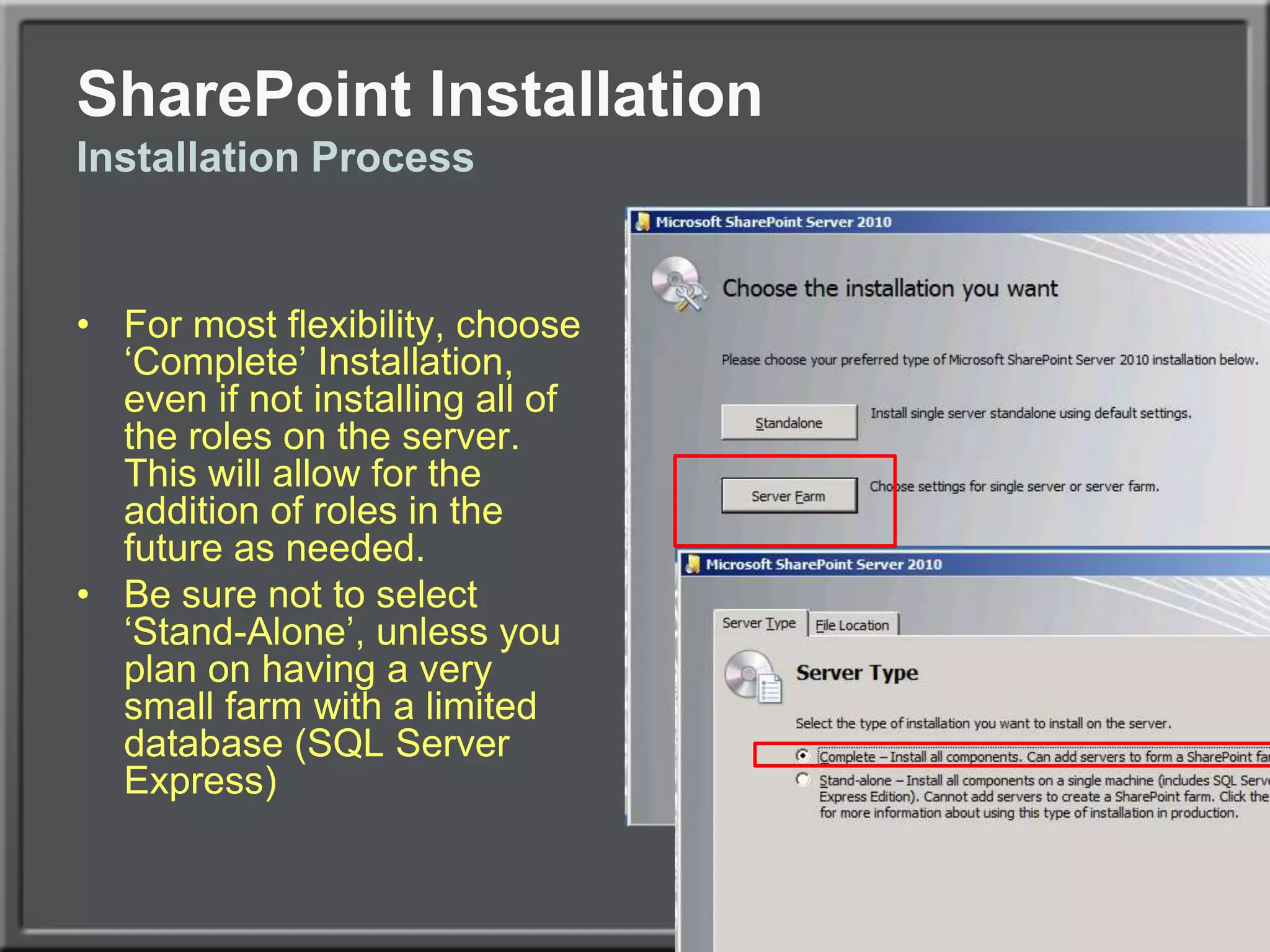
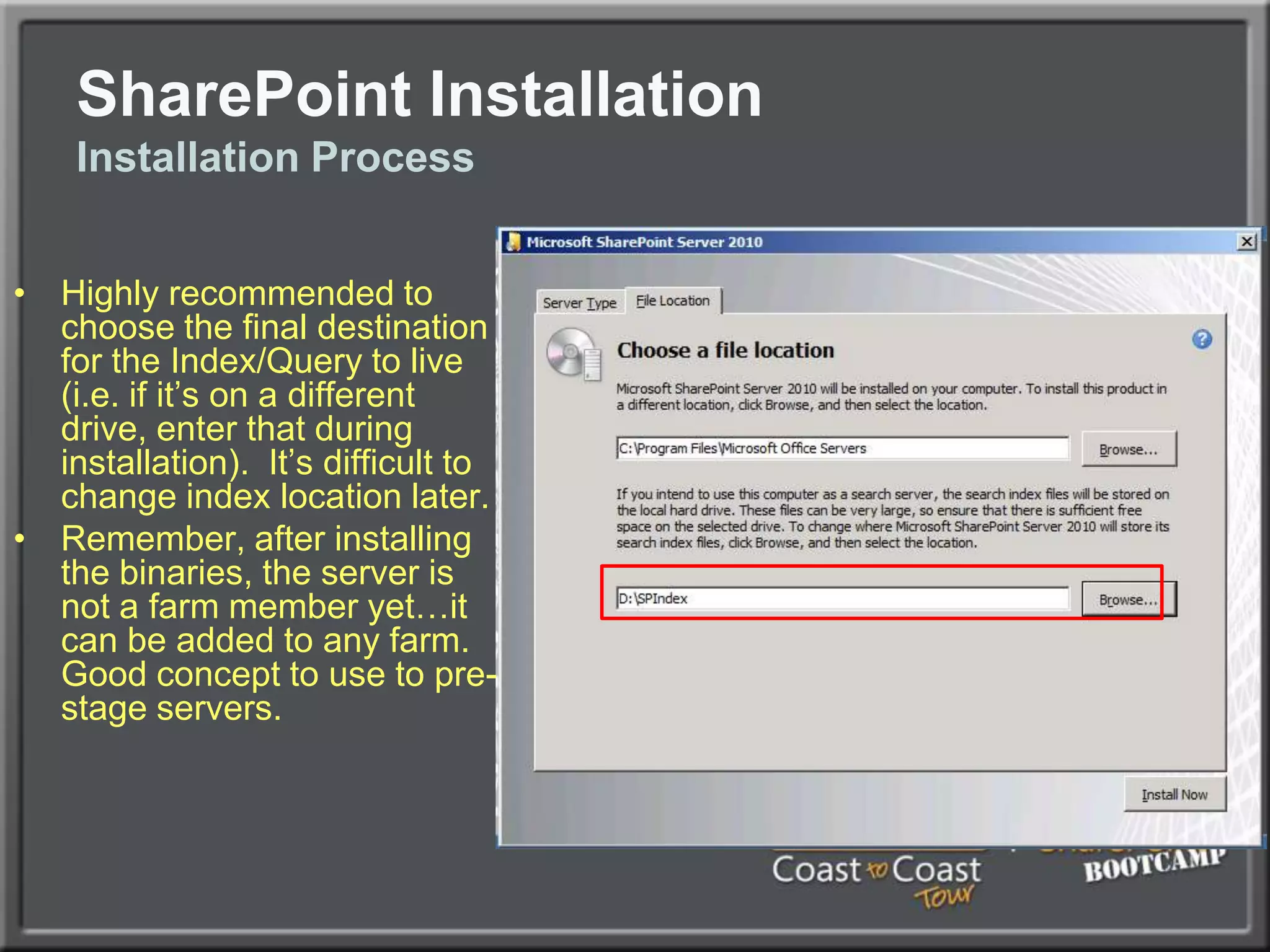
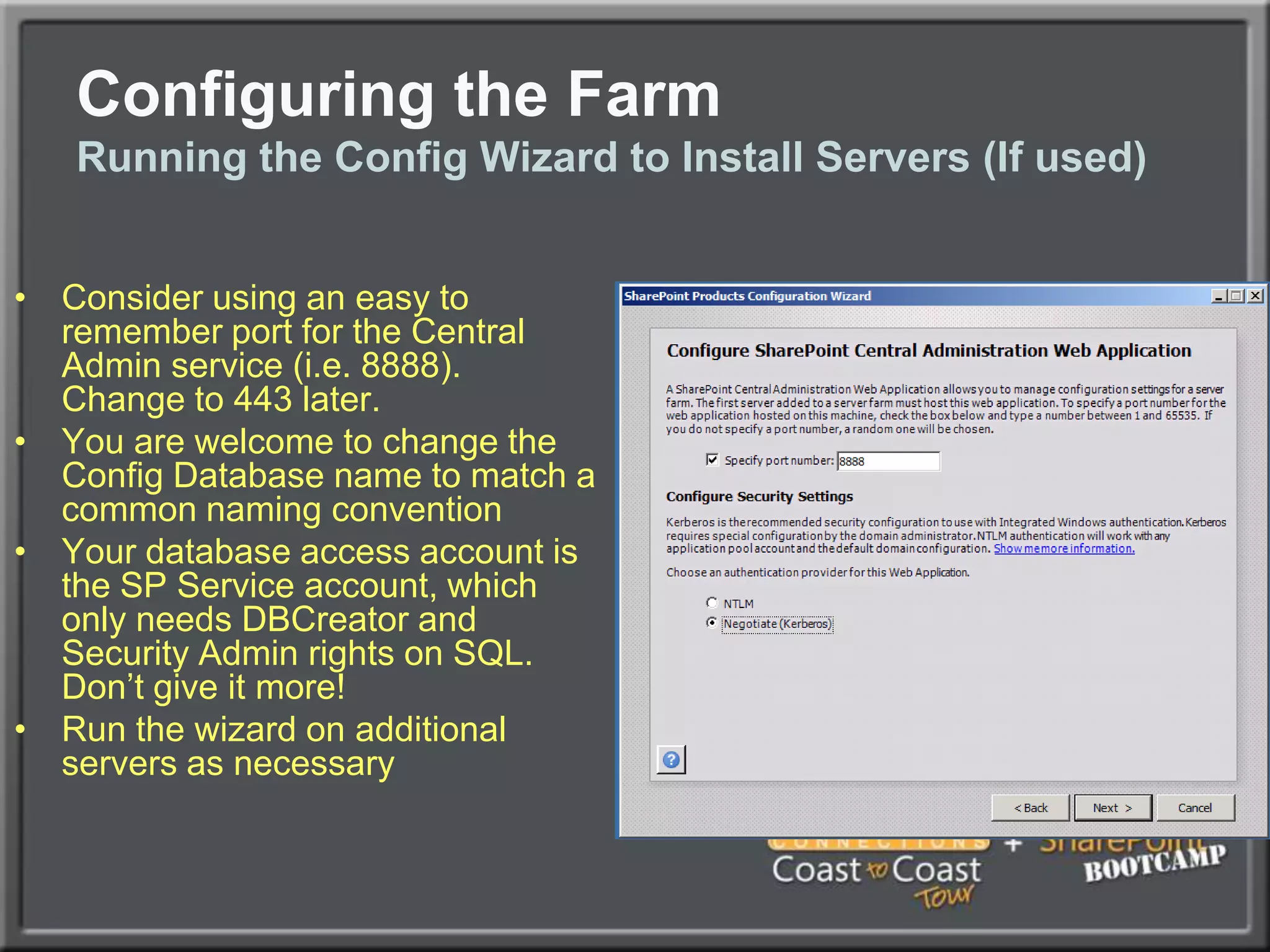
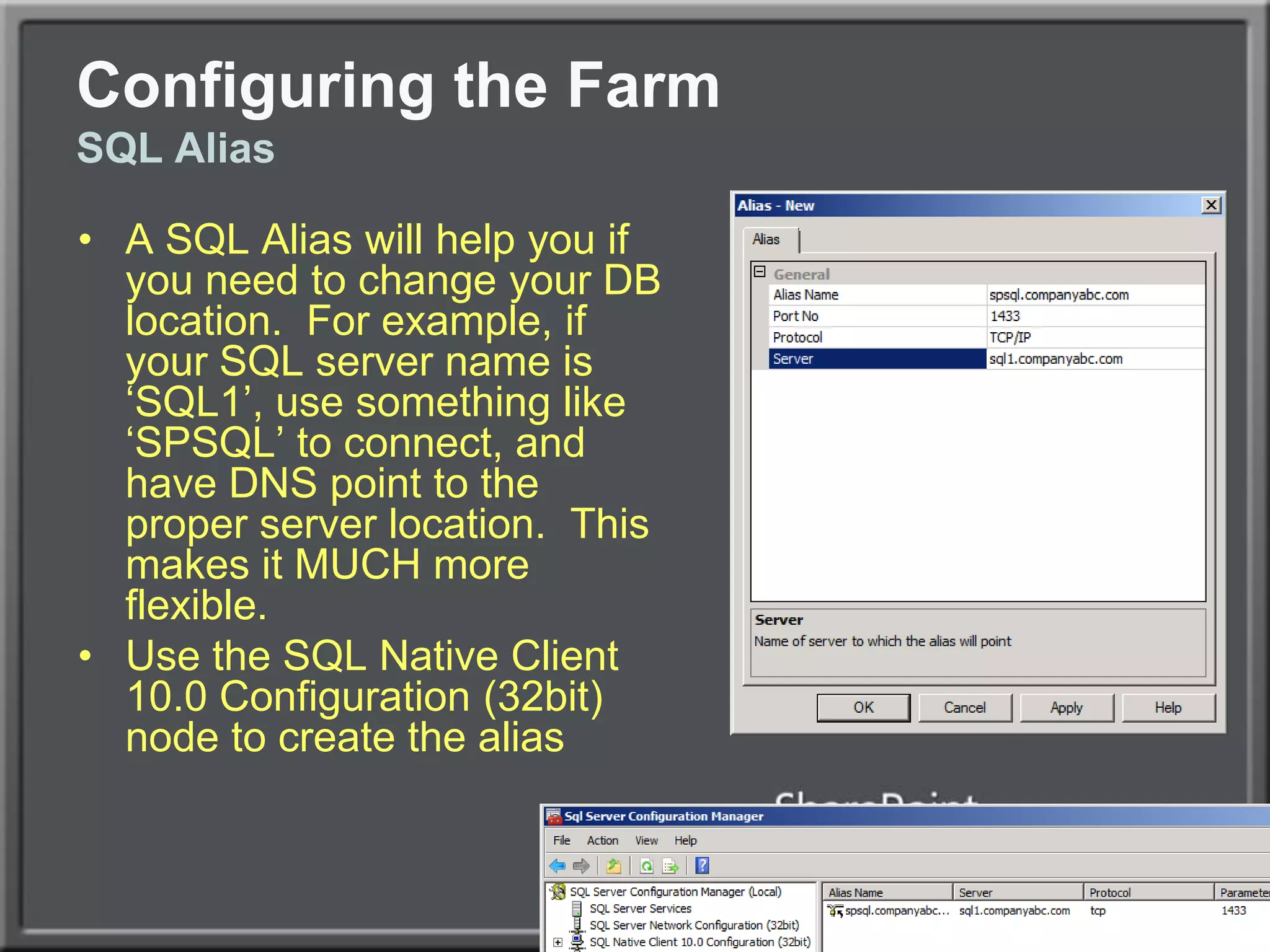
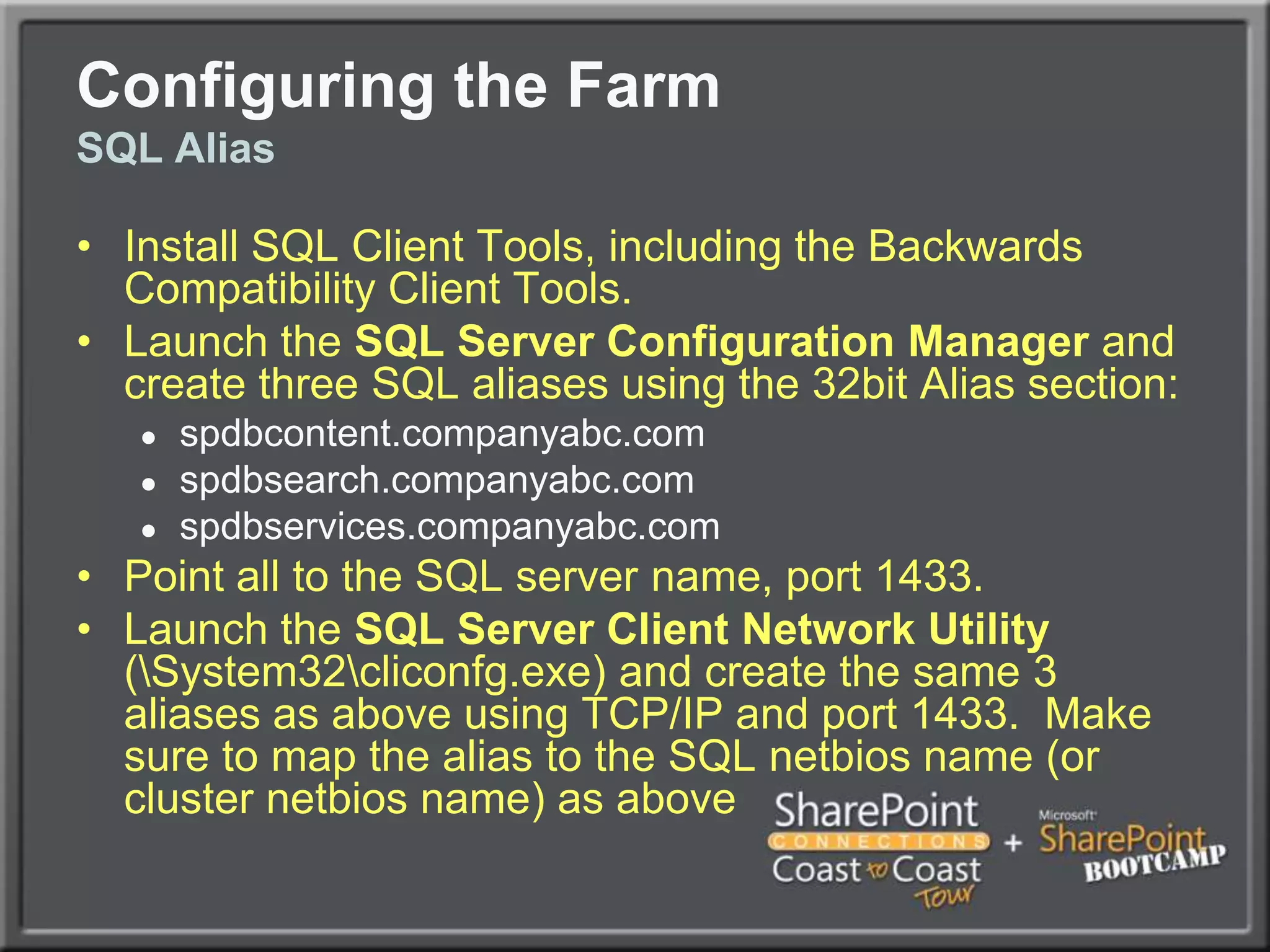
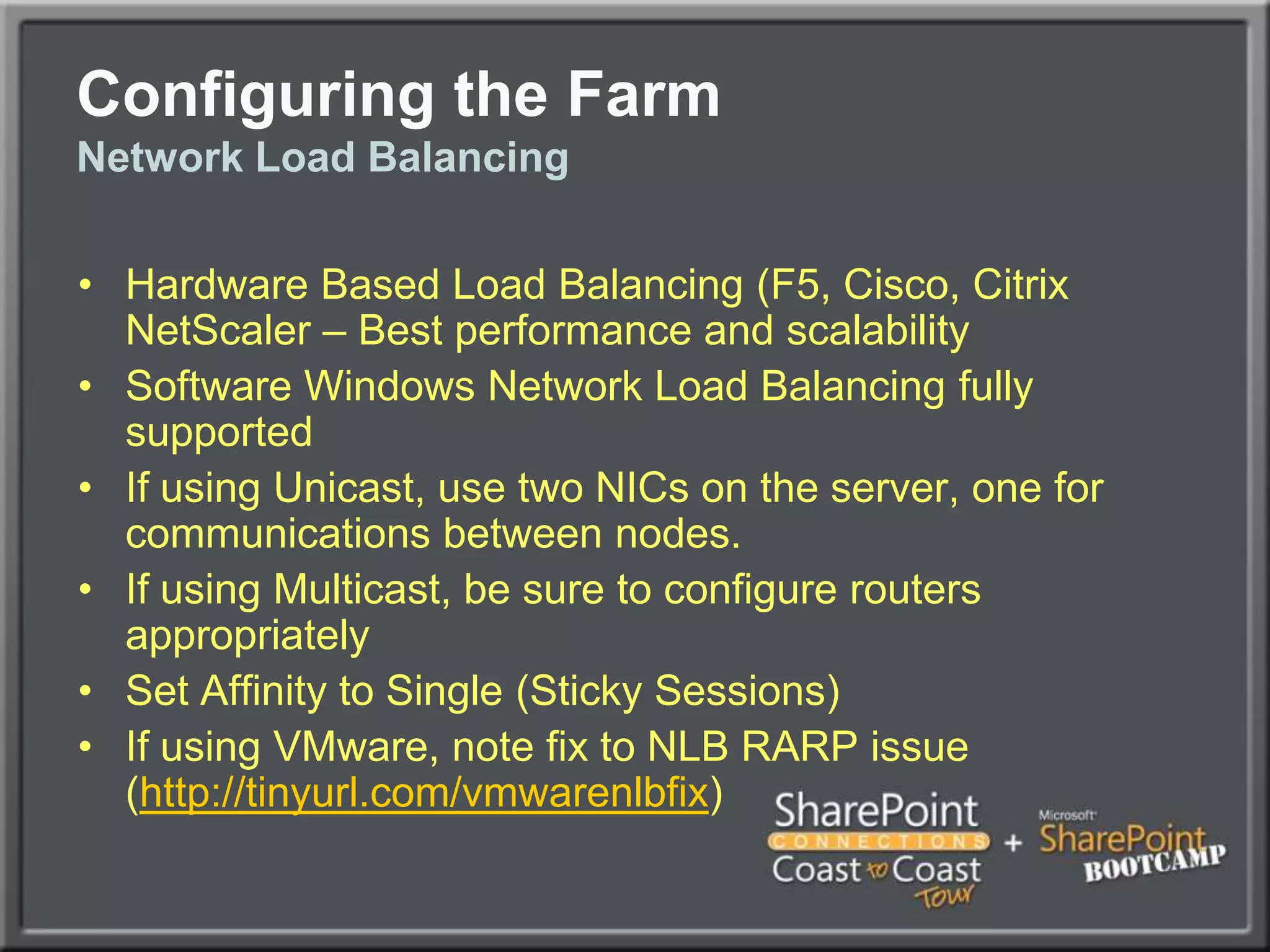
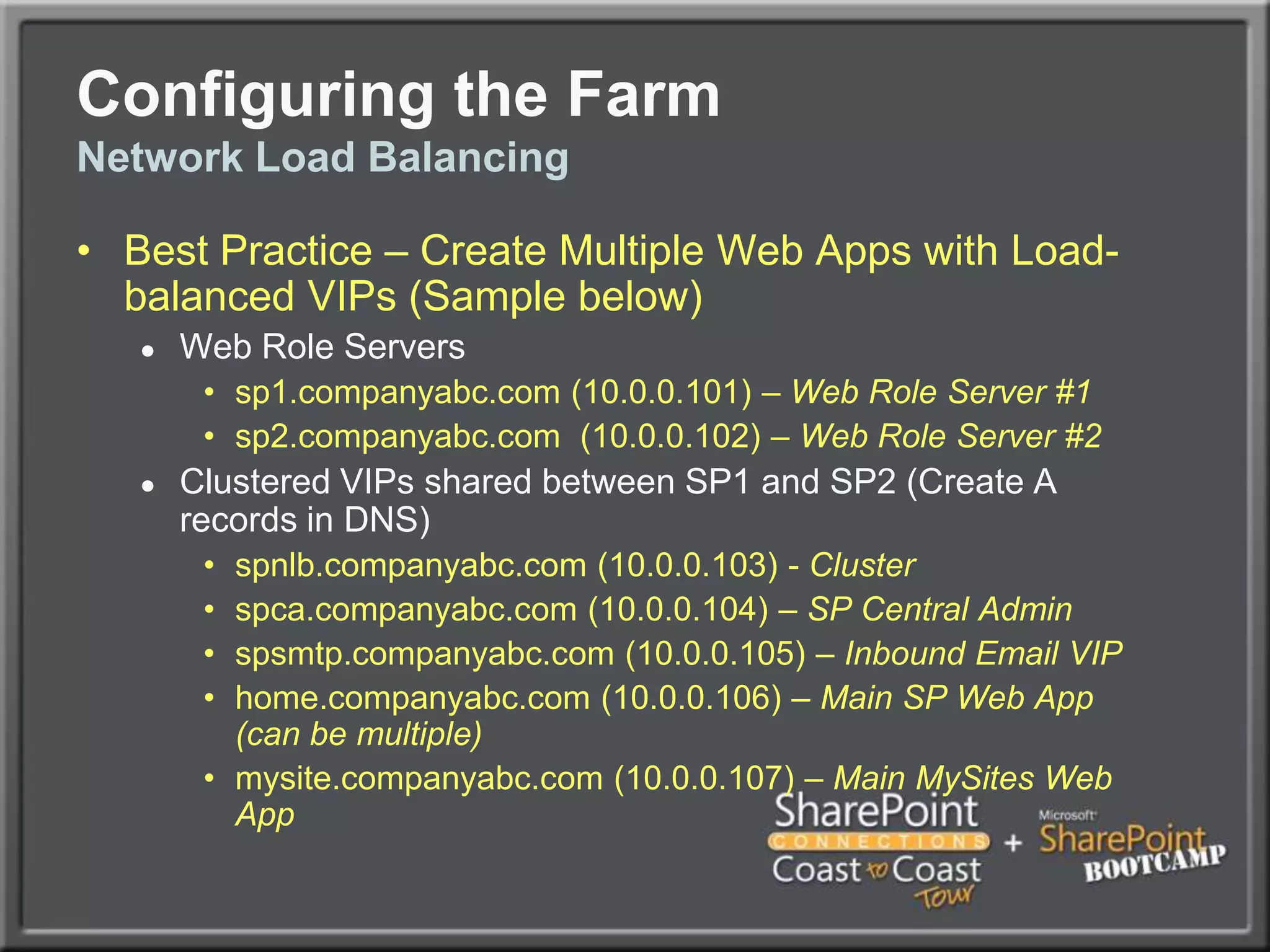
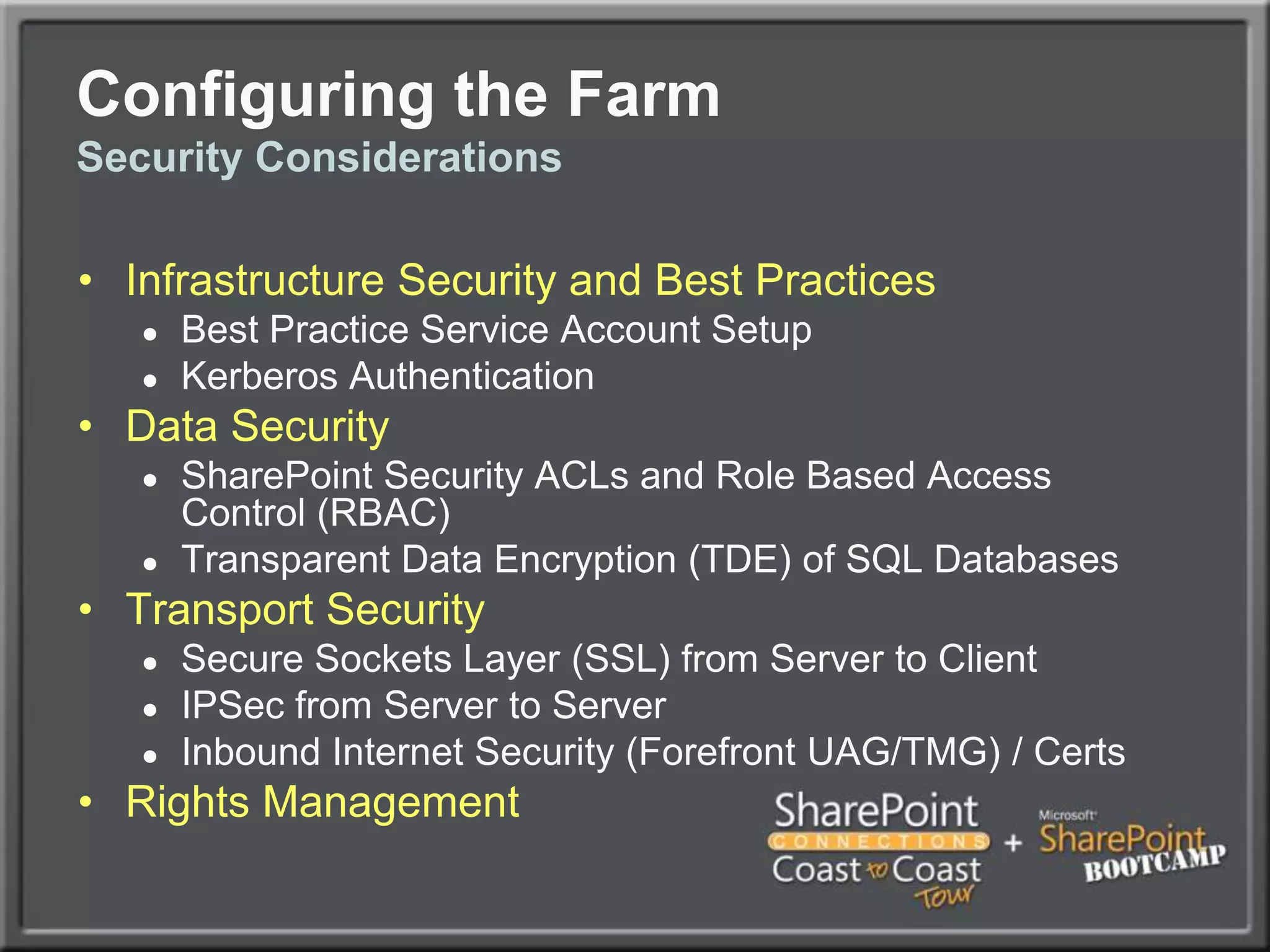
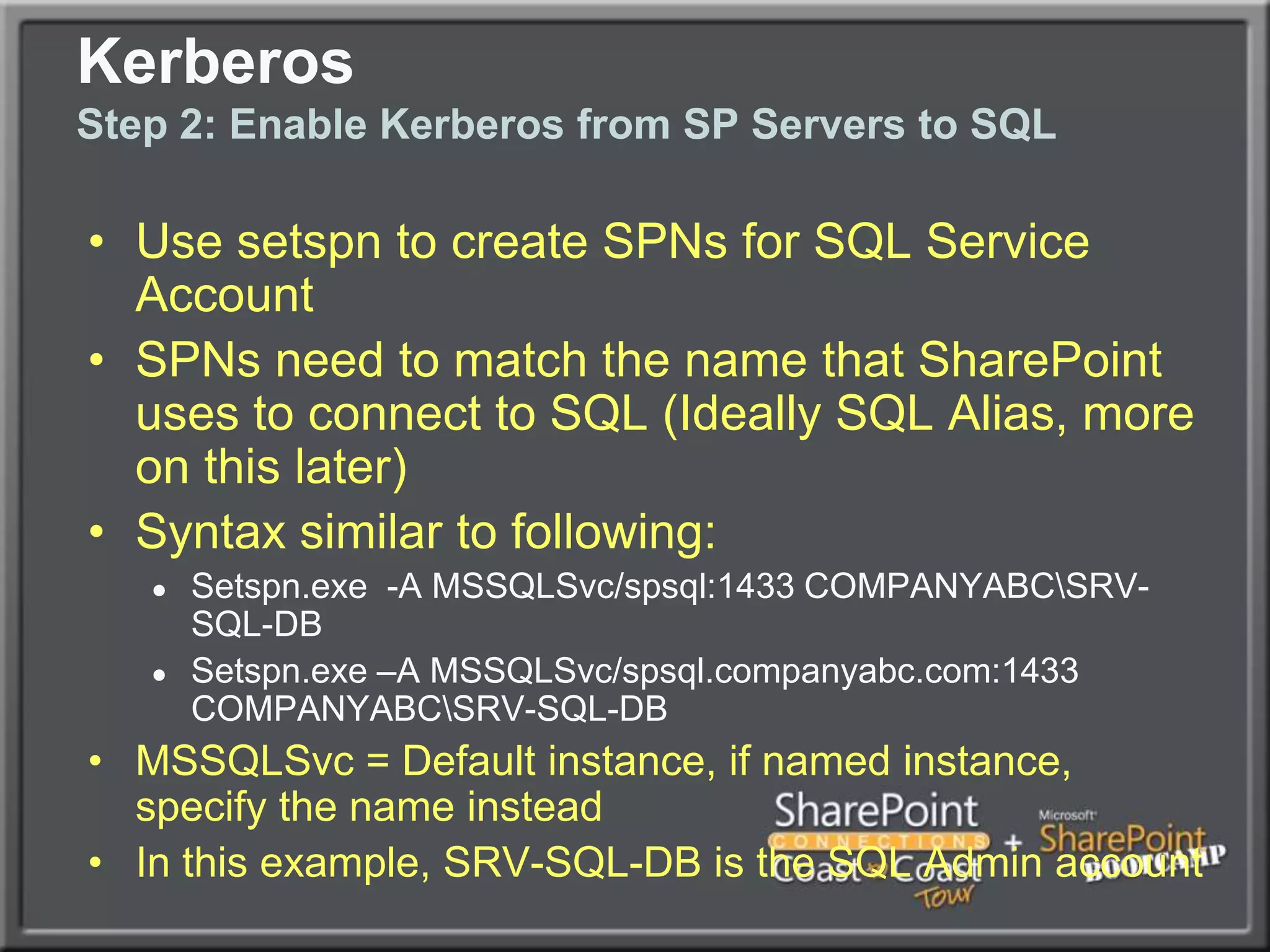
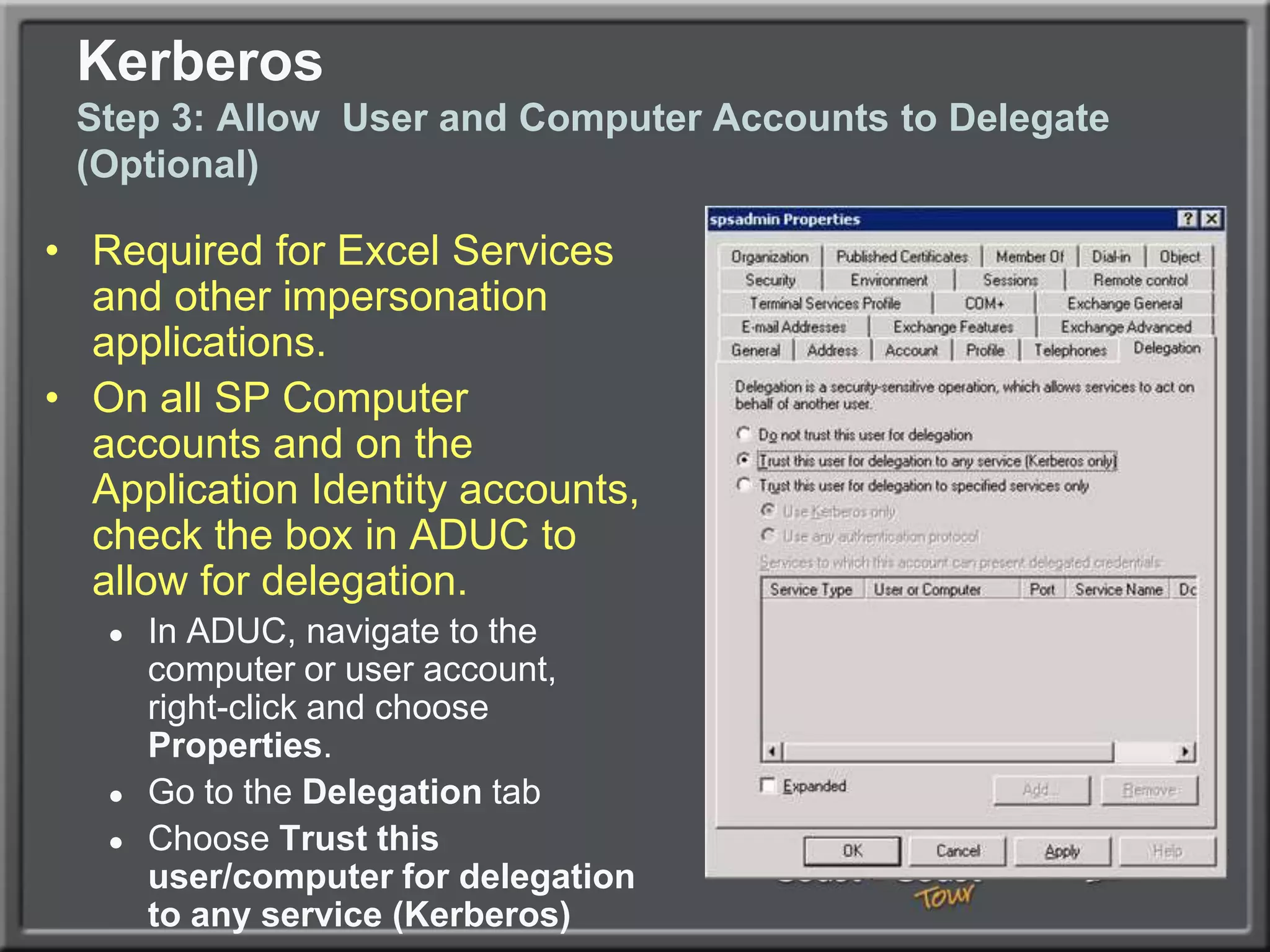
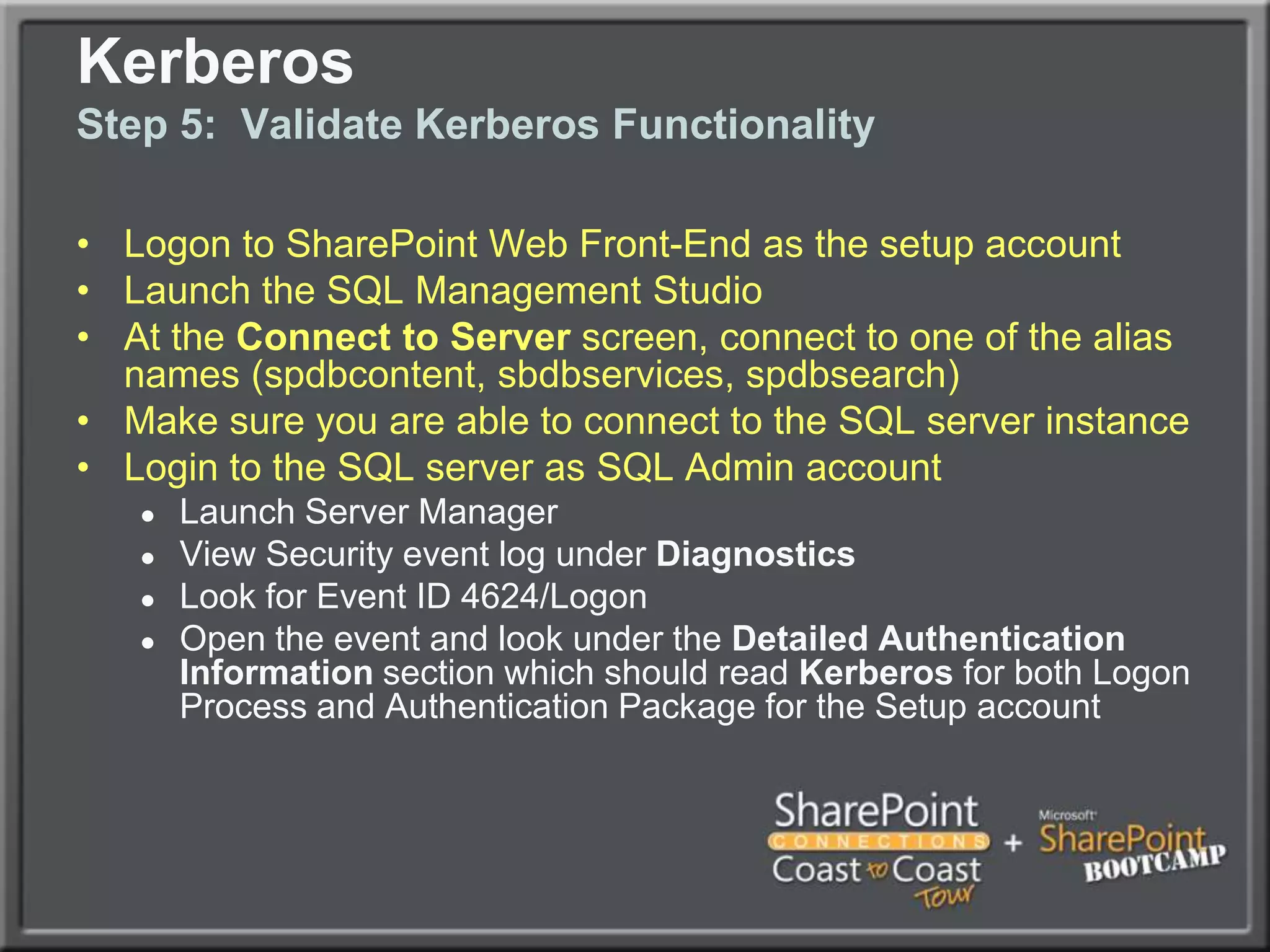
The document outlines best practices for architecting and managing a SharePoint 2010 farm, covering various configurations such as small, large, and virtualized farms. It emphasizes the importance of high availability, security measures including Kerberos authentication, database optimization, and effective server deployment strategies. Additionally, it provides guidelines on SQL database roles, service accounts, network load balancing, and configuring critical components for a successful SharePoint implementation.