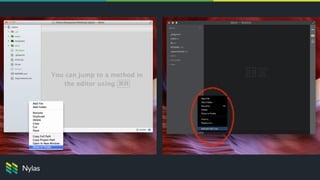
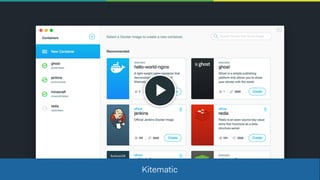
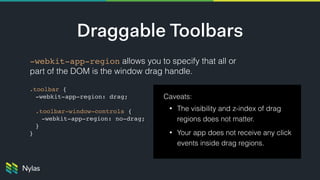
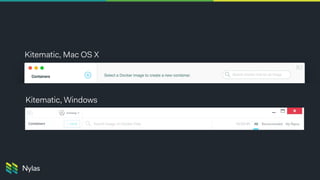
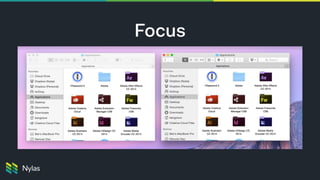
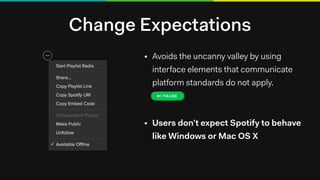
The document discusses building native-like experiences using Electron, focusing on user interface elements, custom window controls, and platform-specific styles. Key points include managing window behavior, implementing drag regions, handling focus events, sound considerations, and ensuring proper image display on Retina screens. It emphasizes meeting user expectations while maintaining a distinct application identity across different platforms.