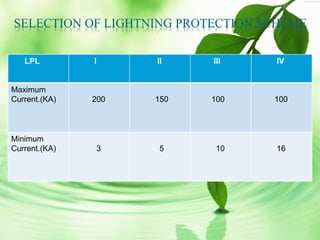
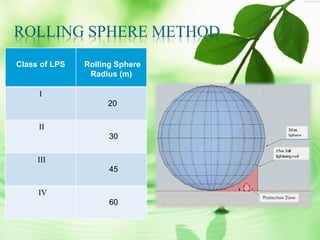
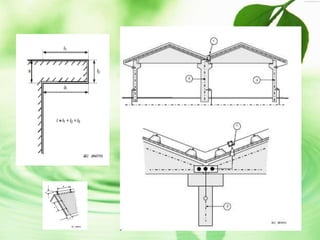
The document discusses lightning protection standards and procedures for buildings. It compares the Indian standard IS 2309 to the international standard BS EN/IEC 62305, which considers risks to human life not addressed in IS 2309. The procedure involves calculating lightning risks, selecting a protection level class, and employing measures like the rolling sphere, protective angle, or mesh methods to determine placement of air terminals and down conductors. A case study examines risks for the Joka station building and proposes design changes like repositioning air terminals to improve protection according to the rolling sphere method.