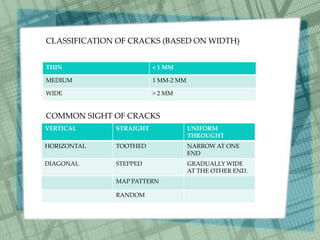
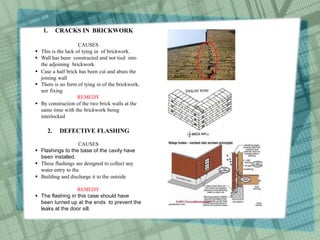
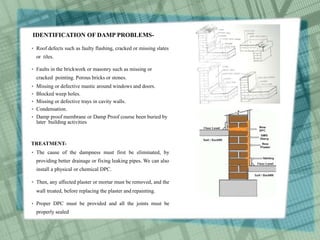
The document discusses common construction defects in buildings such as cracks and dampness. It defines construction defects and lists main causes as application of forces, effects of materials, temperature changes, and biological agents. Common cracks are categorized based on width and appearance. Cracks are further divided into structural and non-structural types. Main causes of cracks are identified as drying shrinkage, thermal movement, elastic deformation, creep, chemical reactions, foundation movement, and vegetation growth. Specific defect examples and their causes are outlined, such as cracks in brickwork from lack of tying and defective flashing. Remedies for preventing common defects are also provided.