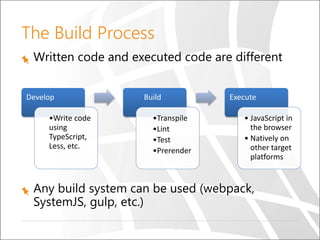
This document provides an overview of the MEAN stack and its components. It discusses Node.js and its asynchronous and non-blocking architecture. It introduces MongoDB for data storage. It also covers Express, a web application framework for Node.js, and Angular 2, a front-end framework. Code examples and demos are provided for Node.js, Express, MongoDB integration, and building an Angular 2 application. The document is intended to educate developers on the MEAN stack technologies.






























![A router is an isolated instance of middlewares
and routes.
The router can have middleware and http VERB
routes added just like an application.
var router = express.Router([options]);
router.get('/events', function(req, res, next) {
// .. some logic here .. like any other middleware // ..
});
Routers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meanjs-160922091523/85/Building-Applications-With-the-MEAN-Stack-31-320.jpg)