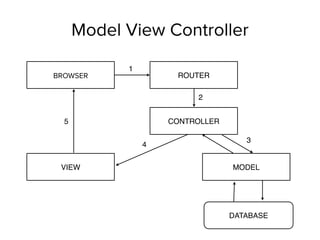
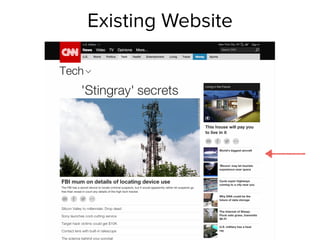
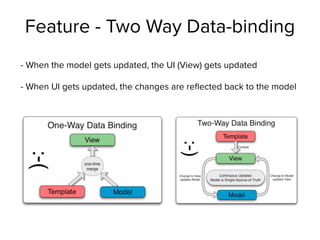
This document provides an overview of the MEAN stack and demonstrates how to build a sample application with it. It begins with defining each component of the MEAN stack: MongoDB as the database, Express as the web application framework, AngularJS for the frontend framework, and Node.js as the runtime environment. It then demonstrates setting up a basic Express app, integrating authentication with Passport, and interacting with MongoDB using Mongoose. The document also discusses key concepts like asynchronous I/O in Node.js and model-view-controller patterns in AngularJS. Overall, it serves as a high-level introduction to the technologies that make up the MEAN stack.














































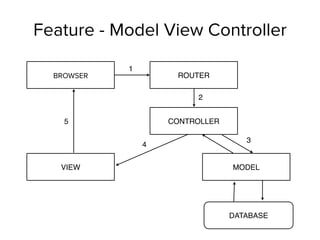













![Creating Controllers
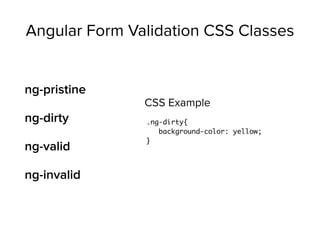
var app = angular.module('myApp', []);
app.controller('MyController', ['$scope', function($scope){
$scope.name = "hello";
}]);
<div ng-controller="MyController">
{{ name }}
</div>
app.js
index.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mean-150322104736-conversion-gate01/85/Beginning-MEAN-Stack-83-320.jpg)

![Creating Controllers + Two Way Data Binding
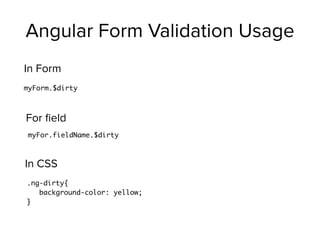
var app = angular.module('myApp', []);
app.controller('MyController', ['$scope', function($scope){
$scope.name = "hello";
}]);
<div ng-controller="MyController">
{{ name }}
<input type="text" name="name" value="" ng-model="name"
placeholder="Type your name">
</div>
app.js
index.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mean-150322104736-conversion-gate01/85/Beginning-MEAN-Stack-85-320.jpg)














![Using ng-click
var app = angular.module('myApp', []);
app.controller('MyController', ['$scope', function($scope){
$scope.showAlert = function() {
alert("Show Alert!");
};
}]);
<div ng-controller="MyController">
<a href="" ng-click="showAlert()">Show Alert!</a>
</div>
app.js
index.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mean-150322104736-conversion-gate01/85/Beginning-MEAN-Stack-100-320.jpg)



![AJAX using $http service
app.controller('MyController', ['$scope', '$http', function ($scope, $http)
{
$http.get('people.json').success(function(data){
$scope.people = data;
});
}]);
app.js
https://docs.angularjs.org/api/ng/service/$http](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mean-150322104736-conversion-gate01/85/Beginning-MEAN-Stack-104-320.jpg)



![How to make angular routes?
1. Include angular-route.js
library
2. Inject ‘ngRoute’ to app
module
3. Inject ‘$routeProvider’
to your app as a config
4. define your routes!
app.config(['$routeProvider',
function( $routeProvider ) {
$routeProvider.when('/', {
templateUrl: 'homepage.html',
controller: 'HomeController'
});
}
]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mean-150322104736-conversion-gate01/85/Beginning-MEAN-Stack-108-320.jpg)
![How to make angular routes? (2)
- Nest other routes by
appending ‘.when()’
- the fallback route is
defined “otherwise”
app.config(['$routeProvider',
function( $routeProvider ) {
$routeProvider.when('/', {
templateUrl: 'homepage.html',
controller: 'HomeController'
}).
when('/about',{
templateUrl: 'about.html',
controller: 'AboutController'
}).
otherwise({
redirectTo: '/'
});
}
]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mean-150322104736-conversion-gate01/85/Beginning-MEAN-Stack-109-320.jpg)


![How to make angular routes? (3)
app.config(
['$routeProvider', function($routeProvider){
$routeProvider.when('/people', {
templateUrl: 'people.html',
controller: 'PeopleController'
}).
when('/person/:id', {
templateUrl: 'single_person.html',
controller: 'PersonDetailController'
}).
otherwise({
redirectTo: '/people'
});
}]
);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mean-150322104736-conversion-gate01/85/Beginning-MEAN-Stack-112-320.jpg)