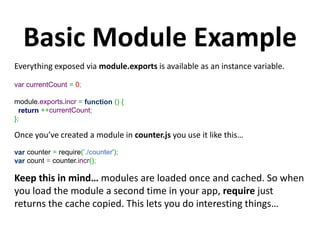
This document serves as an introduction to Node.js by Chris Cowan, outlining its essential features such as non-blocking I/O and its utility in creating scalable server-side applications using JavaScript. It provides installation instructions for different operating systems, basic examples to demonstrate Node.js functionality, and warnings about callback hell, along with solutions using the async library. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of the Node Package Manager (npm) for managing modules within Node.js projects.














![Non-Blocking I/
// Get User – 20ms
var query = 'SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = ?';
db.query(query, [userId], function (err, results) {
console.log(results);
});
// Get Activities – 100ms
var query = 'SELECT * FROM activities ORDER BY timestamp LIMIT 50';
db.query(query, function (err, results) {
console.log(results);
});
// Get Leader Board – 150ms
var query = 'SELECT count(points) as total, user_id FROM activities LIMIT 50';
db.query(query, function (err, results) {
console.log(results);
});
150ms = MAX(user, activities, leaderboard)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtonodejs-120926101645-phpapp01/85/Intro-To-Node-js-16-320.jpg)


![Callbacks are the Devil’s Work!
Don’t go down this rabbit hole…
var userQuery = 'SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = ?';
var activityQuery = 'SELECT * FROM activities ORDER BY timestamp LIMIT 50';
var leaderBoardQuery = 'SELECT count(points) as total, user_id FROM activities LIMIT 50';
db.query(userQuery, [id], function (userErr, userResults) {
db.query(activityQuery, function (activityErr, activityResults) {
db.query(leaderBoardQuery, function (leaderBoardErr, leaderBoardResults) {
// Do something here
});
});
});
One of the biggest mistakes is to get yourself in
to callback hell by nesting callbacks inside of
callbacks inside of more callbacks.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtonodejs-120926101645-phpapp01/85/Intro-To-Node-js-19-320.jpg)

![Async to the rescue!
var async = require('async');
var db = require(’db');
function getUser (callback) {
var query = 'SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = ?';
db.query(query, [userId], callback);
}
function getActivities (callback) {
var query = 'SELECT * FROM activities ORDER BY timestamp LIMIT 50';
db.query(query, callback);
}
function getLeaderBoard (callback) {
var query = 'SELECT count(points) as total, user_id FROM activities LIMIT 50';
db.query(query, callback);
}
var tasks = [getUser, getActivities, getLeaderBoard];
async.parallel(tasks, function (err, results) {
var user = results[0][0];
var activities = results[1];
var leaderBoard = results[2];
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtonodejs-120926101645-phpapp01/85/Intro-To-Node-js-21-320.jpg)