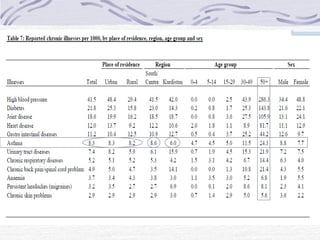
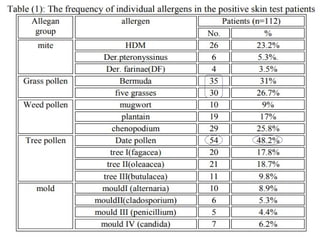
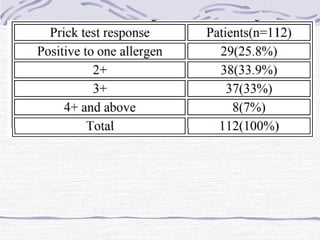
Bronchial asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by airway obstruction, dyspnea, cough, and wheezing, affecting 1-18% of the population globally. In Iraq, pollen from trees, grasses, and weeds is a significant allergen, exacerbated by modern lifestyle and environmental factors. The study highlights a strong correlation between asthma and allergic rhinitis, particularly prevalent in urban residents and those with a family history of allergies.