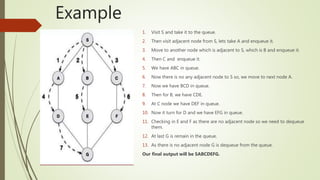
Breadth-first search (BFS) is an algorithm that searches data structures or trees in a breadth-wise manner using a queue. It visits the adjacent unvisited node, marks it as visited, displays it, and inserts it into the queue. If no adjacent nodes are found, it removes the first node from the queue. It repeats this process until the queue is empty. BFS guarantees finding the shortest path and avoids getting stuck on useless paths, though it requires more memory than depth-first search as the solution path increases in length.