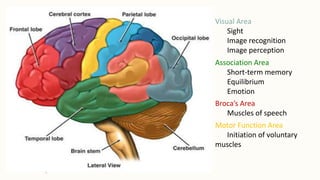
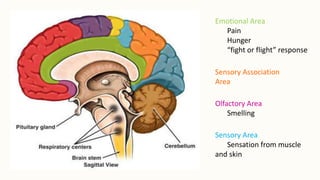
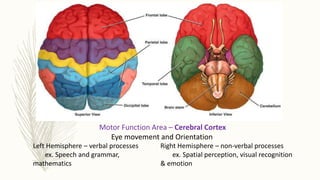
The brain is the most complex organ in the body that allows humans to think, have emotions, and dream. It weighs about 3 pounds and is made up of around 100 billion neurons. The brain is covered by meninges and housed in the skull. It is responsible for various functions like sight, hearing, smell, movement, memory, language, emotion, and autonomic processes through different areas like the visual, auditory, motor, and emotional areas. The cerebellum controls movement coordination while the brain stem regulates vital functions. The two hemispheres of the brain have specialized functions with the left controlling language and the right spatial skills and emotion.