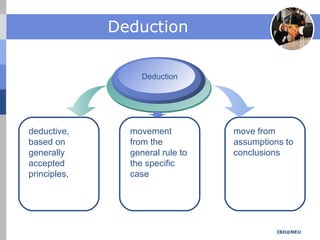
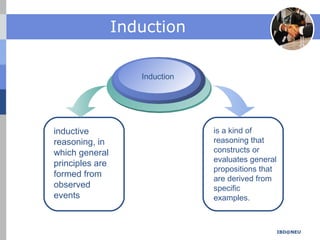
The document summarizes key concepts in banking, finance and economics including induction, deduction, framing, abstraction and modeling. It provides examples to illustrate each concept. Induction reasons from specific observations to broader generalizations. Deduction moves from general rules or assumptions to specific conclusions. Framing refers to how information is presented influencing decision making. Abstraction ignores details to focus on core aspects while modeling creates simplified representations of reality.