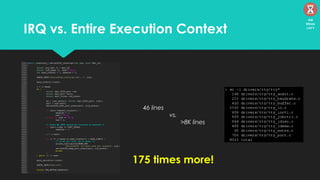
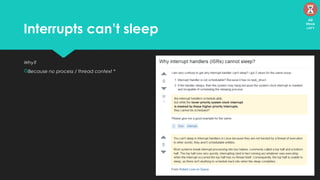
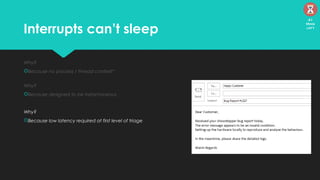
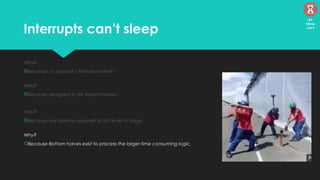
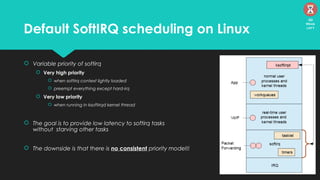
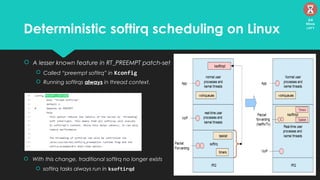
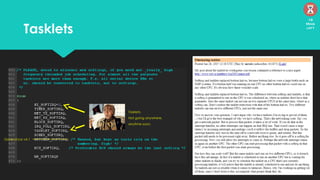
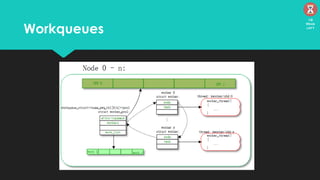
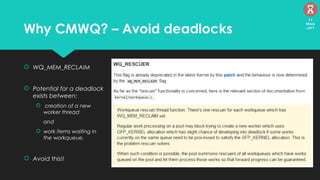
The document discusses the Linux kernel's interrupt handling, specifically the concept of bottom halves, which include softirqs and tasklets, and explores their evolution to workqueues for better concurrency management. It highlights the importance of low latency in interrupt processing and the necessity for non-blocking behavior, elaborating on the implications of threaded interrupts and scheduling models. Additionally, it presents potential issues such as deadlocks and performance considerations, along with references for further reading on these topics.