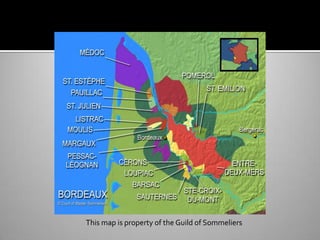
The document provides an overview of Bordeaux wines, including the main grape varieties, soil and climate characteristics, classifications, and key information about different appellations. It discusses the five main red varietals and three white varietals of Bordeaux. It also summarizes the 1855 classification of top Bordeaux chateaux and premier crus, as well as classifications of other Bordeaux regions. Sauternes is highlighted as a premier sweet wine appellation known for its noble rot-affected grapes.