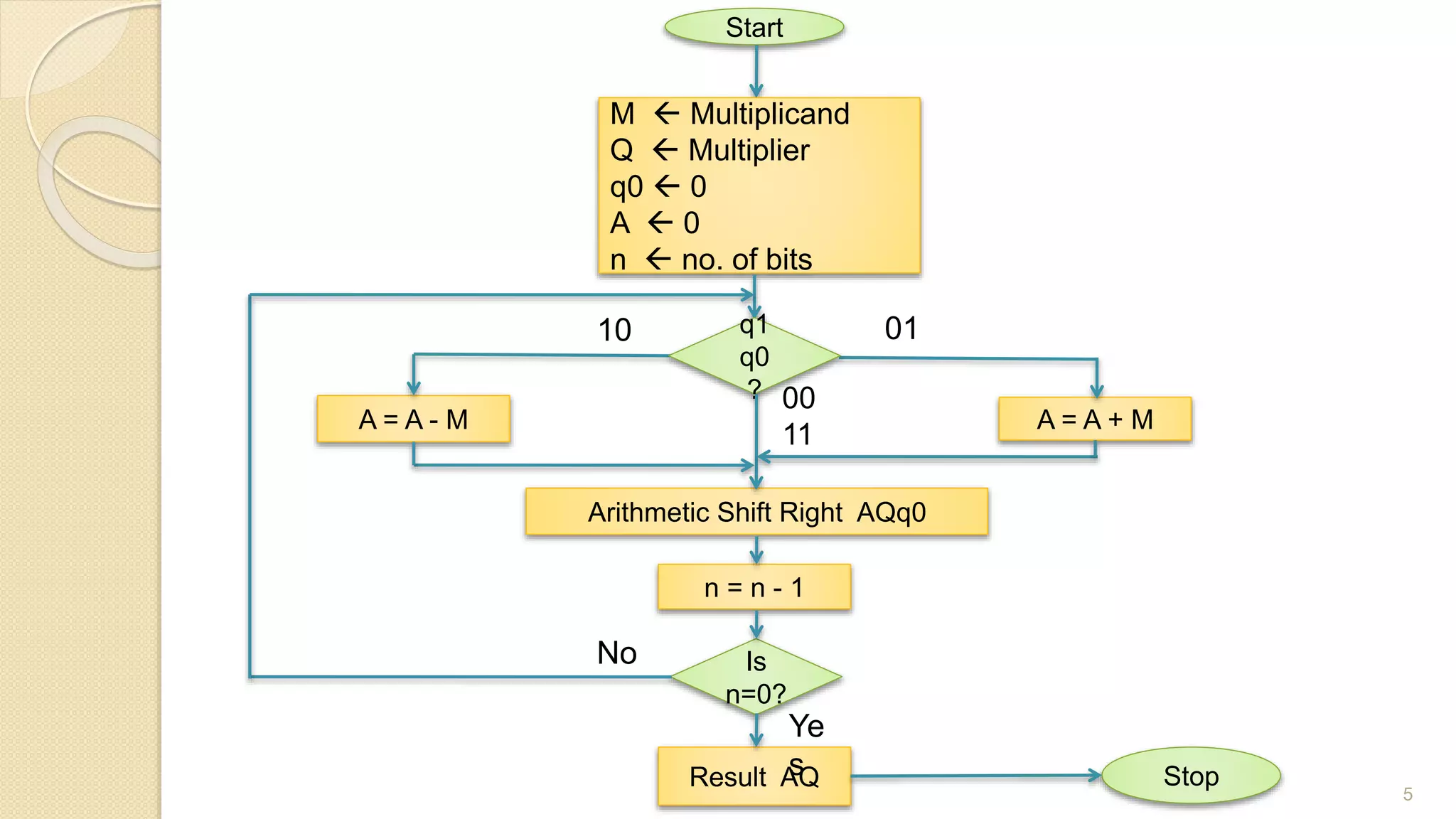
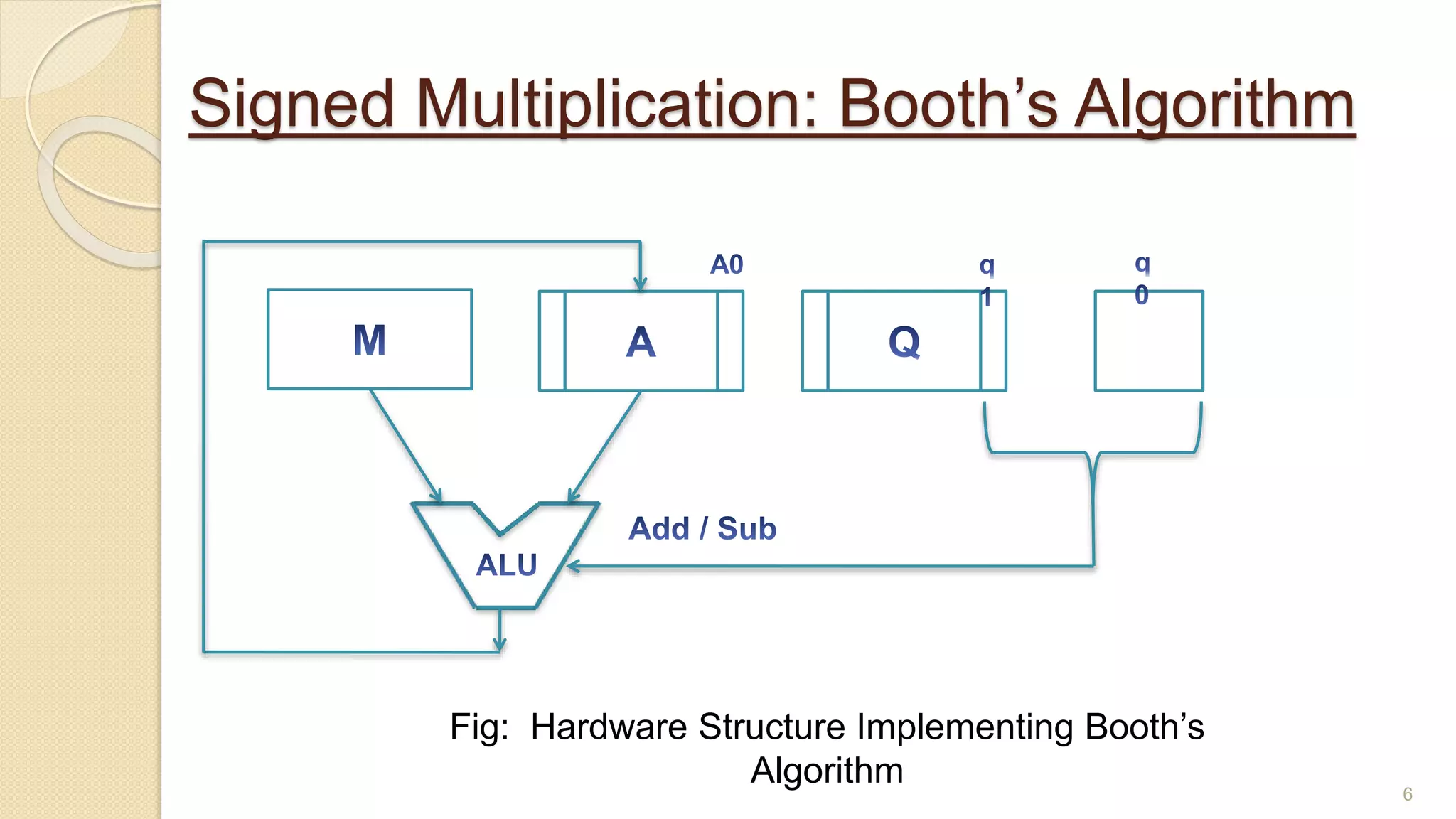
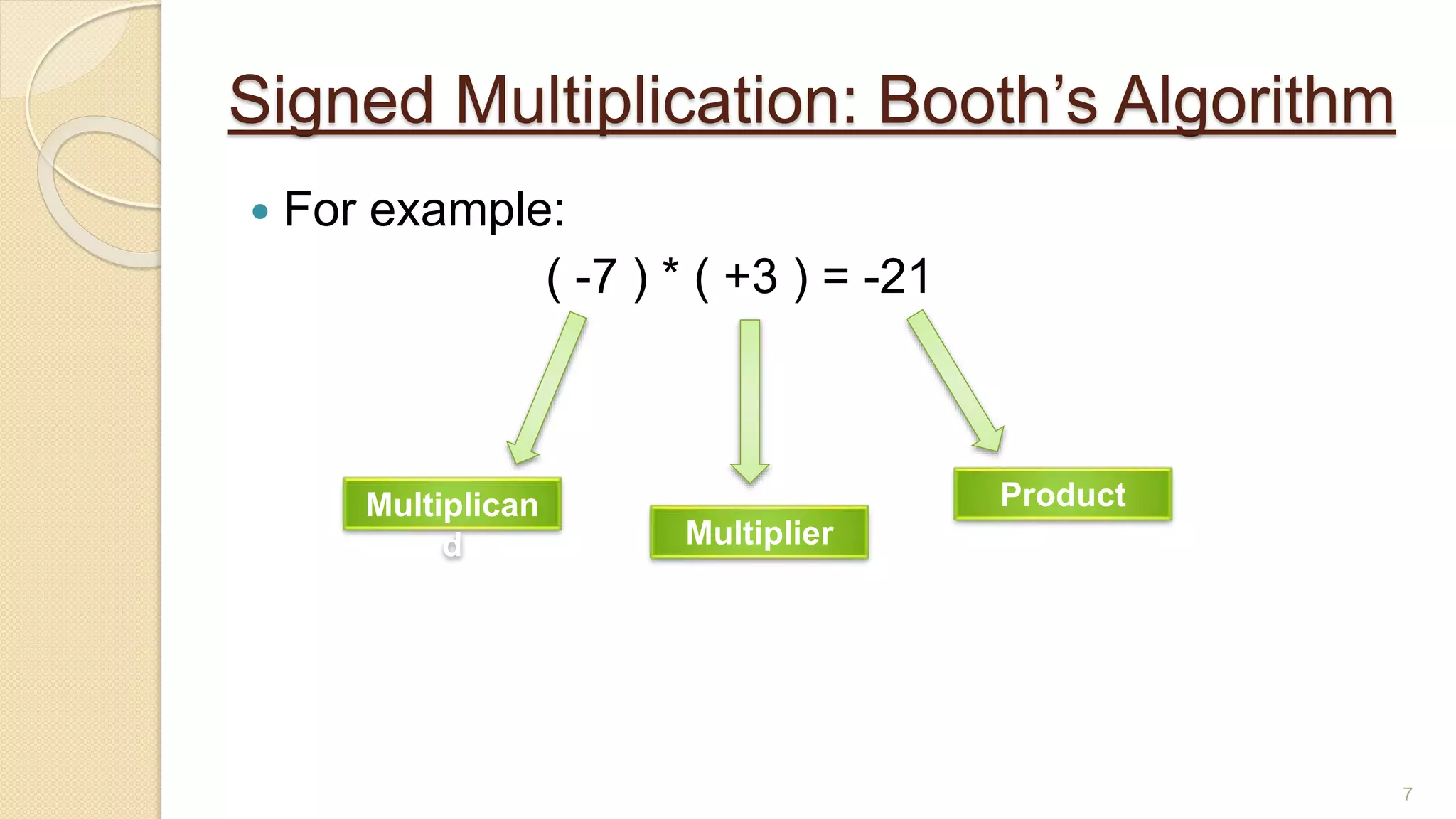
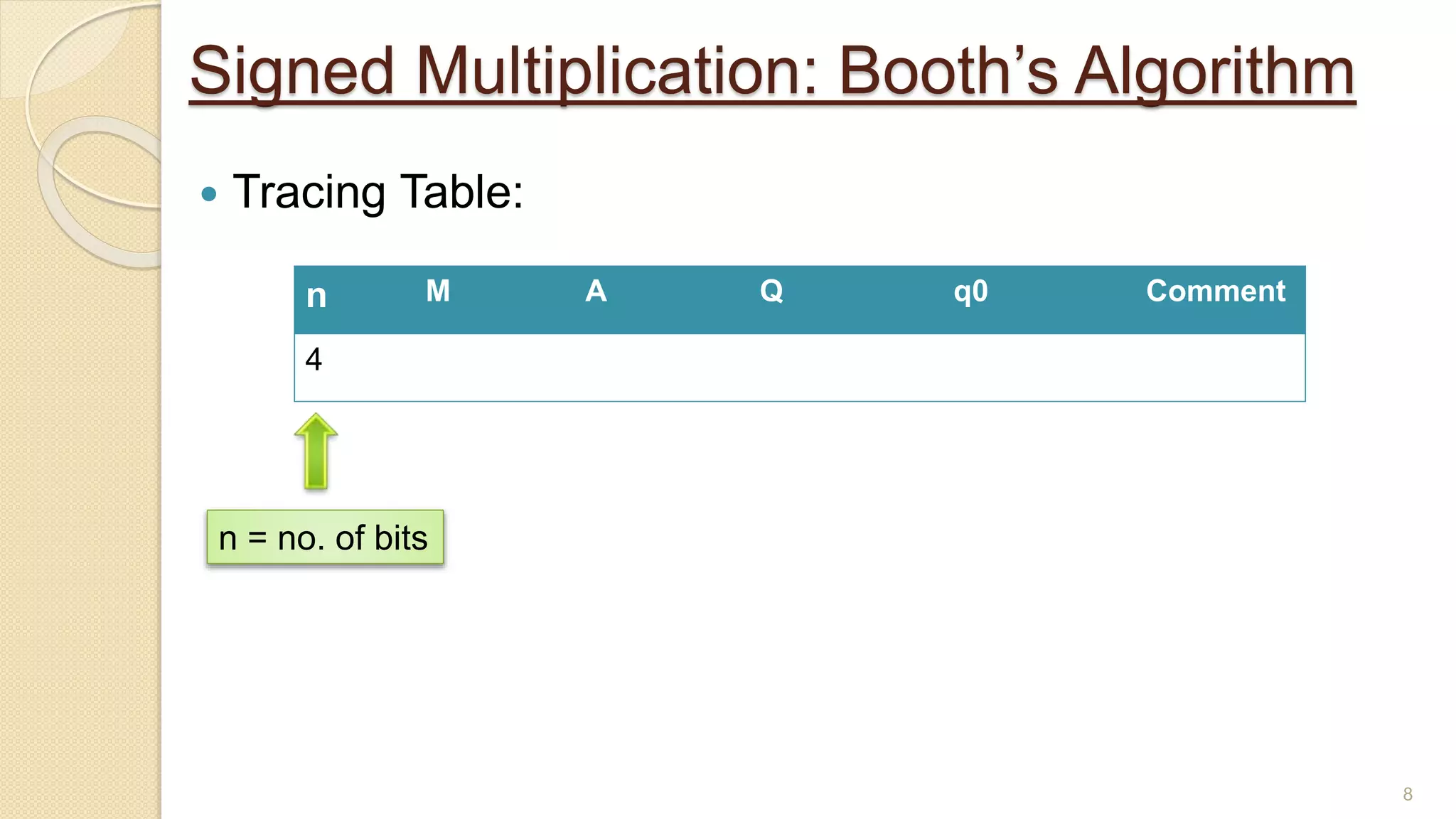
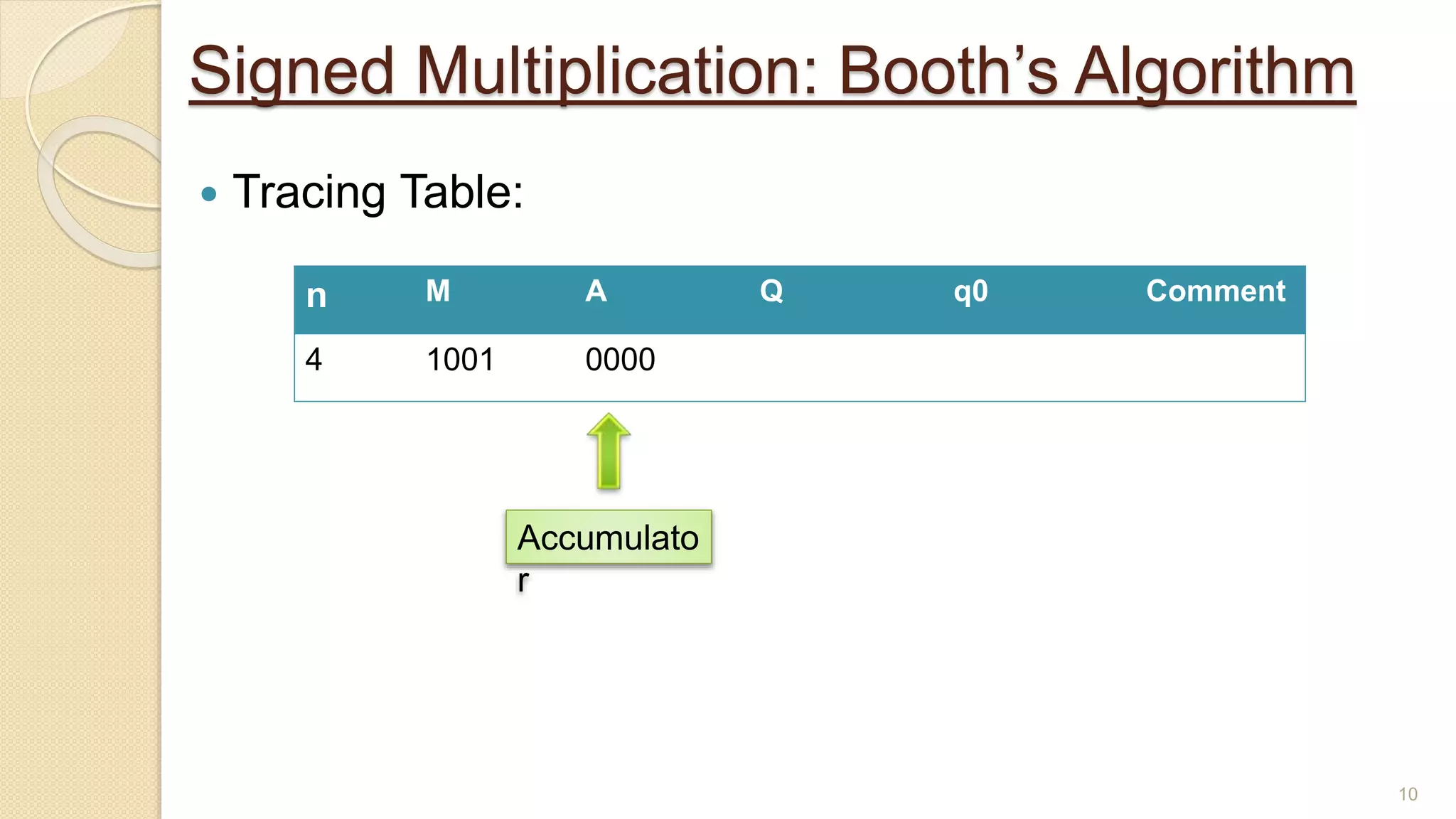
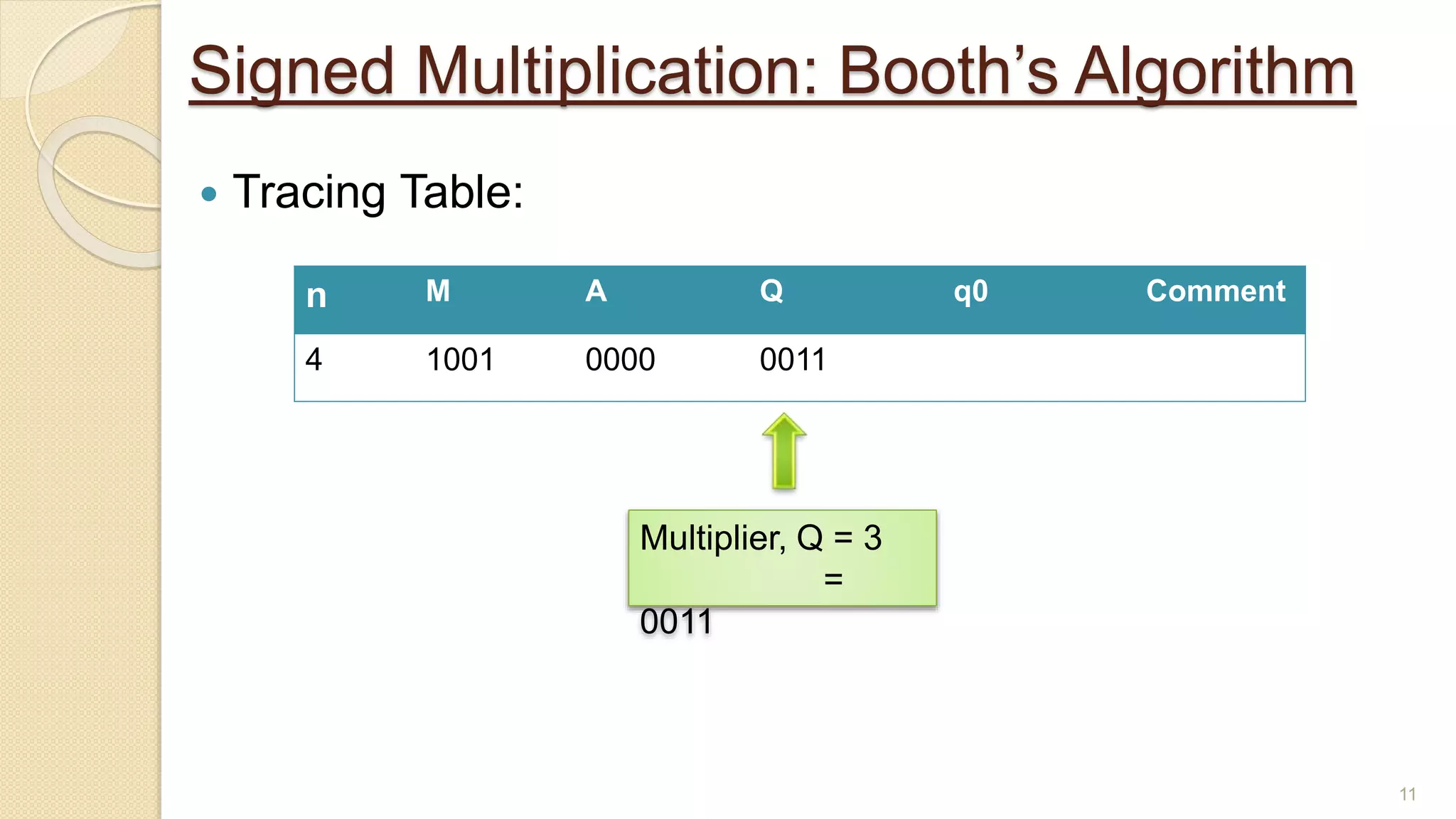
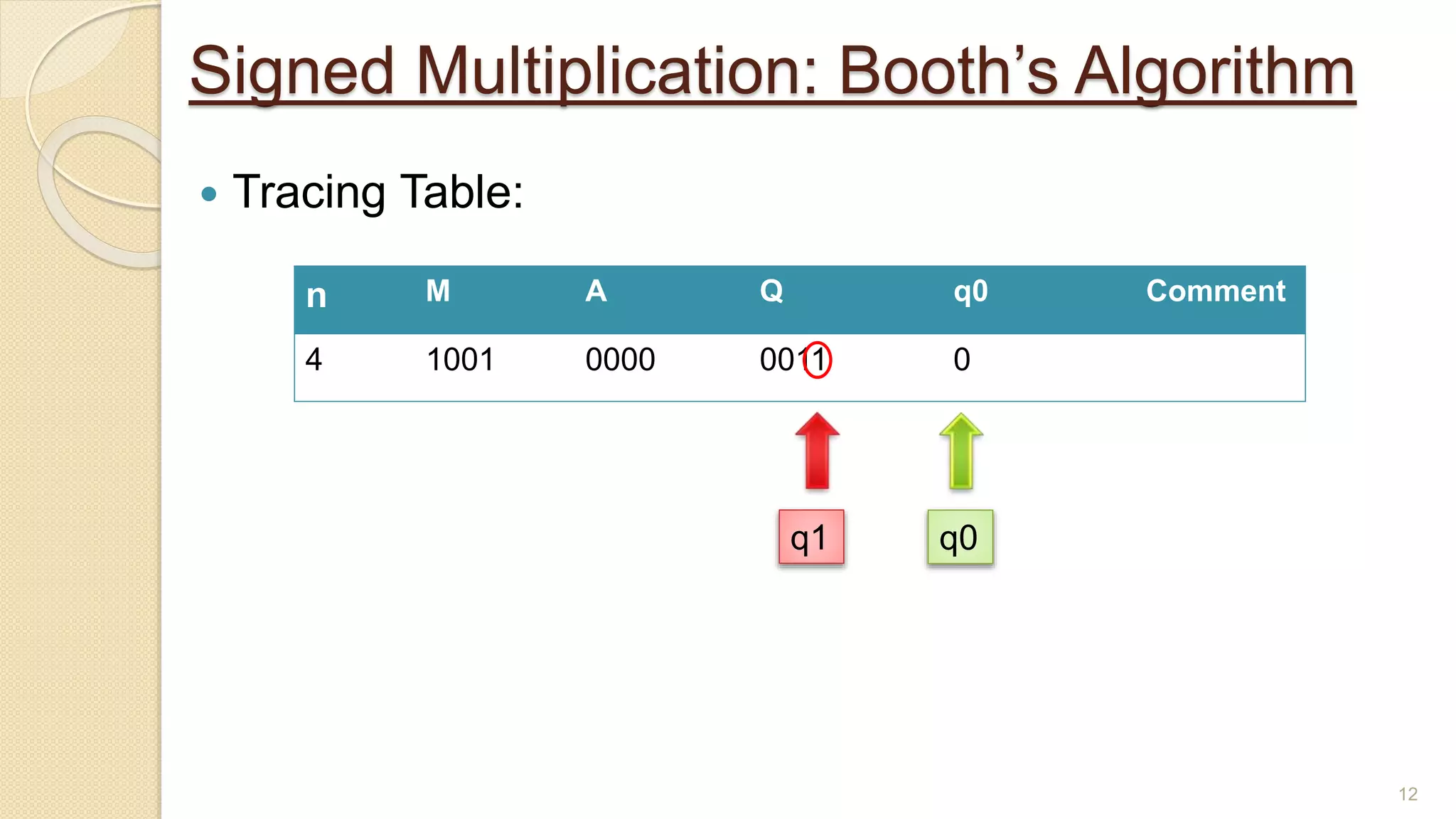
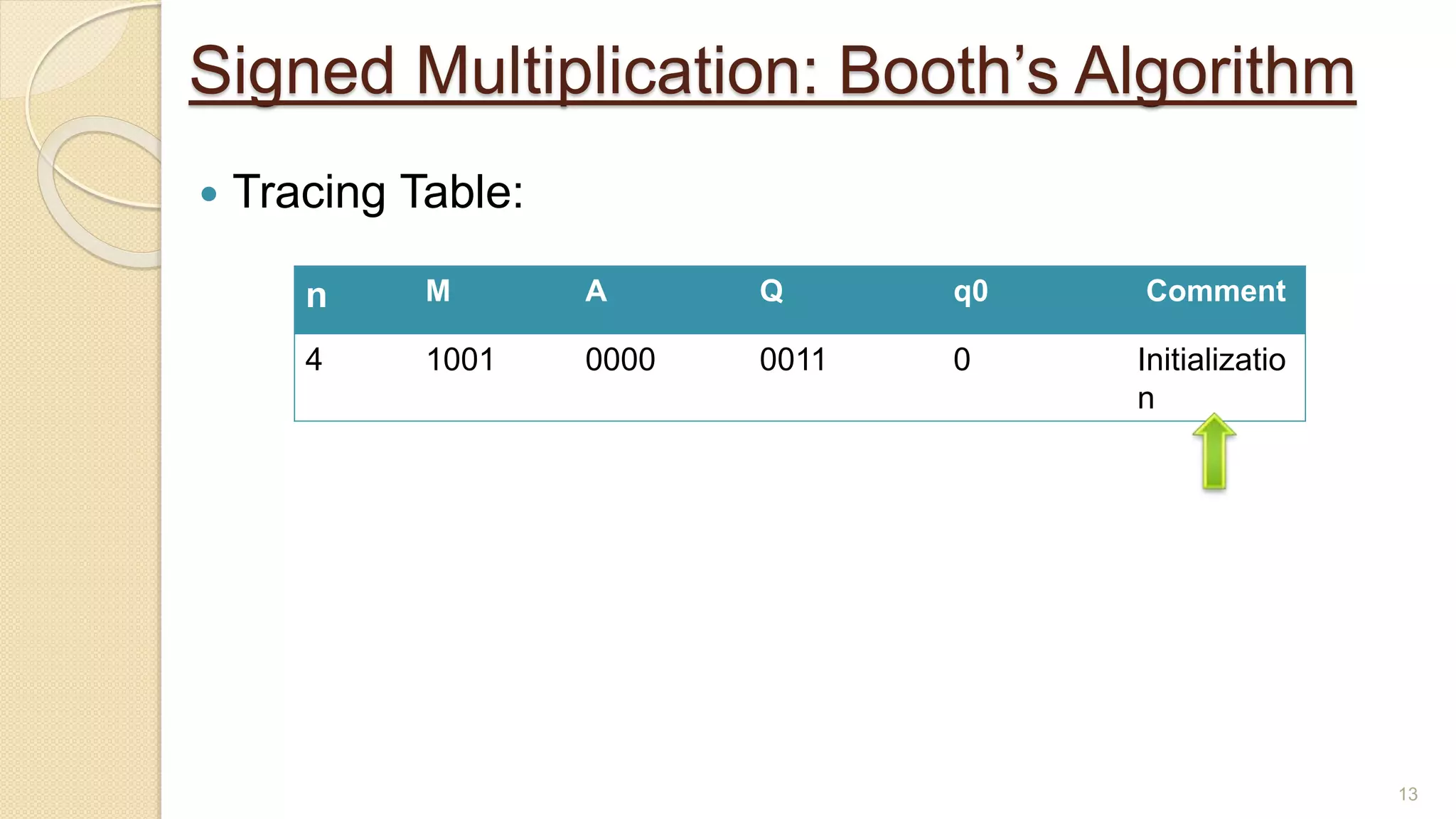
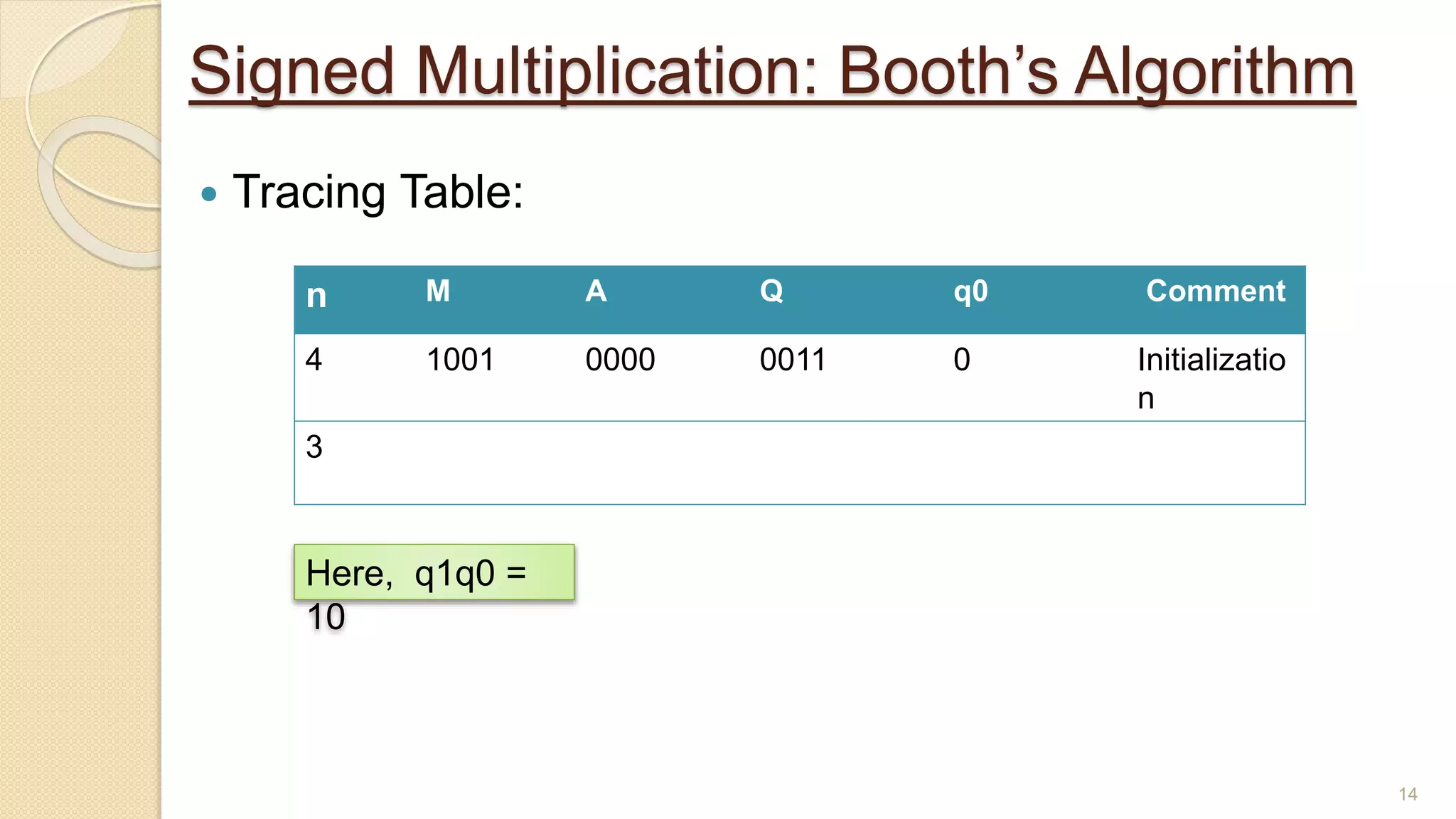
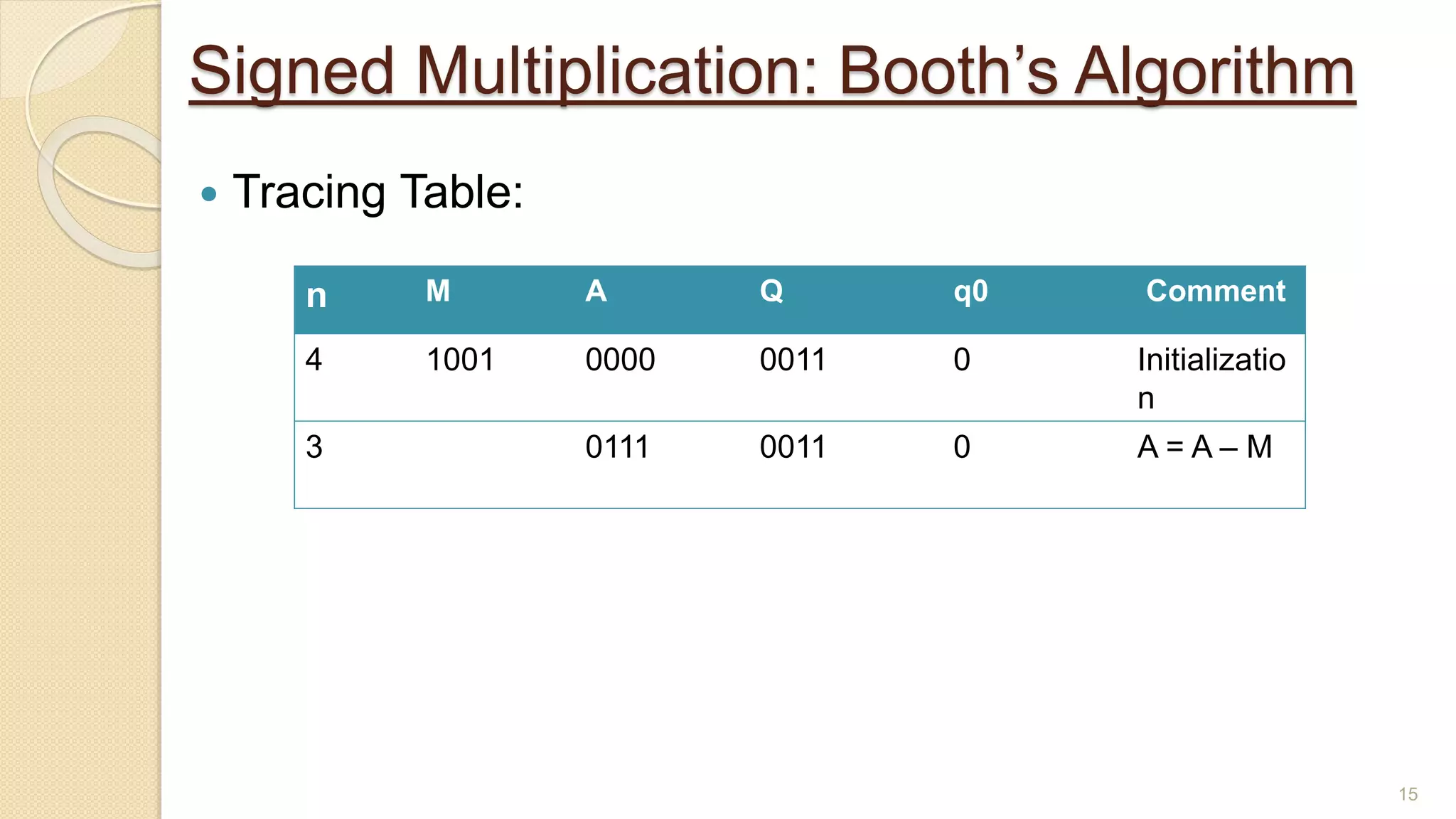
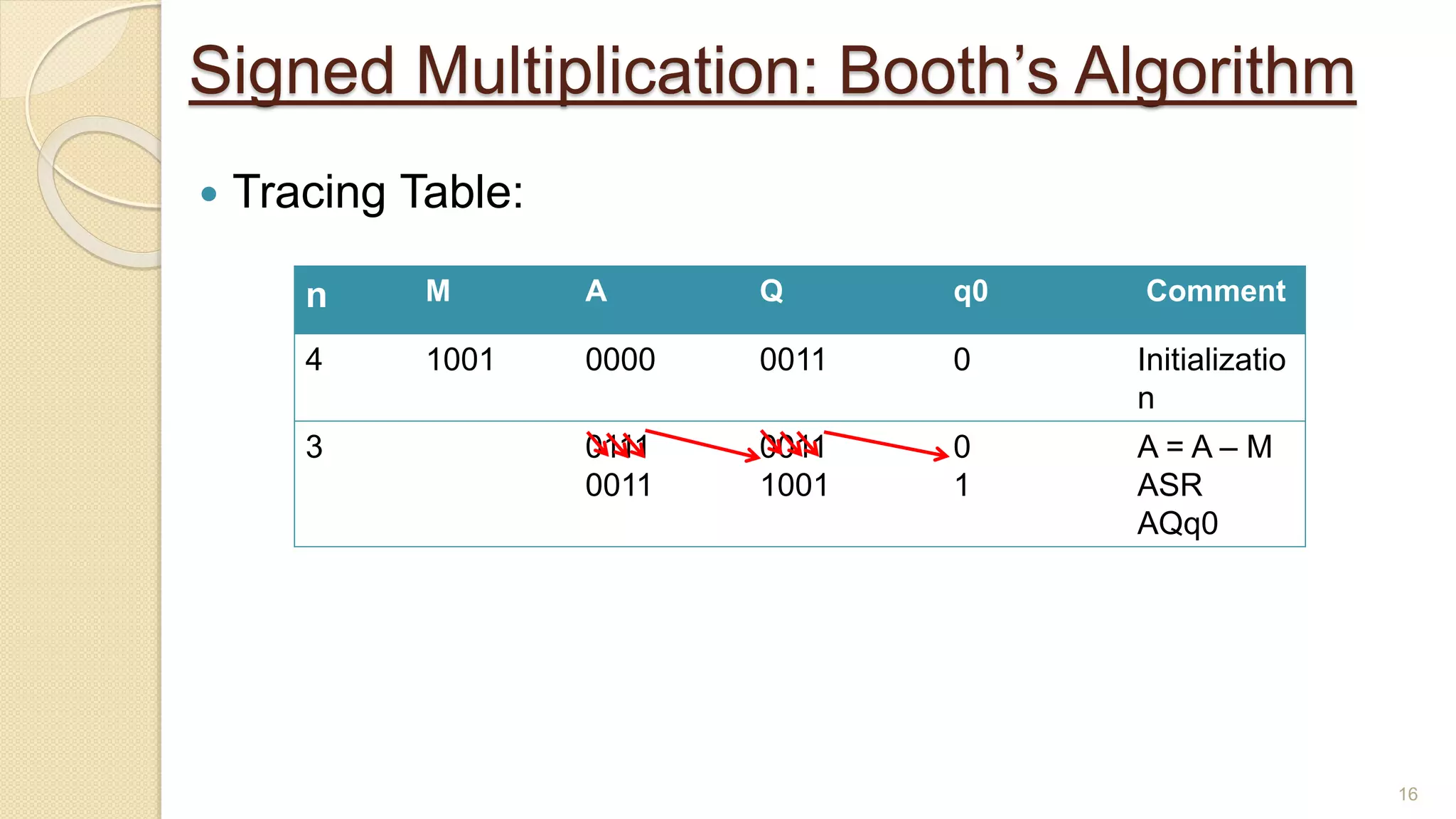
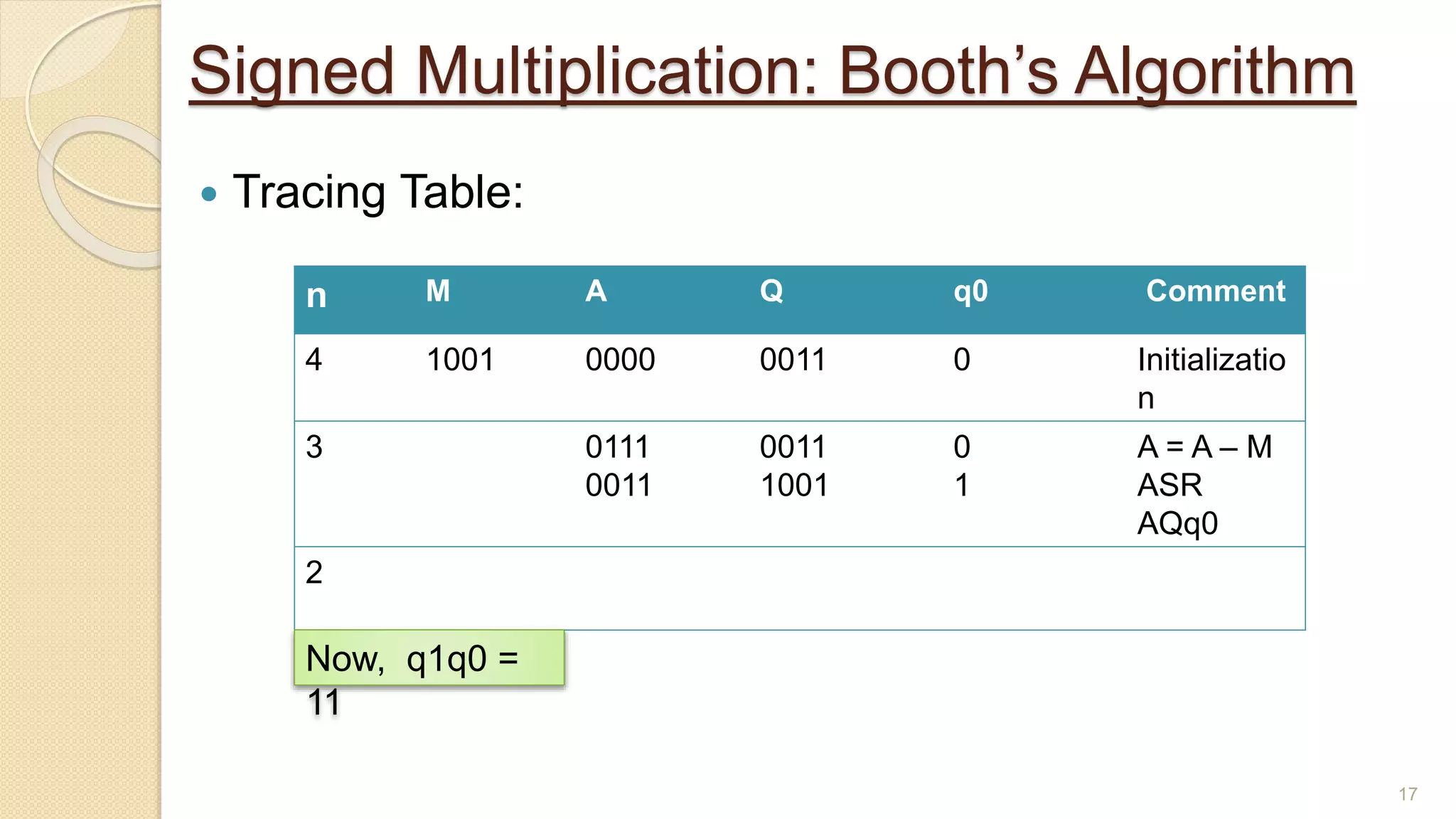
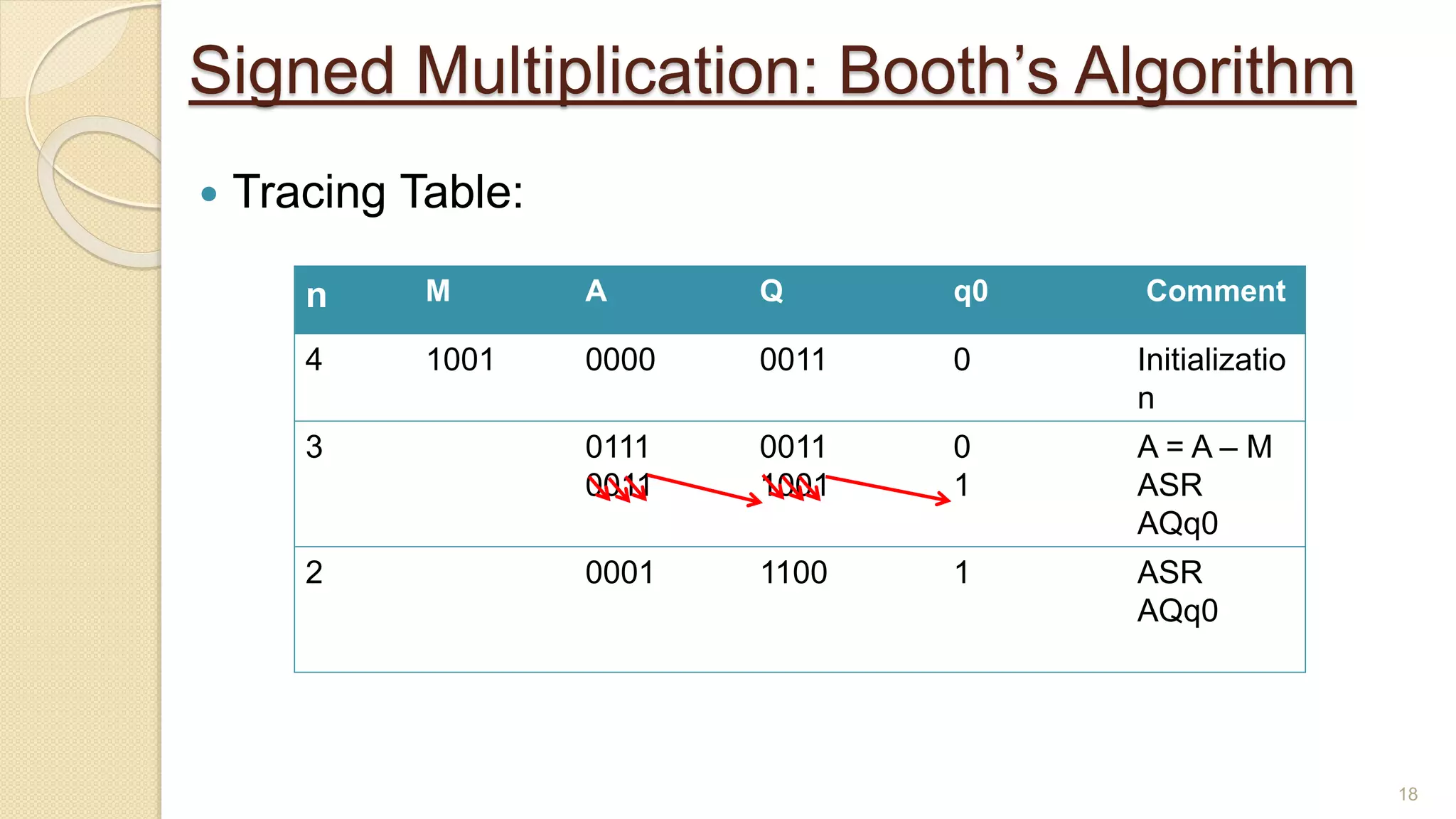
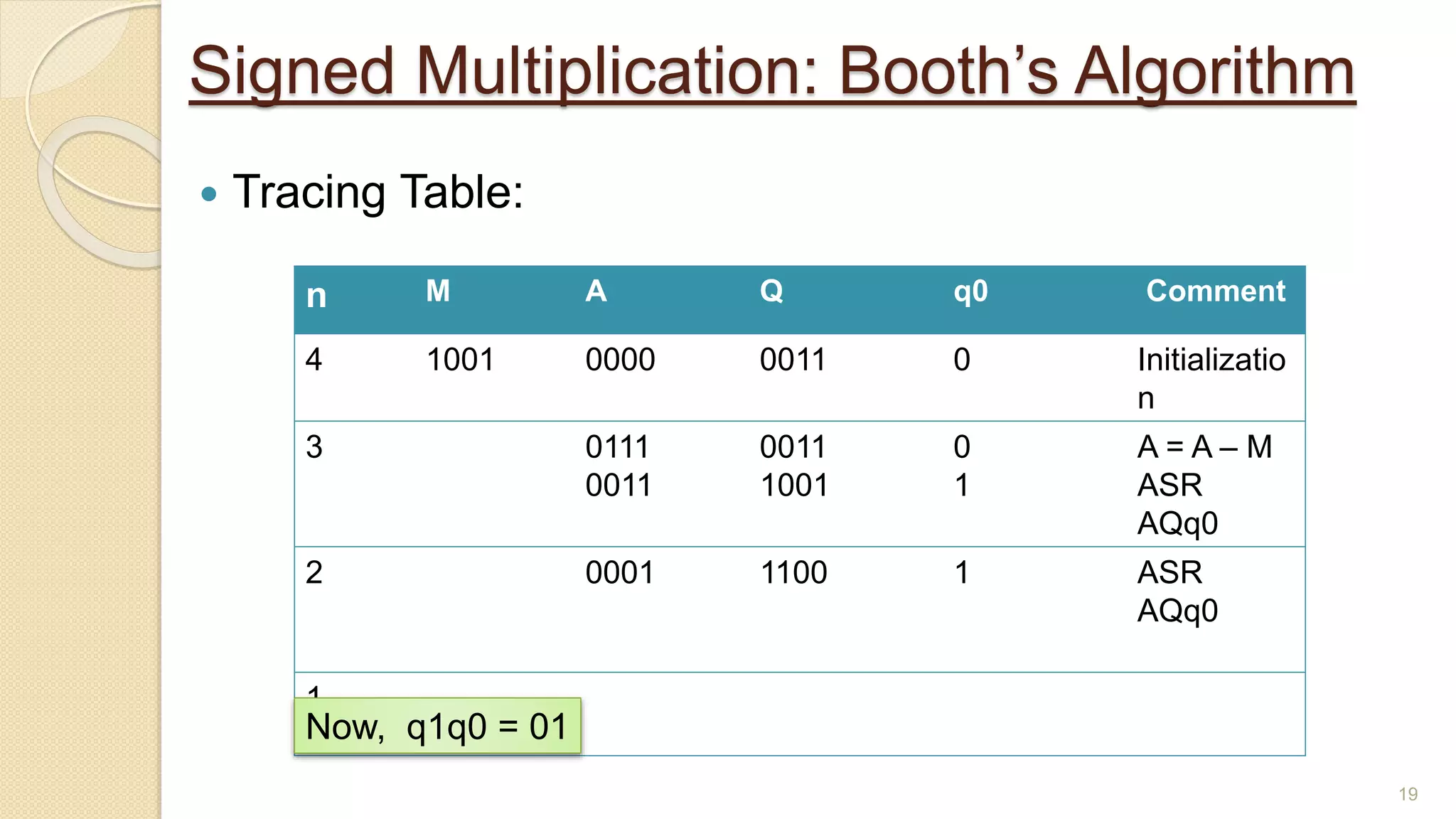
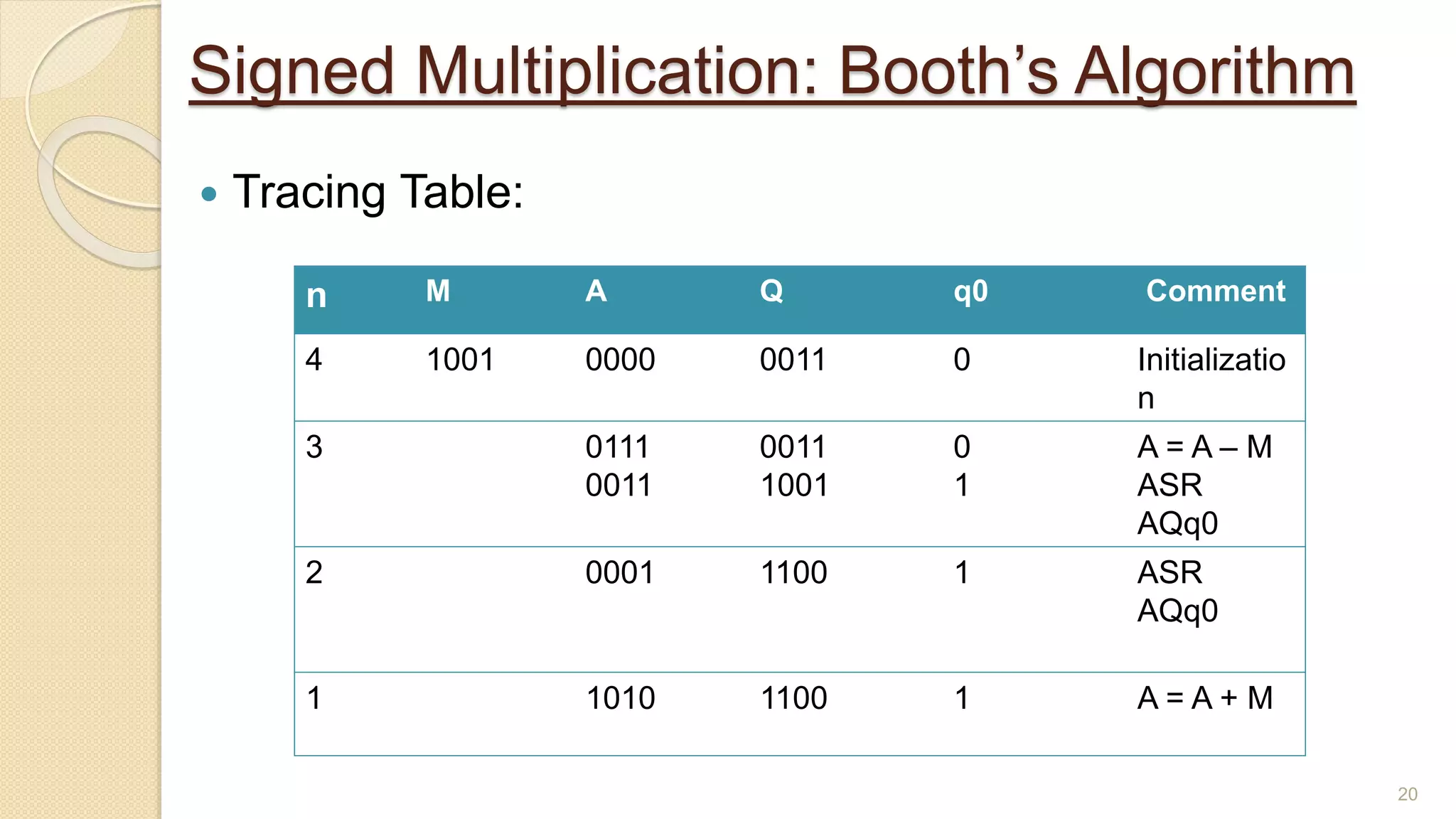
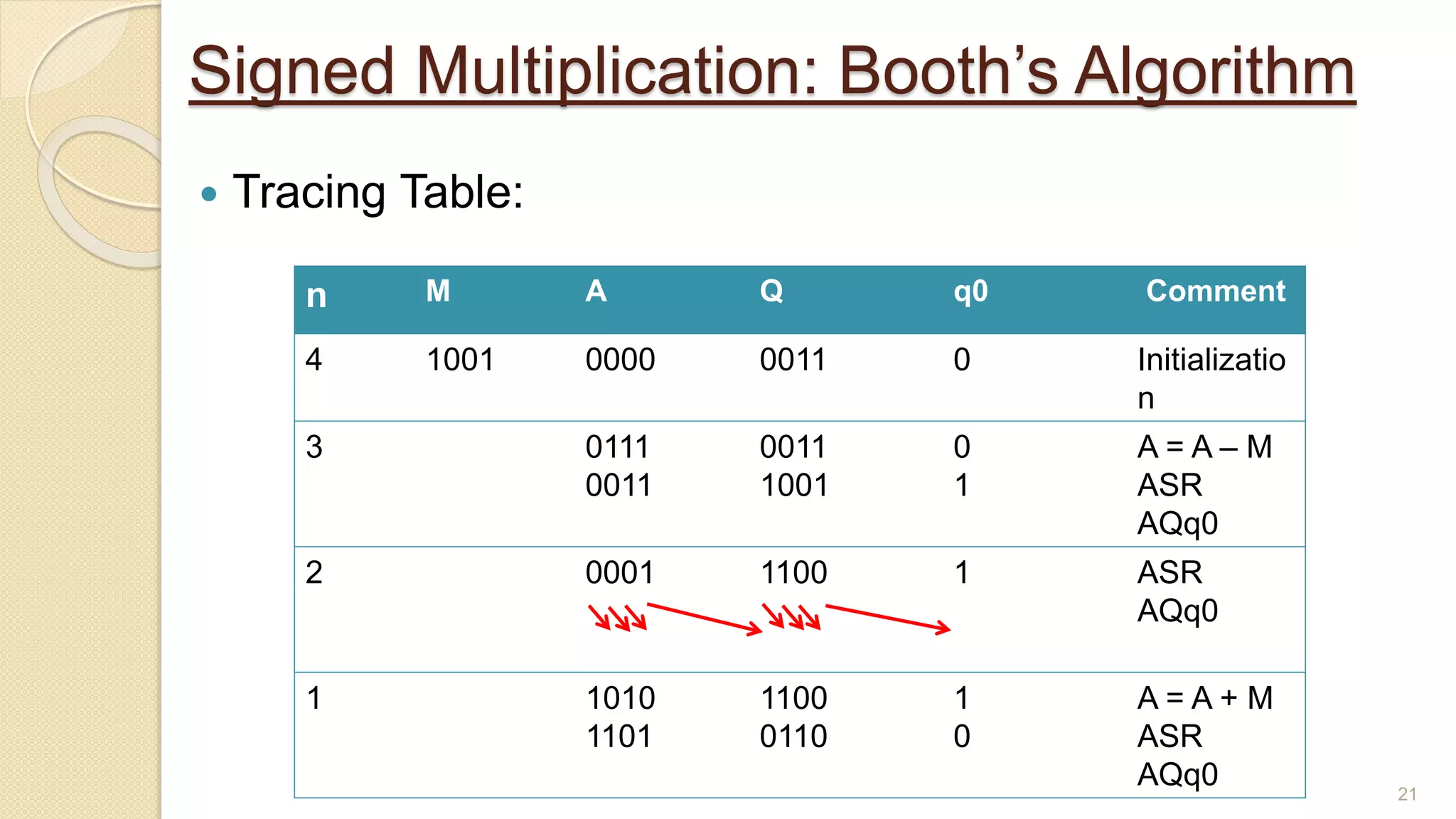
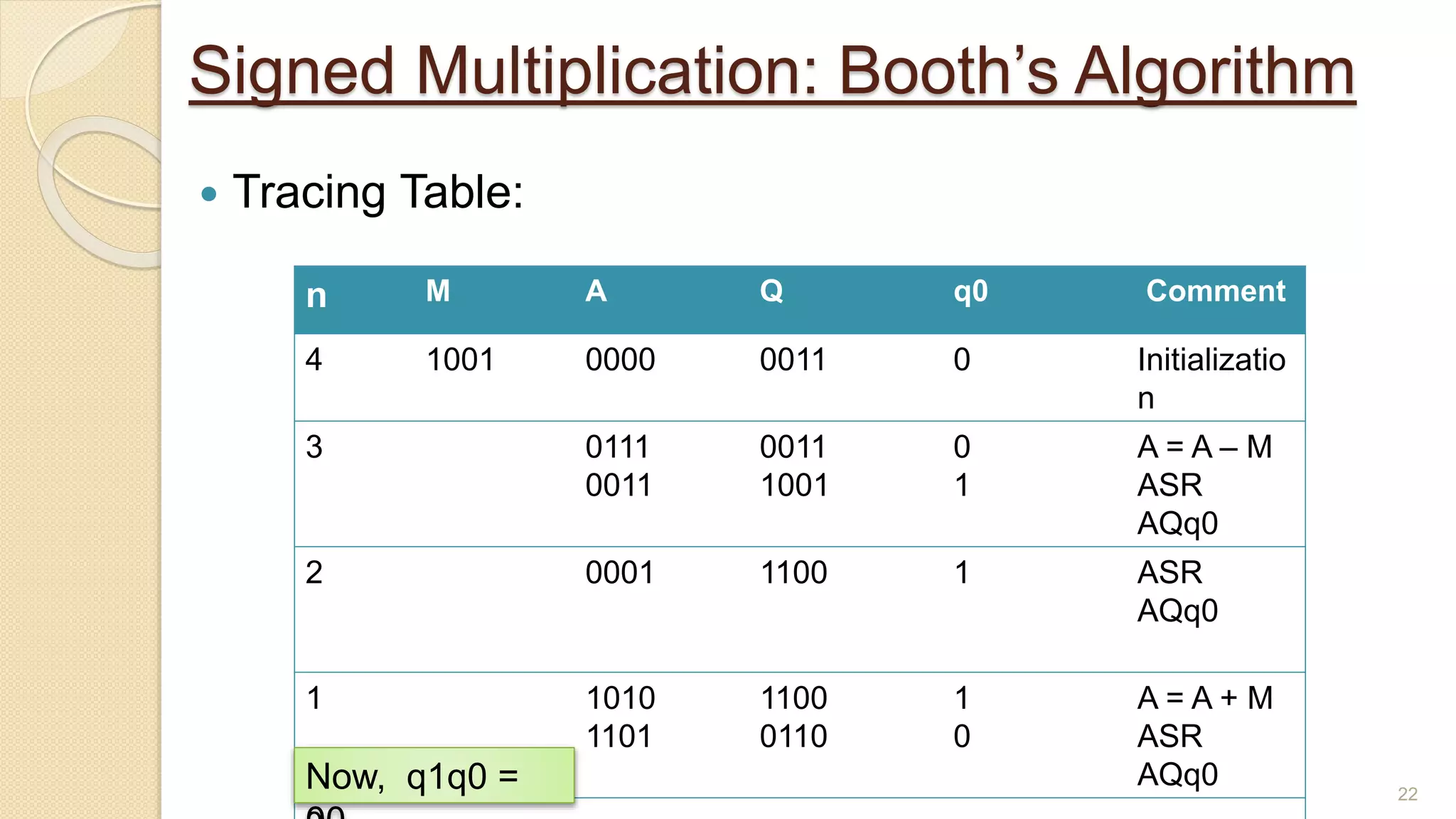
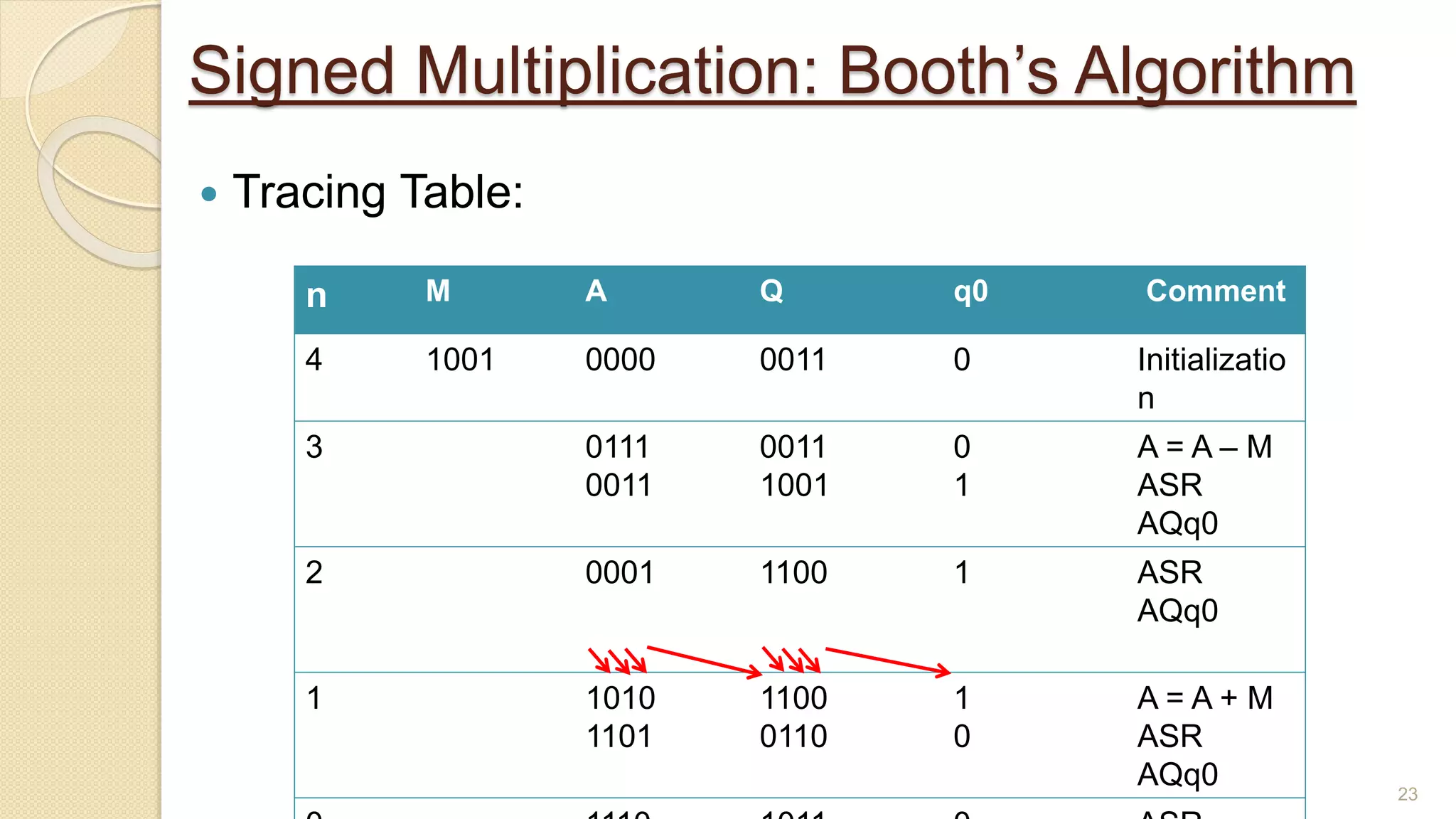
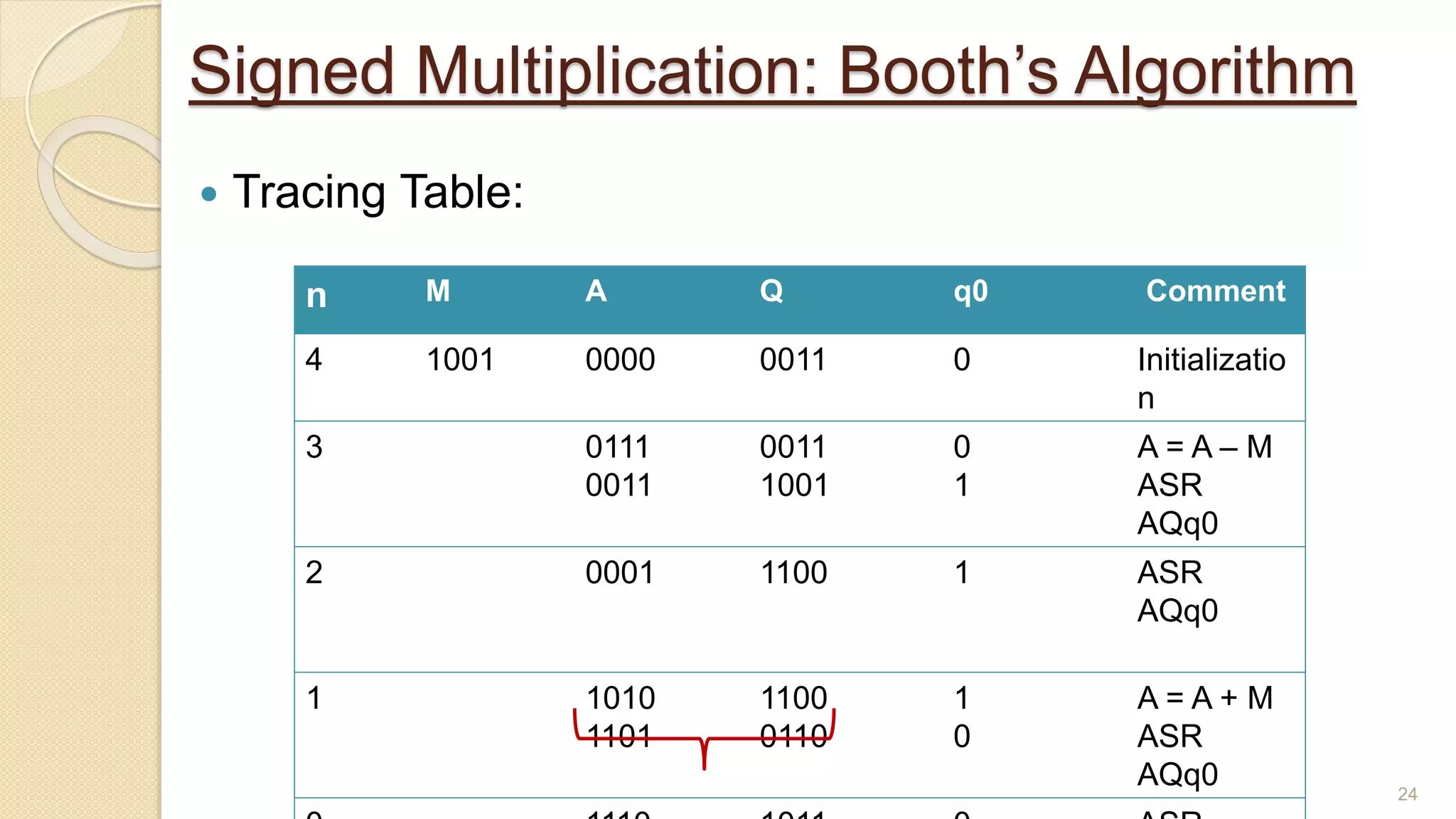
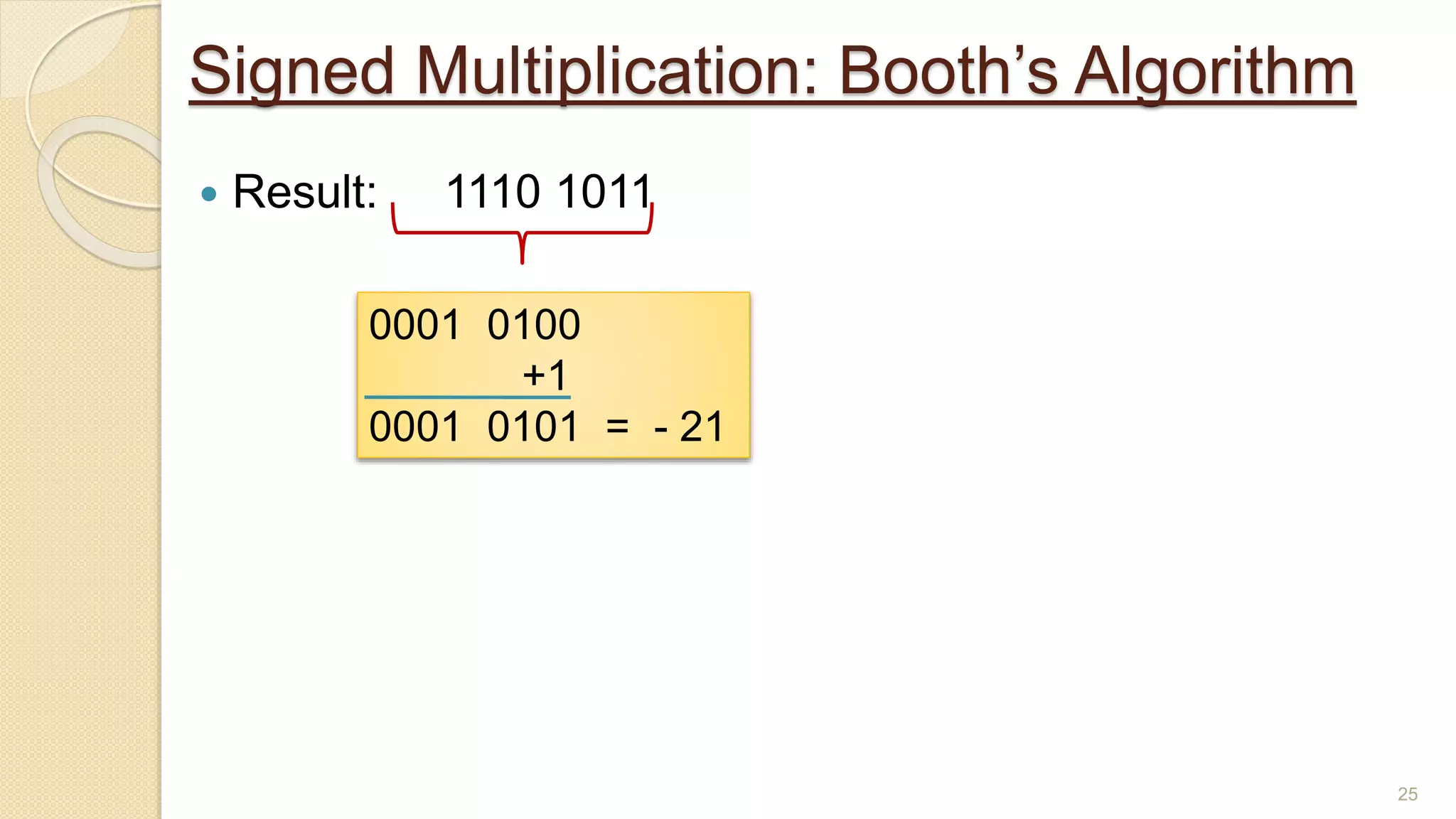
The document presents a lecture on Booth's algorithm for signed multiplication, outlining its history, process, flowchart, and hardware structure. It details how the algorithm multiplies two signed binary numbers using 2's complement notation, including example calculations and tracing tables. The presentation was delivered by Raisa Fabiha to Mostafiz Ahammed at Notre Dame University, Bangladesh on November 30, 2022.