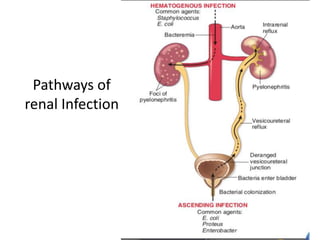
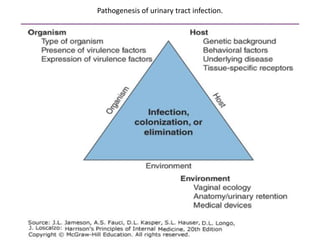
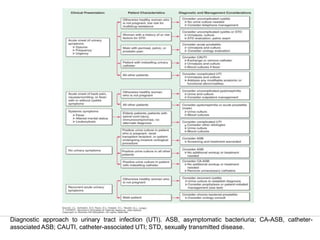
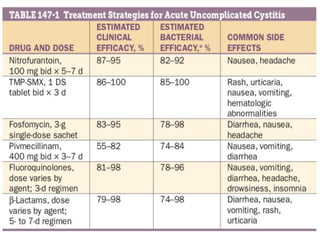
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) can be asymptomatic or symptomatic, affecting the bladder (cystitis) or kidneys (pyelonephritis). Escherichia coli is the most common cause of uncomplicated UTIs, while complicated UTIs involve other gram-negative rods or yeasts. Diagnosis involves urinalysis, urine culture, and symptom assessment. Treatment consists of short courses of antibiotics like nitrofurantoin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, or fluoroquinolones. Recurrent UTIs may be prevented with continuous or postcoital antibiotic prophylaxis.