This document discusses the distribution of energy states in a system of molecules. It introduces concepts like:
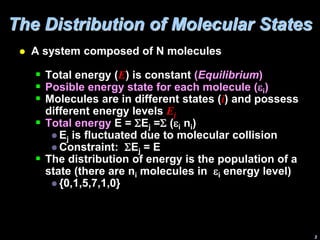
1) A system's total energy is constant, while individual molecules can have different energy levels. The distribution of molecules among different energy states will dominate the overall configuration.
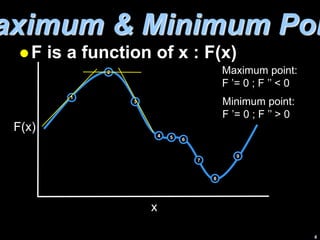
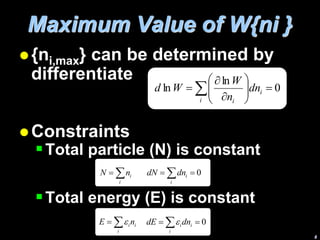
2) The dominating configuration is the one that maximizes the function W, which represents the probability of a given distribution of molecules among energy states.
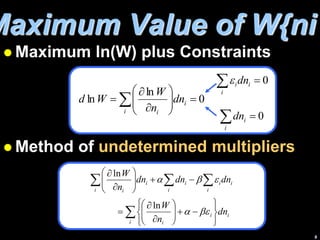
3) Finding the maximum of W involves taking its derivative and applying constraints like constant total energy and number of molecules. This leads to an equation that can determine the most probable distribution of states.