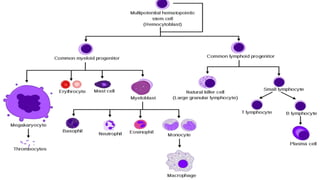
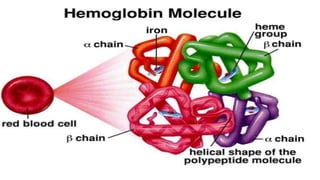
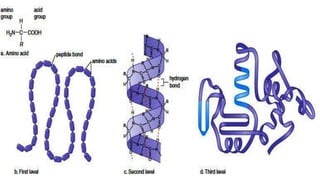
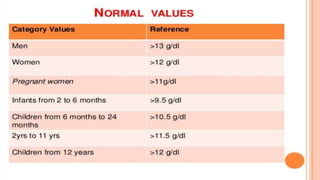
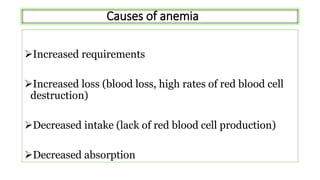
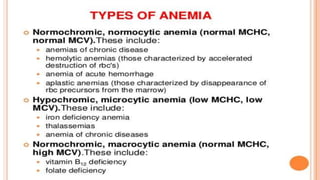
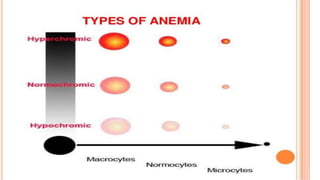
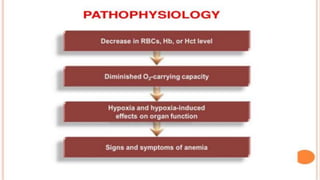
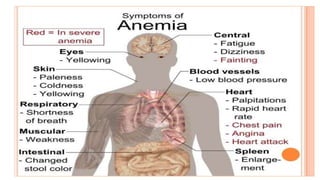
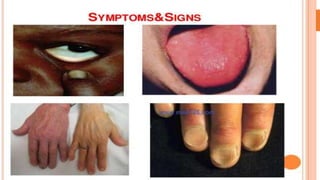
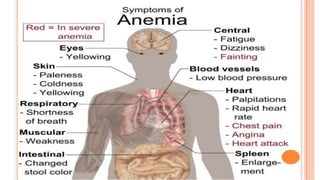
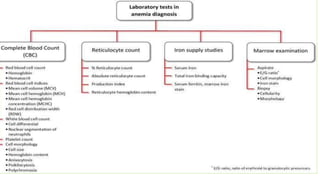
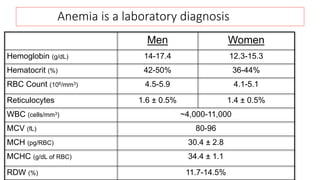
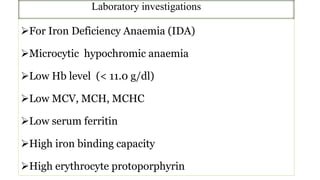
This document provides an overview of anaemia, including its objectives, a review of red blood cells and haemoglobin, definitions of anaemia, risk factors throughout the lifecycle, causes, types, signs and symptoms, assessment methods, and interventions for prevention and control. It describes the anatomy and physiology of red blood cells and haemoglobin, defines anaemia, outlines the major types including their causes, and discusses methods for assessing and managing anaemia through laboratory investigations, history taking, and potential interventions.